Every day a person is faced with many images, information, emotions and impressions. Many people dream of remembering this without stress. Memory is a treasure trove and wealth, and its importance in our lives cannot be overestimated.
Many people believe that the ability to remember without extra effort is an innate gift, a gene that we have as a given. However, this is not quite true.
How memory works, properties of human memory and its development
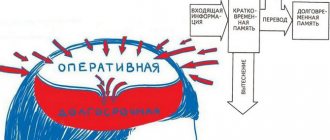
To understand how human memory works, scientists studied not only the activity of neurons, but also the effects of various substances on them. The process of memorization occurs at the molecular level. It is caused by the synthesis of a substance such as protein. It makes active neural chains located in some parts of the brain. The process is highly dependent on genes. When a person remembers the information he needs, the same system of neurons that was involved in memorizing it begins to work.
Different parts of the brain are responsible for different types of memory. For example, a person can learn to play a musical instrument through the functionality of the parietal cortex, and ride a bicycle through the activity of the hippocampus. The same department is responsible for reproducing information received recently.
Mnemonic properties include accuracy of reproduction and volume of memorized information. In addition, the peculiarities of this mental process is the speed with which a person can remember the information he needs, and then reproduce or forget it.
How to prepare your brain?
The brain, like any other part of the human body, needs a balanced diet, sufficient rest, and moderate physical activity. By normalizing your lifestyle and maintaining it at the same level, you can significantly increase your mental abilities and improve your memory.
Dream
Healthy sleep helps brain activity reboot. In this way, the body “sorts out” all the information it receives during the day, and gets rid of unnecessary information.
During sleep, nerve fibers sort through memories, analyze what is important and what is not. Next, the brain stores the information received in certain areas of memory. This process is called consolidation.
Scientists recommend monitoring the quantity and quality of sleep. The normal duration of rest hours should be 7-8 hours.
Nutrition
The functioning of the nervous system is greatly influenced by proper nutrition. It is normal when the diet includes a sufficient amount of vitamins, fiber, proteins and healthy fatty acids.
It should be borne in mind that flavor enhancers and preservatives reduce mental performance, as well as red meat and alcohol, so it is recommended to include more natural foods in the menu. The Mediterranean diet is especially beneficial in summer.
The diet must include:
- fresh fruits;
- dairy products;
- whole grain dishes;
- pasta;
- leguminous plants;
- nuts, seeds;
- vegetable oil;
- fish;
- bird.
Physical exercise
The physiological side of the issue implies not only the presence of proper nutrition and a rational regime of wakefulness and sleep, but also moderate physical activity in the form of:
- morning exercises;
- walking in the fresh air;
- running;
- dancing.
Research has shown that regular physical activity improves cognitive function. During exercise, a substance is produced in the brain that promotes the restoration of neurons and the reconstruction of connections between them.
Ways to develop photographic memory in children
In order to develop the ability to quickly remember information, there are a huge variety of different exercises. They can be simple, for the youngest children, or more complex, for older children and adults. Let's look at the most popular exercises:
Exercises related to observation. There are a large number of variations, but the essence of these exercises is approximately the same: a person focuses on an image (a picture in a book or the Internet, an advertising brochure, a sign on the street), tries to examine and remember all its details as much as possible. Then you need to close your eyes and try to recreate the image, and then compare it with the original. Exercises for visualizing information. It is necessary to select associations with the images. This exercise allows you to speed up the recall of previously learned information. Sequence memorization exercises. You can take a numerical expression, a mathematical formula, or just a set of different symbols, try to remember it, and then recreate it on paper
For this exercise, it is important to use sequences of signs that would be unfamiliar to a person. Exercises related to rearrangement. To complete this exercise, you can prepare the necessary materials yourself.
You need several cards of the same size with different images. Place them in a random order on the table, take a photo of the result, then mix them and try to recreate their original order. Compare with photo. There are also many variations of this exercise on the Internet.
Undoubtedly, these exercises can help improve the ability to remember what you see. But, unfortunately, their implementation cannot be compared with a structured, consistent approach to developing this skill. In addition, it is difficult for a child to study independently and maintain motivation for a long time. For this reason, it is better to entrust children’s memory training to professionals - qualified teachers.
Today, there are many additional development centers that offer classes to improve a child’s memory. Give preference to those institutions that teach using original, time-tested methods. Over time, such activities will bear fruit: the child’s performance at school will increase, studying will begin to be easier, fatigue of the nervous system will decrease, since completing homework will take much less time. In addition, such courses are a good investment in the child’s future, in the development of his intellect.
