Can a person's character influence their likelihood of employment? Is it possible to cheat and pass psychological tests correctly? And, most importantly, is it necessary to do this?
In 90% of cases, the answer to these three questions is “Yes.”
Do you want to take a psychological test?
Get ready
Although not a single company explains what “psychological portrait” it considers appropriate to those who “do not fit into it”
employers refuse to obtain a position. This work falls on the shoulders of candidates when preparing for employment tests.
And if everything is clear with the assessment of abilities, then psychological tests cause the most problems for candidates. According to Russian law, assessment results are not considered grounds for dismissing an employee or refusing to hire. But in practice, companies often rely on testing reports and reject candidates for formal reasons, for example, based on the wording “inadequacy for the position.”
Szondi test
The test is aimed at identifying psychological abnormalities.
It consists of several stages. At each of them you will be shown portraits, from which you will need to choose the least and most pleasant ones in your opinion. This testing method was developed by psychiatrist Leopold Szondi in 1947. The doctor noticed that in the clinic, patients communicated more closely with those who had the same diseases. Of course, an online test will not give you a diagnosis - it will simply help you identify certain tendencies. Moreover, depending on the state of the psyche, the results will be different, so you can take the Szondi test in any incomprehensible situation.
Take the test →
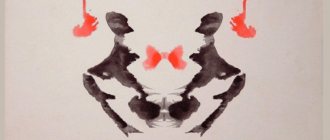
Rorschach ink blots
Swiss psychiatrist and psychologist Hermann Rorschach developed a test based on the interpretation of inkblots of different colors: pastel red, gray and black. According to the researcher, colors, contours and shapes have a certain emotional impact on the subject and influence what he sees in the blot - an animal, a person, a fantastic creature or an inanimate object.
Rorschach test. Blot No. 2 © Hans Huber Medical Publisher, Bern (CH) / Wikimedia Commons
If someone or something from the above is seen not in the entire picture, but in a fragment, or the image is built along the white spaces between the spots, this indicates a defensive position of the subject.
If an image is seen primarily due to its shape rather than color, this is a sign of well-controlled emotionality, an indicator of the superiority of thought over feeling. On the contrary, if the subject primarily pays attention to color, emotions and affects predominate.
Beck Depression Inventory
As the name suggests, this test assesses how susceptible you are to depression. It takes into account common symptoms and complaints of patients with this disease. When answering each question, you have to choose the closest one from several statements.
Even those who are absolutely sure that they are healthy should take the test. Some statements from the questionnaire will seem strange to you, but many of them are true for a person with a disease. So if you think that depression is when someone is depressed from idleness, it's time to rethink your attitude.
Take the test →
Cattell Multifactor Questionnaire, 187 questions
A technique developed in the 1940s by British and American psychologist Raymond Cattell. It is one of the first structural models of personality, based on the "lexicographic approach" of psychologists Gordon Allport and H. S. Odbert. From their point of view, the most significant individual personality differences of members of a particular society sooner or later become encoded in their language, in certain words.
The researchers sifted through the most detailed dictionaries available at the time, selected 18,000 words important to characterize individuals, and identified 4,500 adjectives that, in their opinion, described relatively stable personality traits.
Cattell, using a computer, reduced the list to 171 words, creating a 16-factor personality inventory. Its standard version contains 187 questions (16PF). There is a shortened version of 105 questions and options for children (8-12 years and 12-16 years).
Based on the survey results, we receive a graph with a detailed description of the results by scales and factors. For example, factor A is a character trait in the “withdrawn/sociable” range. A high value (A+) - from 5.5 to 10 - is characterized by "naturalness, ease, willingness to cooperate, adaptability", a low value (A-) - from 1 to 5.5 - "isolation, criticality, a tendency to rigidity , coldness, skepticism and aloofness - things attract more than people...” Intelligence, emotional stability/instability, introversion/extroversion, etc. are described in a similar way.
