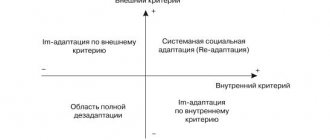
Characteristics of parent-child relationships
Municipal autonomous educational institution "Secondary school No. 19"
Characteristics of parent-child relationships as a factor in the formation of the personality of a primary school student
Atyushina Nadezhda Olegovna
primary school teacher
2019, Balakovo
Characteristics of parent-child relationships as a factor in the formation of the personality of a primary school student
The family acts as a model of behavior and interpersonal relationships. The role of parental behavior as a role model, according to the point of view of A.Ya. Vargi is important not only in the process of acquiring habits [8]. The way of overcoming stress and behavior in stereotypical situations is also determined based on the parents’ line of behavior familiar to the child. Parental attitudes and attitudes towards children at this age can positively or negatively influence their attitudes. Parents' reinforcement of these child positions will contribute to the development of a strong and self-confident personality. Parents who pay attention to their child's successes, positively reinforce his achievements - they will raise a successful person. By instilling an interest in new things, paying the child as much attention as he needs at this age, and without interfering with his communication with peers, parents will cultivate in the child cognitive interest, communication skills, and the ability to communicate. It is very important, at this age, to consult with the child, solve some issues together, listen to his opinion on this, because This is a confirmation of his adulthood and importance for his parents.
The influence of parents is of great importance for the child, as noted by A.S. Spivakovskaya and V.S. Mukhina, it is a source of accumulation of necessary social experience [37]. Communication and behavior skills are the same
Like any other skill, it requires training. Experiences with other children determine how easily a child can later make friends. Children who have been through many, many different situations and have learned to cope with communication problems and enjoy varied social contacts will be able to adapt to a new environment better than others and are likely to respond positively to the changes happening around them.
The attitude of parents, according to A.V. Mudrik, can also cause the opposite result [24]. If you do not notice the child’s successes, but only scold him for his misdeeds, focusing only on mistakes, the child will lose interest in his activities, he will lose the desire to correct his mistakes. A fear of new things will arise - the child will not want to do something, explaining that he will not be able to do it, that he will not succeed anyway. This is how self-doubt is formed, which will most likely accompany the child throughout his life. In the process of close relationships with mother, father, brothers, sisters, grandfathers, grandmothers and other relatives, the child’s personality structure is formed from the first days of life. He enters the world of his relatives and adopts the norms of their behavior. Therefore, parents play a large and responsible role in a child’s life. They provide the first examples of behavior. The child imitates and strives to be like his mother and father. When parents understand that the formation of the child’s personality largely depends on them, they behave in such a way that all their actions and behavior as a whole contribute to the formation in the child of those qualities and such an understanding of human values that they want to convey to him. This process of upbringing can be considered quite conscious, since constant control over one’s behavior, attitude towards other people, and attention to the organization of family life allows one to raise children in the most favorable conditions that contribute to their comprehensive and harmonious development.
Family characteristics. Sample characteristics for a family
In their activities, teachers, psychologists, and social workers are constantly faced with a variety of documentation. Every year it is supplemented and modified, and sometimes it is difficult to keep in mind all the aspects that need to be described. Family characteristics are one of these basic documents. In order not to ask questions about where to start describing a family, what data needs to be collected, in what sequence it should be drawn up and correctly formulated conclusions, you need to familiarize yourself with the structure of this document and create for yourself a sample description of the family.
Psychological characteristics of the family
The psychological component that includes the characteristics of a family includes the following main points:
- Type of upbringing (authoritarian, democratic, liberal) and its subtypes: overprotection, connivance, rejection, demandingness, love and others.
- Description of the psychological climate in the family: stability, tension, stability of the situation, prevailing emotions and states (joy, aggression, apathy, indifference, fear, calm, etc.).
- The degree of interest of parents in the child’s relationships with peers, his achievements, success in educational activities.
- Availability of joint activities with the child, how leisure time is spent in the family, how parents react to the successes and failures of their son or daughter.
Based on these data, we can draw a conclusion about how effective and correct the methods of raising a child are, and whether he or she has pedagogical neglect.
Housing and household characteristics of the family
The next step will be a description of the living conditions in which the family lives. Based on them, you need to draw a conclusion about how comfortable it is for the child to be there, and how much his basic needs are met.