You can train daily with exercises
Exercise 1. Take a photo of the object
Take some object, for example, a figurine, look at it for ten seconds, take a photo of it, then close the figurine and tell it or draw it from memory.
Check your story with the original figurine and compare whether you photographed everything or not.
Exercise 2: Take a photo of the painting
Take a picture, if there is no picture, you can take a picture in a book, look at it for ten seconds, take a photograph of it, then close the picture and tell from memory what is depicted in this picture.
Check your story with the original picture and compare whether you photographed everything or not.
Exercise 3: Take a photo of the carpet
Look at the carpet, if there is no carpet, you can take a picture of the carpet, look at it for ten seconds, take a photo of it, then turn away from the carpet and tell from memory what is depicted on this carpet.
Check your story with the original carpet and compare whether you photographed everything or not, compare the correctness of the description of patterns and colors.
Exercise 4: Take a photo of the formula
Take any complex mathematical or chemical formula.
Take a photo of it, then close this formula and try to write it from memory. Open the formula and check whether you wrote it correctly or not.
Exercise 5: Take a photo of a paragraph in a book
Take any paragraph in a book from five to ten lines, look at it carefully for thirty seconds, take a photograph of it, then close the book and tell from memory what is written in this paragraph.
Check your story with the paragraph in the book and compare whether you have photographed everything or not. Repeat the exercise again.
Exercise 6. Take a photo of a series of numbers
Take any series of numbers, look at it carefully for thirty seconds, take a photo of it, then cover it and write it down from memory. First memorize the first line and write it down, then memorize the second line and write it down, and so on.
92374859
4758603647
95736247596745
9837564424237587977
34868708846241315756879
Check what you wrote and the written series of numbers and compare whether you photographed everything correctly or not. Repeat the exercise again to make sure there are no mistakes.
Exercise 7: Take a photo of the words
Take any words, look at them carefully for thirty seconds, take a photo of them, then cover the words and write from memory. First memorize the first two lines and write them, then memorize the second two lines and write it down, and so on.
Car, hare, raspberry, lungwort, pluto, ermine, bird cherry, turtle, sensor, universe, bear, ocean, formula, cinema, flora.
Dacha, garden, dinosaur, article, twenty-sided, mug, horns, money, picture, bed, rebus, engine, lark, carousel, dolphin.
Check what you have written and the words you have written and compare whether you have photographed everything correctly or not. Repeat the exercise again to make sure there are no mistakes.
Exercise 8. Take a photo of the matches
Take twenty matches and throw them on the table to make some kind of drawing, look carefully at the drawing from the matches that you get.
Take a photo of it, turn away from it and try to post it exactly the same as you took the photo.
Check these two pictures and see if they are different or not. If they are the same, then take thirty matches and do the same thing.
Description of the phenomenon
In psychology, there is a concept called photographic memory (or eidetic memory) - which means a person’s ability to remember information through visual images without comprehending it.
Information remains in the mind as a “picture”; when associations arise or a conscious desire to remember, it comes to life.
What is the difference between normal and photographic memory?
- Ordinary memory operates on the principle of “filling” free resources, so we remember the events of our lives worse every year, because over time, consciousness is filled with new impressions and old ones are displaced. Also, the specificity of ordinary memory is that it records significant events, or emotionally charged ones.
- Eidetic memory – fixes an image and, accordingly, it does not mix with new events. The image does not depend on mood or associations - when you try to remember something, you see the entire image in front of you and can reproduce even little things in your memory.
Study of the phenomenon
The first in psychology to talk about the concept of “eidetism” was the Serbian scientist V. Urbancic, and in the 20s of the last century, E. Jensch conducted the first experimental studies. He developed a classification according to the severity of the phenomenon. Then, eidetics was studied by Russian and foreign psychologists - M. P. Kononova, m, S. L. Rubinstein, V. A. Artyomov, A. R. Luria. In particular, A.R. Luria and scientists working together with him proved that images from memory can be stronger than real images of perception, and sometimes even influence human physiology and change his condition.
Auditory Memory Training
Despite the fact that the famous Russian proverb states that “it is better to see once than to hear 100 times,” auditory memory can sometimes be no less useful. Thus, without auditory memory it is difficult for musicians, actors, politicians and even intelligence officers to achieve success. To understand how important auditory memory is, remember that listening to a lecture is remembered better than just reading a textbook or viewing slides.
The peculiarity of auditory memory is that, unlike visual impressions, which are perceived more quickly, memory often retains well-remembered auditory impressions better. Below are some techniques and methods that will help you learn how to effectively remember auditory information.