Psychological states of the individual
At the moment, there are several main types of psychological states of the individual. Until the mid-twentieth century, this factor was not assessed and was not clearly defined for the formation of a psychosomatic portrait of an individual. Although these indicators are often ready to become decisive in determining many of the leading factors in the formation of a person’s comfortable daily lifestyle and his readiness to engage in various types of activities.
Moral and psychological state
It is determined on the basis of a comparison of the interaction of the surrounding reality with mental experiences generated at the level of the individual’s psyche. In such a situation, an important factor that needs to be taken into account when forming a psychological portrait is the correspondence between internal experiences and the state of the environment.
A large role is given to including the individual’s psychotype and personal characteristics into the characteristics under consideration. Often, a major role in an adequate assessment of the moral and psychological state is the willingness to take into account the natural makeup of character. A sanguine person's assessment of what is happening will always differ from the choleric person's view of a similar situation.
Psychological states of a person
The analysis examines the structural organization of all mental components of a particular person. It is determined taking into account the positions of personal and orientational attitudes. Such an analysis helps to compare the personal state with the state of the environment capable of satisfying personal needs, subjective realities in relation to specific needs. Personal attitudes and beliefs play the main role in such a situation. It is analyzed with the use of which components a person reaches the optimal level of satisfaction of needs and whether the environment around him is capable of providing the opportunity to form the necessary indicators.
Psychological state of the child
Until late adolescence, it is quite difficult to objectively assess the psychological state of a child. An incompletely formed psyche is prone to sudden changes in mood and perception of the surrounding reality.
At the same time, analyzing the psychological state of a minor becomes an adequate way to assess the psychological state of his environment. The psychological state of the child suffers and this is clearly noticeable to the specialist in the event of a breakdown in contact with adult relatives and peers. Negative tendencies can lead to significant cognitive impairment. The readiness to perceive knowledge decreases, well-being worsens, and self-esteem falls. All these indicators can negatively affect adult life.
Social psychological state
The socio-psychological state can have a significant impact on the positive or negative perception of life in general. In this situation, experts consider all the relationships into which an individual enters to varying degrees, and how confident he feels in them. Is the environment capable of generating support for an individual’s actions or does it become a provocateur for the formation of violations.
A negative socio-psychological state can become the basis for the formation of psychosomatic disorders.
Types of psychological states
Currently, the following types of psychological states are distinguished:
- Defined by the source of formation as personal and situational.
- Separated into a separate type according to the level of severity as superficial and deep.
- They may differ in duration; in such a situation, short-term, long-term, and medium-duration are distinguished.
- Differing in degree of awareness as unconscious and conscious.
- Characterized by emotional characteristics as neutral, positive and negative.
- Sorted according to the degree of influence: depressing (asthenic), activating (sthenic), negative and positive.
- The manifestations are divided according to the level of psychological, physiological and psychophysiological.
If we simplify all these types as much as possible, then all psychological states are divided into three leading groups: positive, negative and specific.
- The list of positive ones includes love, kindness, interest in learning, happiness and other positive factors. They are characterized by an increased level of social activity, positive mood, and a high degree of performance.
- Negative ones include anger, envy, fear, anger and other manifestations of states that are completely opposed to positive types; accordingly, they lead to a decrease in the level of performance and a positive perception of life.
- The list of specific states includes wakefulness, sleep, a state of altered consciousness and similar states.
In most cases, a person is able to determine his condition independently and assess the cause of its occurrence. Violation of self-determination indicates the presence of psychological disorders. At the moment, psychological states are just beginning to be closely studied as a separate area. Many criteria have not yet been clearly identified.
Mendelevich Questionnaire, 68 questions
This test for determining neurotic conditions was invented in 1978 by psychiatrist Davyd Mendelevich and medical psychologist Kausar Yakhin. The test contains 68 questions assessing the subject’s condition on six scales:
- neurotic depression,
- asthenia (increased fatigue),
- mental and physical hyperesthesia (increased sensitivity to irritants),
- autonomic disorders (pressure, respiratory rate),
- conversion disorders (change/loss of sensory and motor function),
- obsessive-phobic disorder (obsessive fears).