- The number of rooms, the presence of a separate room for the child, the presence of a separate place for rest.
- Compliance with sanitary and hygienic standards of housing: regular cleaning, cluttering of the premises, etc.
- Availability of necessary furniture, space for the child’s educational or play activities, equipment and educational supplies or toys.
- Conclusion about how much the place of residence influences the success of a child’s development.
Family characteristics: where to start?
Before a family profile is drawn up, you need to go through a number of preparatory steps, as a result of which information for the document will be collected:
- Conduct a conversation with the student, observe his behavior, use psychological techniques aimed at studying the child’s perception of his family, and assessing the psychological climate within the family.
- Visit the place of residence of the child and his family, draw up a report on the inspection of living conditions.
- Talk to the parents about the relationship with the child. The degree of parental participation in a student’s school life can be assessed by their participation in parent-teacher meetings, checking his diary, and visiting an educational institution on his own initiative.
To get a more objective picture, it is better not to study the family’s place of residence alone. You can involve a representative of the parent committee, a social teacher or a psychologist (especially in the case of dysfunctional families).
Peculiarities of family characteristics in the work of a psychologist
In addition to the above-mentioned aspects of parenting style and psycho-emotional state, the psychological characteristics of the family can be supplemented with other data:
- who serves as the head of the family (matriarchal or patriarchal decision-making style);
- family structure: open (they allow other people into the family’s social circle), closed (they mostly communicate only with each other), mixed;
- presence of traditions;
- who and how has the greatest influence on the child in the family, to what extent his need for protection and love is fulfilled;
- compatibility of family members according to basic parameters (temperament, character, orientation).
For this type of activity, it is advisable for a school psychologist to have the “Parental Attitude Test Questionnaire” method by Varg and Stolin in the arsenal of a school psychologist.
Social characteristics of the family
The social and psychological characteristics of the child’s family are the most important and massive part of the entire document. Social characteristics of the family include:
- Status: full-time, part-time, with many children or with one child, information about adoption or guardianship of the child.
- Financial security of the family: how stable is the income, what factors does it depend on (payment of alimony, seasonal work, unemployment or disability of family members), does the child have pocket money, how well is he provided with necessary things (food, clothing, school supplies), is he experiencing family financial difficulties, how financial status affects the psychological climate in the family (satisfaction, feelings of inferiority, conflicts).
- Social stability/instability of the family, tendency to addiction (alcohol, drugs, gambling) or crime.
- Distribution of responsibilities and main functions (household, financial, emotional-therapeutic, educational, etc.).
- Who has the formal or actual role in raising a child? It may not necessarily be performed by the same people. For example, parents working abroad are formally the educators of their child, but in fact these functions are performed by another relative (grandmother, grandfather), who is in close proximity to the child.
Assessing the influence of the family on the child
In this block, family characteristics include data on parental participation in the child’s school life and general conclusions are drawn.
Parents can monitor educational activities constantly, periodically, or not be interested in this issue at all. They may be motivating or indifferent to the child's desire to learn and develop their interests. The frequency of attendance at meetings and the nature of the reaction to recommendations and comments from teachers (adequate and inadequate) are also different.
General conclusions are drawn based on the data obtained: how prosperous or dysfunctional the family is in material, social and psycho-emotional terms, what aspects and how they influence the development of the child, what parents or other educators will be advised to pay attention to.
Primary (formal) data about the family
The characteristics of a family should begin with basic, primary data about its members:
- Full name, year of birth, education, place of work and position, contact numbers of mother, father or people who replace them.
- Information about other family members (full name, relationship to the student, field of activity, contact information): grandparents, brothers, sisters and others.
- Information about other people who are not family members, but live in the same house for a long time (full name, field of activity, who the other family members are, contact information).
- Address where family members live.
Description of work carried out with the family
In this block, the profile of the student’s family includes a description of all the work that was carried out by specialists of various profiles with the family: conversations, consultations with a psychologist, social or medical worker, trainings, seminars. It is worth mentioning all the cases when and by whom home visits were carried out, whether family members themselves sought help, and what changes did (or did not) occur as a result of all the activities.
This sample family profile is the most complete because it covers all areas of life, the characteristics of upbringing and the conditions in which the child develops.