Exercise 1: Reading aloud
Reading aloud is undoubtedly one of the most effective exercises for developing auditory memory. It is reading aloud that helps to increase working vocabulary, improve diction, intonation, emotional coloring and brightness of speech. Reading aloud helps us better remember the auditory components of the material we read.
You need to read aloud slowly, at an optimal conversational pace, observing some technical nuances:
- pronounce words clearly, expressively and with placement;
- pronounce the text not monotonously, but as if you were expressing your own thoughts (telling).
If you read aloud for at least 10-15 minutes every day, then within a month you will notice obvious results in both your speaking abilities and your auditory memory.
Exercise 2. Poems
Memory training does not have to be limited to any specific exercises. Make it a habit to memorize a short poem every day, or at least every week. Try to delve deeply into its meaning, think about the techniques that the poet used.
When learning a poem, you will repeat it either out loud or silently, using your articulation apparatus. The more repetitions you do, the better your memory will remember the poem. Over time, you will train your memory and begin to memorize verses as a result of much less repetition.
In addition, the poems themselves are often used for long-term memorization of any abstract information. You can see the applied use of the method in some materials on our website, which describe the principles of memorizing information such as:
- Numbers after the decimal point in Pi;
- Multiplication table.
Exercise 3. Eavesdropping
When walking down the street or while on public transport, try to hear and retain in your memory a fragment of a conversation between strangers. Then try to reproduce to yourself what you heard with the right intonation, and also mentally imagine the faces of the people who said it. This exercise allows you to learn to comprehend text fluently by ear, and will also allow you to be more attentive and sensitive to the tone of speech.
— Mnemonics or “the art of memorization.” Example
______
However, there are special techniques that can significantly improve memory in a very short time and almost forever remember a large amount of information: unrelated data, numbers, texts, foreign words. This is possible thanks to the methods of mnemonics (the word “mneumonica” comes from the Greek language and means “the art of remembering”).
Almost all mnemonic methods are based on creating associations for memorized information with very vivid, grotesque images that are difficult to erase from memory.
4 steps to memorize using the associative method:
1) Encode information into vivid images.
2) Create grotesque associative connections between images. 3) Remember the sequence of connections through a grotesque plot or scene. 4) Mentally visualize a plot or scene to reinforce the sequence of connections.
This method is used to remember information such as unrelated data, long numbers, historical dates. Once you master this technique, you can memorize all this data in a matter of seconds and store it in your memory almost forever. Miracle? No, this is just another innate ability of our brain - the ability to create associative connections between memories.
The memory stores simple images that are used as reference points to reconstruct more complex images or scenes. In computer science terms, such images are the root directory for our memory.
The more simple and grotesque the images into which information is encoded, the better they will be retained in memory and will never be mixed with similar images. You can illustrate the application of this method in practice using a clear example. You need to remember which clients of your company and in what order you need to call during the day. Even if you remember the clients' names, it will still be difficult to remember in what order you should communicate with them. Exercises to improve memory and brain function can help you here.
Let's say you spend a lot of time learning a sequence of phone calls, but the next day you won't be able to accurately remember all the information, and a week later you'll even forget the sequence of four clients. If you show creativity and create vivid images that are associated with each of your clients, and then come up with an associative connection, you can easily remember everything a month or even a year later.
Suppose the clients in the telephone call list are in the following order: Maria (housewife), Peter (lawyer in a law firm), Lucia (flower seller), Andres (airplane pilot), Monica (secretary of a consulting holding company), Nicholas (engineer), Isabel (bus driver), Carmen (psychology professor).
Step one: encode information into images.
Maria (housewife): you can imagine a girl in a swimsuit with a huge MARK on her back (the initial letters of the word help you remember the name), flying on a broom along the shore (a broom is associated with housekeeping). It's rare to see a girl with a broom at sea, isn't it? This is a grotesque image that is perceived by our consciousness very easily. It cannot be confused with a real life image.
Now we need to build a grotesque image for the next client, Peter. You can imagine a man dressed in an ancient robe with a COCK in his hand (association based on the initial letters of the name). The clothes in which we present Peter immediately associate him with the profession of a lawyer. To help you remember the image even better, you can add more details (for example, an unusual hairstyle or facial expression).
Step two: create an associative connection between the created images.
For example, Peter wants to catch and protect Mary, since she is wanted by the Inquisition on suspicion of witchcraft. This is a grotesque connection that would hardly be possible in the real world, so our memory will not be able to confuse it with a real event.
Step three: remember the sequence of connections by constructing a plot.
Now you need to come up with a specific action that will connect the characters in a certain sequence. This must be an action, and not a static image, if we want to remember the entire chain of clients in a certain sequence for a long time. For example, we can imagine Peter running along the shoreline with a rooster in front of him to catch up with Mary, who is flying ahead on her broom.