Problems of psychological states
The problems of psychological states are just beginning to be studied closely. The occurrence of disorders is often associated with external symptoms. But they can become the basis for discomfort and a feeling of psychological distress.
The occurrence of mental health problems leads to a sharp decrease in the quality of life. Patients feel general dissatisfaction. Psychological problems can become the basis for the formation of psychosomatic diseases. At the level of general dissatisfaction with life, patients often experience asymptomatic headaches or pain in the gastrointestinal tract. Insomnia often occurs. Psychosomatic conditions can manifest themselves in the form of dizziness and fainting, and lead to eating disorders. The most common violation is a decrease in the level of performance and readiness for social adaptation in the team.
Levels of psychological state
When analyzing the psychological state of an individual, various levels of psychological state are taken into account. At the moment, experts identify several parameters that form the basis of this characteristic:
- Socio-psychological, when determining which indicators of personality, activity, and interpersonal relationships are taken into account.
- Psychological, on which the formation of psychological functions and changes in mood directly depend.
- Psychophysiological, on which the autonomic reactions of the body, possible changes occurring in sensory and psychomotor function depend.
- Physiological, showing neurophysiological characteristics, changes in physiological functions, morphological and biochemical changes in the body.
When studying the influence of levels of psychological state, the basic characteristic is the state of the individual in a good mood, at the moment when he is completely satisfied with the fulfillment of his physiological and moral needs. When considering the situation in each specific case, it is necessary to take into account the parameters “variability-constancy” and “long-term-situationalism”. Such an analysis makes it possible to determine the levels and parameters of the psychological state by comparing stable personality traits and character and mental processes. The readiness of a short-term parameter to move into the stage of a stable indicator is assessed.
If a long-term disturbance in levels is detected at any stage, it may be recommended to consult a psychotherapist to correct the perception of the surrounding reality and identify the possible presence of psychological diseases.
Clinical methods
The main methods for diagnosing mental illness remain clinical. To determine a mental disorder, the doctor uses information about the symptoms of the disease that he receives from the patient and his relatives during a conversation. In addition, the doctor observes the patient: his motor activity, facial expressions, emotions, speech, and character of thinking. Assessing the development and modifications of signs of the disease gives an idea of the speed of the disease and its nature. Analysis of the totality of clinical data obtained allows us to establish a specific mental disorder.
Clinical methods depend on subjective factors:
- frankness of patients and their relatives in presenting the picture of the disease and biographical facts
- doctor's experience and knowledge
The use of additional objective research methods - laboratory, instrumental - increases the reliability of the diagnosis of mental disorders and allows you to select the optimal means of therapy.
Most public and private psychiatric clinics are limited to only “necessary and sufficient” clinical examination methods. First of all, we are talking about the diagnosis of functional mental disorders - those that occur in the absence of brain damage. In case of functional disorders, x-rays or tomography do not show any abnormalities.
Common functional disorders include:
- endogenous psychoses, including schizophrenia, schizoaffective and delusional disorders
- schizotypal disorder
- mood disorders (depression, mania, bipolar affective disorder)
- neurotic disorders
The symptoms of these diseases can be very similar to each other or “overlap”, acting as nonspecific signs of mental pathology. This often occurs in the early stages of development or temporary attenuation of painful conditions.
Distinguishing between outwardly similar but essentially different diseases is a difficult task, the solution of which can take several months (!). To recognize a mentally ill person, it is necessary to use different diagnostic methods in combination (clinical, psychometric, laboratory and instrumental).
Making a correct diagnosis early is also important because thanks to early treatment, the patient goes into remission or recovers faster, his quality of life and social prognosis improves.
What is SPD
Socio-psychological maladjustment is a violation of the ability to adapt to the influences of society and unfavorable living conditions. It manifests itself through deviant behavior, which can be expressed in the following forms:
- clinical (medical problems);
- socio-legal (deviations in behavior);
- pedagogical (educational and educational);
- psychological.
The Leus scale shows predisposition to deviant behavior and establishes its types. The survey does not take much time, which is valuable when examining unbalanced, difficult, and easily excitable adolescents. The method is easy to process results and is suitable for mass screening studies.