Step four: mentally visualize the scene.
We present the invented plot as a movie on the screen. The resulting scene should be vibrant, with all the details we've created for the characters. This will allow you to remember the entire chain for a very long time, if not forever.
The method may seem complicated, but if every time you need to remember unrelated information with different parameters (as in the example described), instead of cramming, you use images and connections, you can develop your creativity so much that it will take several minutes to think through the plot. In addition to improving memory, it also develops creative abilities, which is highly valued today in any profession.
You may also be interested in the topic of visual memory development.
_______
Causes of poor memory
Simple folk methods for improving memory Phenibut for improving memory How to develop photographic memory
Poorly developed visual memory is not necessarily the key to all troubles
This is not fundamentally important. But still, most information passes through the eyes
And in order to fully embrace the entirety of the world around us, we need to have a developed visual analyzer. Well-developed visual memory is the key to adequate learning and good memorization. The level of development of this type of memory affects the speed of learning and its quality.
The absence or insufficient attention to the baby, the lack of educational games and activities will certainly affect further learning and activity. But there are also acquired reasons for the deterioration and decrease in the quality of the “work” of the visual analyzer
Before this, my memory was good, no one complained, but over time I became absent-minded, you remember poorly and pay little attention to details. What are the reasons?
- Traumatic brain injuries, previous neuroinfections and cerebrovascular accidents - these pathological conditions will necessarily entail the destruction of a large number of nerve synapses and the nerve cells themselves. Trauma can damage precisely the department that is responsible for visual analysis.
- Age-related changes - every person develops encephalopathy to one degree or another. This occurs due to the gradual emptying of blood vessels, the formation of small blood clots in the lumen and disruption of the nutrition of glial cells and the neurons themselves. Brain cells gradually die off, and the number of actively working cells decreases sharply. The remaining nerve cells cannot cope with the previous flow of information and direct all their forces to more important matters - vital functions. And visual memory remains in the background for those cells that are not involved in important processes to ensure the normal functioning of the body.
- Intoxication and bad habits - any manifestation of euphoria without medicinal intervention of the appropriate group of drugs entails the death of a huge number of nerve fibers. Tissue is replaced and the brain is adjusted to provide more important functions. Therefore, visual memory suffers.
- Lack of nutrients in food - nerve cells need more than just oxygen. But also the nutritional elements that come with food. For example, insufficient consumption of fatty acids and vitamins, glycine lead to deterioration of brain function.
- Emotional and mental overload - nerve cells are on the verge of exhaustion, so we decided to take care of ourselves. They turned on lite mode, in which they protect themselves and do not work at full capacity. In this case, a good rest will return everything to its place.
If visual memory is poorly developed in children, this can lead to problems with memorization, learning ability, and, against this background, behavioral disorders in general.
Sometimes poorly developed visual memory can cause poor adaptation in the environment and society. A sharp deterioration in memory in an adult leads to absent-mindedness, decreased memory, difficulty in temporary adaptation, and psychological problems.
Degrees
There are 5 degrees of severity of eidetism:
- Requires pinning to play.
- Weak visual images.
- Visual images of medium clarity with the appearance of some particular details.
- Clear, complete images of complex objects interspersed with sensory modalities.
- Vivid, detailed eidetic imagery accompanied by clear sensory modalities.
By zero, this implies a short-term preservation of a vague afterimage without detail.
Obvious eidetics with 5 degrees of severity are divided into 2 more types:
- “T-type”: have persistent and overly vivid eidetic images, which can be intrusive and border on hallucinations. They are not always able to control them.
- “B-type”: they reproduce the desired image only when necessary.
It is believed that obvious eidetics can be easily identified in a crowd by certain facial expressions and movements.
What is memory, its types
There are several types of memory, let's look at them in more detail.
Eidetic memory (visual, visual)
Comes from the word “eidos” - in ancient Greek it means “appearance”, “appearance”, “image”. Basically, such memory is called visual, and it is also called photographic. People who have this type of memory remember images best - they are able to reproduce them in their thoughts at almost any moment, even if they contemplated the object for a very short period. So, the basis of such memory is usually a picture, but other types of memory can also join it.
Auditory memory
Those with excellent auditory memory are good at remembering various sounds - speech, music, and so on. As a rule, such memory is especially developed among philologists, musicians, and acousticians. It is characterized by the fact that its owner is accurately and quite quickly able to grasp the essence of the text he heard and remember its details. In addition, he can convey the meaning of what he heard in his own words, and at the same time very accurately.
Motor memory
Also called motor. Manifests itself in the ability to remember and subsequently accurately reproduce various motor operations. It will burn to be cycling, dialing a specific number, swimming and much more. It is the basis for many labor skills and motor acts.
Long-term and short-term memory:
- Long-term. Memory in which information is retained for an almost unlimited period of time. Events recorded by this memory can be reproduced in a person’s thoughts many times, without any loss. The owner of such memory, at any necessary moment, can remember what was once remembered. Although it is worth noting that sometimes this requires some effort of will.
- Short-term. With this type of memory, information is stored for a very short period. At the same time, not the complete, but only the general image of what was perceived, the most significant moments, is preserved. Operates without pre-setting to remember. It has a connection with the so-called actual consciousness. From instant memory, only information that is conscious and relevant to a person’s current interests and needs gets into short-term memory.
Possibilities of eidetism
Photographic memory provides many opportunities for a person - it is worth remembering the people who had this talent:
- Maxim Gorky - had the skill of speed reading and remembered the books he read for many years;
- Alexei Tolstoy - before he wrote his books, he “saw” their content and text figuratively;
- Lev Vershinin - knew the text of the Soviet Historical Encyclopedia by heart from his student days;
- Ronald Reagan could remember a text in its entirety at one glance.
Developed eidetic memory opens up new opportunities for a person - success in studies, professions, and hobbies directly depends on how quickly and efficiently you remember new information.
However, in your quest to develop photographic memory and become more efficient, smarter and better, don't forget that it is important not to harm yourself. Excessive enthusiasm for eidetism can ultimately threaten to “eclipse” reality with internal images.
Ways and methods of memory development
To begin with, it is worth noting that we often train our memory and attention using various everyday situations in everyday life. We remember what we want to buy in a store, try to remember the birthdays of relatives, friends and acquaintances, retell the contents of a recently read book or textbook - all this and much more is good memory training
We remember what we want to buy in a store, try to remember the birthdays of relatives, friends and acquaintances, retell the contents of a recently read book or textbook - all this and much more is good memory training.
However, the use of special exercises gives us the opportunity to concentrate on the specific goal of developing a certain ability of our memory.
When talking about memory training, it is important to understand that it is almost impossible to directly train a specific ability to memorize material.
Memory always develops in close connection with our attention, perception, thinking, sense organs and other phenomena of human nature
Therefore, most of the exercises below produce a complex effect on our thinking, as well as on our memory as an important component of thinking.
For convenience, the exercises are divided into 2 groups: visual and auditory, and together they form an important part of our memory improvement training.
How to develop visual memory in an adult
First of all, in order to improve your visual memory, you need to normalize your work and rest schedule, eliminate overload, and remove bad habits. Then start “pumping up” your visual analyzer.
Constant practice will definitely bear fruit. Here are some effective exercises on how to develop visual memory. They can be used at any free time.
Schulte tables - they contain 25 scattered numbers. We need to find their sequence as quickly as possible
This exercise develops visual memory, lateral vision, attention and observation.
Visualization - an assistant is needed. A person reads out successive descriptions of the images to be imagined.
After the first part of the exercise, the trainee must reproduce all the images in the same order, based on his ideas.
Aivazovsky's method - for several minutes you need to look at some landscape, room or other landscape. Then close your eyes and sketch everything in your head in great detail. You can also draw on a piece of paper. Gradually reduce the landscape memorization time.
Matches - Scatter several matches randomly on the table. In a few seconds, remember their location. After 10 seconds, repeat the picture from memory.
Games - 2 identical pictures with differences can be found both in magazines and online. You are given two seemingly identical pictures. You need to find a certain number of differences between them in a short period of time. This exercise is suitable for both children and adults.
What is the difference between visual and photographic memory, and which one needs to be developed?
Visual memory is the ability to remember visual images. If she is able to remember objects for a long time and accurately, then she moves into the region of the eidetic type.
Photographic memory, which can be developed over long periods of training, differs from visual memory by effortless memorization, that is, a lack of interest in retaining information.
In the case of a phenomenon, the process of storing information in the brain is as close as possible to photographing, that is, literally capturing the picture: as it is with all the details.
Visual memory captures an object without focusing on details, and possibly distorts them.
On a subconscious level, experts recommend developing photographic memory by expanding the capabilities of visual touch. There are developed training methods and exercises that you can perform at home in your free time.
Exercises to help quickly develop photographic memory
Constant surveillance
Choose any object, indoors or outdoors, and watch it for 2-3 minutes without taking your eyes off. You need to try to remember all its features. Next, close your eyes and reproduce this object in your imagination. They remember what color, shape and size it is. If it was not possible to completely remember these details, the eyes are opened, looked at the object again and closed again. Usually it takes about 5 such approaches to get an accurate picture in your mind. After several exercises with objects, you can move on to more complex workouts, using pictures or texts to memorize. This is much more difficult, since there are much more elements in the paintings. First, remember 5-6 elements, close your eyes and reproduce them. On the next approach, 5 more elements are memorized. Such actions continue until it is possible to completely reproduce the picture in your imagination.
Casual observation
This is a very simple exercise that can be done, for example, while going to work or just sitting on a bench during your lunch break. They count how many floors the nearest house has, how many trees grow in the alley, how many steps there are at the entrance to the house. Then, when they come to work, they try to remember all the details they saw. You can also choose some interesting building or tree, trying to remember it in the smallest detail. Such training takes only a few minutes a day and over time becomes a habit.
Associations
To see the content you need a flash player
Associative understanding helps to develop photographic memory quite quickly. It is necessary to create lists of pictures in memory that are associated with specific words. In this way, you can soon learn to memorize fairly large texts. The situation is the same with numbers. When memorizing combinations of numbers, you need to break them down into numbers, each of which will be associated with some event in life.
Training with texts
Plain text is printed on one sheet of paper. On the second sheet, the assistant should print out the same text, adding one or two extra words to it. The essence of the training is to quickly find extra words. Each time, more words can be entered, giving the person less and less time to search for them.
Reading words backwards
This exercise begins with simple phrases that are played backwards. They start with the simplest phrases and work their way up to complex texts. When your photographic memory is sufficiently trained, you can connect an auditory analyzer and move on to songs, singing them from the end.
Paired pictures
To carry out this exercise, you will need to download a children's game, which is often called “Paired Pictures”. The essence of the game is to quickly find pairs of identical pictures. In this game, initially all the pictures are flipped to the other side. Turning over two of them, they look for pairs. When the pictures match, they are deleted. If this does not happen, you need to remember the location of the picture and look for a match for it.
Visual memorization of text in a dark room
To do this exercise you will need a dark room, a sheet of xerox paper and any book or magazine. Turn on the table lamp and cover the page in the book with a sheet, leaving a small piece of text open. Next, turn off the lamp, get used to the darkness, and turn it on again for a few seconds to read the text. This is done 4-5 times. With the help of such training, a photograph of a given text is stored on the retina of the visual analyzer, which is easy to remember at the right moment.
Training information reproduction
However, eidetic memory is not only about remembering, but also about recalling what you remember. Consequently, we must learn to recall not only what happened an hour ago or the day before, but also “the affairs of days long past.”
One of the exercises is to cling to some bright event and try to unwind the chain: what happened before, what during, what after. Try to remember the details, restore the picture and sequence of events as if you were there again. The further you continue your training, the less significant the “starting” point may be for you.
Try for yourself various mnemonics (for example, the mnemonics we presented for memorizing numbers) - having moved to the same automatic level, they will help you consolidate this or that information for a long time.
The general development of memory will also be very useful.
(not only visual), as well as general training of brain activity - neurobics, learning languages, solving logic puzzles and even crosswords: don’t let your brain idle, and it will show you what you are capable of.
Photographic memory is a person’s ability to remember information he sees, without understanding it. The data is stored on the eye's internal screen and can be recalled in the future. The memorization process is very fast. It takes no more than 10 seconds. Photographic memory helps a person feel more confident in this world, since in just a moment he can remember a lot of useful information. Very often people wonder how to develop photographic memory? The answer is quite simple. She should be trained. To do this, there are special exercises that need to be performed daily. The duration of training depends on the characteristics of human perception. On average they take 1-3 months.
How to quickly develop your memory to remember better
1.
A method that can not only improve memory, but also develop imagination well! Surely, before going to the store, you often make a shopping list. After studying the list before going out, try to come up with a short fairy-tale story, the heroes of which will be all your potential purchases. This exercise can be interesting not only for adults, but also for children. When you come to the store, try to make purchases based on your “fairy tale”. Of course, before leaving the supermarket, check the list and check how well you remember your own work.
2.
Another interesting method that can be used using a regular grocery list as a basis. Remember to remember it by first dividing it into groups - five products from the vegetable department, three products from the dairy department, two products from the meat department. Make sure that by grouping your list you will remember it faster.
3.
This exercise can be done regularly before bed. Remember all the details of the past day, scroll through it in your head. remember what you did today, starting in the morning - what you ate, who you talked to, what you did, and so on. Now try to remember the past day from the current moment until you woke up - that is, in reverse order. This can be challenging, but is very effective for memory development.
4.
If you want to develop your memory, then remember that for this you need to get enough sleep in order to ensure full brain function. In the absence of normal sleep, the memory will not be able to work “at full capacity.” In addition, the human brain is tuned to a biological rhythm in which day gives way to night, so you should sleep in the dark, at least seven to eight hours!
5.
If you want to have an excellent memory, avoid drinking alcohol. It has long been known that drinking alcohol contributes to a significant weakening of memory. By the way, the more alcohol you drink, the weaker the fixation of your attention, and, accordingly, the memory itself. It is especially undesirable to drink alcohol if you have an important meeting, participation in a conference, and so on.
6.
Try to eliminate smoking from your life, if it occurs. According to scientists, tobacco has a negative effect on memory, which has been confirmed by numerous studies. If you set out to improve your memory, then this is a great reason to quit smoking.
Famous people who had a photographic memory:
- Ronald Reagan, American President, he could memorize an entire page of text in a few seconds just by looking at it.
- Shereshevsky Solomon, writer, artist, journalist, had a good photographic memory.
- A librarian in Italy who lived in the 17th century read over 40,000 books and knew them by heart.
Photographic memory can be developed like any other memory. You choose an object that you want to capture, photograph it and then reproduce it in your memory. Photographic memory, like a camera, pointing the camera, clicking and that’s it.
You can train your photographic memory everywhere at home, at work, on the street, in a store, in the theater, and so on.
For example, you are walking down the street and a person comes towards you, take a photograph of this person and stop looking at him, create his image in front of your eyes, describe this person in your mind. What is he like? What are you wearing? What are the facial features? What does he have in his hands? And so on.
You may not be able to take a high-quality photograph and describe the image of a person; this requires constant training. Over time, you will notice the improvements yourself.
Training should take place in a good positive mood; a positive attitude always helps to achieve the desired result.
Associations
Associative thinking is another key to developing photographic memory. You need to create your own list of associative pictures, which psychologists call an “anchor list.” Words from this list should, according to psychologists, be associated with any arbitrary word, causing a strong association in your mind.
Thus, you can “add” two or three words to each word from your list. After two weeks of such exercises, you can memorize entire texts. It's the same with numbers. Any combination of numbers can be divided into numbers that will cause you a certain association with some event in your life or the lives of other people (even on the scale of an entire country).
The best advice from doctors and coaches on how to develop memory
Human memory can be developed through exercise and systematic training. They improve memory abilities. This was confirmed by championship participants from around the world. Many of them claimed that they did not have phenomenal memory abilities until they began to train constantly.
To increase the effectiveness of exercises, you should give preference to those that are pleasant to perform. If any exercises cause discomfort or irritation while performing them, you should not practice them.
The development of logical thinking plays an important role in the process of memorization. Memory formation is based on systemic perception of information
Solving logical problems will help increase concentration, enhance attention and activate mental processes.
To develop memory and attention, it is necessary to take care of improving cerebral circulation. To do this, it is recommended to spend more time in the fresh air, perform breathing exercises and practices, go for a run, etc.
How to develop memory for an adult
In order to maintain a good memory for many years, you must fulfill 1 simple condition: constantly load your brain with new information. Without receiving fresh emotions and sensations, the brain stops working in the correct mode. By doing the same routine work every day, he gets used to it, and actions are performed automatically without concentration.
As soon as a person stops learning and absorbing a lot of new information, his brain begins to slowly age, regardless of biological age. To prevent this process, intellectual work is necessary: learning foreign languages, acquiring new skills, etc. In this way, not only professional memory will develop, but also emotional and mental memory. Curiosity will be the impetus for new knowledge.
Memory development in children
To develop memorization skills in children, the use of special methods and techniques is not required. You can begin to develop memory as early as 6 months. To do this, you need to play exciting games with your child.
When he reaches 10 months - 1.5 years, you can practice the following game: hide various toys with him that he needs to find. Then you need to move them to other places.
At 2 years old, it is recommended to complicate the game: place 3-4 objects in front of the child, and then remove 1 of them. The child must remember what the missing object was.
At the age of 3, it is recommended to actively learn songs, poems, tongue twisters, and dances. At this age, all types of memory can be developed.
How to quickly develop your memory
Neurobics is a brain exercise that helps activate all processes in it that contribute to memory development; the psychology of its formation depends on many factors.
Unusual actions are the best training for brain activity. To activate it, you need to perform the following simple exercises:
- brush your teeth or comb your hair with the other hand;
- use different scents of perfumes;
- regularly introduce new actions into your morning ritual (eat fruit, do exercises, etc.);
- use new culinary recipes more often;
- listen to unusual music and perform familiar actions to it;
- rearrange furniture;
- update your wardrobe.
Courses for the development of intelligence
In addition to games, we have interesting courses that will perfectly pump up your brain and improve your intelligence, memory, thinking, and concentration:
Development of memory and attention in a child 5-10 years old
The purpose of the course: to develop the child’s memory and attention so that it is easier for him to study at school, so that he can remember better.
After completing the course, the child will be able to:
- 2-5 times better to remember texts, faces, numbers, words
- Learn to remember for a longer period of time
- The speed of recalling the necessary information will increase
Sign up for a courseRead more
Secrets of brain fitness, training memory, attention, thinking, counting
If you want to speed up your brain, improve its functioning, improve your memory, attention, concentration, develop more creativity, perform exciting exercises, train in a playful way and solve interesting problems, then sign up! 30 days of powerful brain fitness are guaranteed to you:)
Sign up for a courseRead more
Super memory in 30 days
As soon as you sign up for this course, you will begin a powerful 30-day training in the development of super-memory and brain pumping.
Within 30 days after subscribing, you will receive interesting exercises and educational games in your email that you can apply in your life.
We will learn to remember everything that may be needed in work or personal life: learn to remember texts, sequences of words, numbers, images, events that happened during the day, week, month, and even road maps.
Sign up for a courseRead more
How to improve memory and develop attention
Free practical lesson from advance.
Sign up for freeRead more
Money and the Millionaire Mindset
Why are there problems with money? In this course we will answer this question in detail, look deep into the problem, and consider our relationship with money from psychological, economic and emotional points of view. From the course you will learn what you need to do to solve all your financial problems, start saving money and invest it in the future.
Sign up for a courseRead more
Speed reading in 30 days
Would you like to quickly read books, articles, newsletters, etc. that interest you? If your answer is “yes,” then our course will help you develop speed reading and synchronize both hemispheres of the brain.
With synchronized, joint work of both hemispheres, the brain begins to work many times faster, which opens up much more possibilities. Attention , concentration , speed of perception are enhanced many times over! Using the speed reading techniques from our course, you can kill two birds with one stone:
- Learn to read very quickly
- Improve attention and concentration, as they are extremely important when reading quickly
- Read a book a day and finish your work faster
Sign up for a courseFree lesson
We speed up mental arithmetic, NOT mental arithmetic
Secret and popular techniques and life hacks, suitable even for a child. From the course you will not only learn dozens of techniques for simplified and quick multiplication, addition, multiplication, division, and calculating percentages, but you will also practice them in special tasks and educational games! Mental arithmetic also requires a lot of attention and concentration, which are actively trained when solving interesting problems.
Sign up for a courseRead more
Types of memory depending on what we remember
People encounter a wide variety of information, which reaches the brain in different ways. Experts identify forms of memorization based on what mental processes were involved.
Figurative memory
The memory department has the largest volume, which should store images obtained through the senses.
Vision provides visual information, incl. and in printed form. Human speech, sounds of nature, and music pass through the auditory canal. A person receives tactile sensations through touch, smells through smell, etc.
Pictures of what is happening around enter the human brain immediately after birth, which is facilitated by imaginative memory. Some people have a special type of memory, thanks to which they can reproduce in detail what they saw, heard or felt.
Motor or motor memory
This ability was characteristic of people at the dawn of evolution. A person often does not realize how important the motor type of memory is for him. Thanks to him, he can not only play sports, dance, but also perform simpler actions, such as making notes in a notebook, pouring water, etc.
Emotional memory
Often a person attaches little importance to the reproduction of feelings or emotions. However, without this process, people's lives would lose meaning. Emotional memory is always associated with associations, i.e., memory occurs with the complete or partial repetition of an event. Sometimes one detail is enough for emotions to arise. However, in memories they will be expressed less intensely than at the time they were received.
Information that has an emotional connotation is always remembered better.
Verbal-logical memory
The verbal-logical form is characteristic only of man. Even if an animal remembers some words, it is only as sound combinations that are associated with a visual, auditory or olfactory image. The process of comprehension is inherent in man.
The best way to remember is through the process of perceiving the text, not individual words. Logical memory is one of the youngest types of mental processes. It requires awareness, which can only be developed purposefully.
Main characteristics
Photographic memory, which can be developed if desired, is characterized by the continued visualization of images after they have disappeared. The picture that appears before your eyes is so real that it can be examined in detail.
The main properties of photographic memory are:
- remembering visual images;
- a lasting imprint of pictures in memory;
- the ability to return to memorized material at any time;
- joining the visual image of other senses (auditory, sensory, olfactory);
- subjective interpretation of paintings.