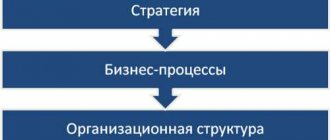
Main types of human activities
Activity is the process of transforming the surrounding reality. A person can try to change material things, nature, society, himself in order to satisfy his needs.
It consists of several elements:
- Subject (performs actions).
- Object (what actions are aimed at).
- Motive (encourages action).
- Goal (expected result).
- Means (what they use).
- Process (order of actions).
- Outcome (result).
There are different types of human activity depending on the goals, the object to which the action is directed, and the result. But this division is conditional. The same concrete action can be material and spiritual.
For example, printing books not only creates physical paper copies. Works are written, edited and read, that is, mental work occurs.
Characteristics
Experts identify the following four main features of human activity, which determine its specificity and characteristics:
- Consciousness , since a person consciously sets a specific goal for his own activity and determines ways to achieve it.
- Productivity (activity always leads to the individual obtaining the final result he planned at the beginning of the activity).
- Transformation , i.e. people changing the surrounding reality or themselves.
- Social character , due to the entry of an individual in the process of activity into various relationships with other individuals.
Practical activities
This variety is aimed at creating or changing material things and the environment. Man produces certain objects, changes their appearance or properties, and influences nature.
This includes:
- sewing clothes;
- creation of equipment at the plant;
- deforestation;
- construction of houses.
That is, all material goods and everything that exists on the planet thanks to society.
Action
An action is a single element of activity.
The latter consists of a set of small steps interconnected. For example, to build a house, you first need to dig a foundation, build walls and a roof, and pour the floor.
Sociologist M. Weber identified 4 types of social actions :
- goal-oriented – striving to achieve a reasonable goal (preparing a speech before a speech);
- value-rational – focused on moral values (a soldier’s refusal to give up his country’s military secrets);
- affective - actions committed under the influence of feelings and emotions (a person in a rage can break something);
- traditional - habitual actions, rituals, customs (throwing a wedding bouquet into a crowd of bridesmaids, fireworks for the New Year);
The first two types underlie activity, the second two appear partially and are of an auxiliary nature.
Spiritual activity
She strives to change the inner world, thinking, consciousness of both one person and society. Views of the world, understanding of good and evil, and awareness of one’s goals are formed.
This includes the scientific, creative, religious spheres of life, that is, everything that is directed inside a person, and not at the outside world. This could be learning something new, painting a picture, reading a prayer.
Target
When internal motivation takes place, we begin to build an image in our head of what we want to achieve in the end. A girl who wants to get married begins to think about what her future husband should be like: age, eye color, social status, nationality, appearance, etc. Thus, she paints for herself a clear picture of what she actually needs to strive for.
Goal setting is an integral part of human activity.
We first create something in our minds, then we try to bring it to life. Animals, unlike us, are guided only by instincts: they do not think about what, how and why they do something. When choosing a female, a wolf does not walk through the forest for 3 years looking for a she-wolf with the most beautiful fur, but a person is quite capable of this.
Maybe this is our happiness - we can choose and adjust our goals.
Leading activities: play, communication and work
Also among the types of activities are play, communication, and work. During the game, actions are performed using imaginary means. It is the process that matters, not the result. Play can be both entertainment and a way to explore the world.
The transfer of information through interaction is called communication. It is needed to exchange news or important information, as well as to improve your emotional state.
Labor is aimed at creating material or spiritual benefits that will be useful to people. It can be physical, mental or a mixture, such as sewing clothes.
Means to achieve the goal
So, I see the goal. I'm going to see her. At this stage we choose the means to achieve what we want. By means here we mean anything - anything that will help you achieve your goal. If you want to become a good cook, you will have to graduate from culinary school, gain experience, and constantly improve your skills by learning new skills.
It is important to know: firstly, the means and the end must be proportionate . For example, you want to make money, you open a personal business (flower shop), but in the end your enterprise operates at a loss. A reasonable person understands that in this way he will never improve his well-being and will try something else - the means will not justify the end.
Secondly, the means must be in the moral category . If this is not so, then all human activity is immoral. Violating the law, lying to achieve personal gain, betraying loved ones for the sake of your goal is immoral. In this case, the end does not justify the means.
Types of human professional activity
When a person performs his duties at work, it is considered a professional activity. It has standards, goals, predictable results. The employee receives specific knowledge and skills to become a representative of the profession.
| View | Description | Example |
| Man-technique | Working with mechanisms | Car mechanic, welder, plumber |
| Man-man | Interaction with others, communication | Teacher, journalist, waiter |
| Man-nature | Working with plants or animals | Veterinarian, biologist, gardener |
| Sign Man | Processing numbers or symbols | Accountant, translator, engineer |
| Man-artistic image | Making art | Artist, actor, musician |
Ways to improve work efficiency
The result of the enterprise’s activities depends not only on increasing the number of employees and improving the material and technical base, but also on improving the skills of existing employees. This is achieved through in-house training. Such training, in essence, is the body’s adaptation to new psychophysiological functions that the employee must subsequently perform.
To achieve the goal of work, the employee needs rest. One of the most effective ways to improve the quality of staff performance is to optimize work and rest schedules. As a rule, the change between work and rest must be observed at certain periods of time, namely during:
- work shift (break)}
- days (standard working day)}
- weeks (weekends)}
- year (vacation).
The specific time allocated for rest depends on the conditions in which the employee works, as well as on the terms of the employment contract. This applies to both short-term breaks (during the working day) and long-term ones (during the year). Thus, for most professions, the norm for short-term rest is 5-10 minutes. In one hour. Thanks to this break, you can restore the psychophysiological functions of the body, as well as relieve tension.
Reactionary activity
Such actions have a negative result, which led to decline. This effect is assessed on a historical scale. Therefore, sometimes the same action can belong to different types at different times.
Examples include the beginning of World War II or the introduction of the oprichnina. These events led to large-scale negative consequences.
Transport industry
The transport economy or transport system is a means of communication between industry and agriculture, as well as between other activities. In order to ensure the exchange of products between different directions, transport is needed that will solve this problem. In addition, transport activities allow people to move to different parts of the country or the world. Today there are several types of transport:
- Zheleznodorozhny
. Includes all trains, locomotives, trains, subways. It is the safest means of transportation and has a high efficiency factor. - Automotive
- these are cars of various classes - trucks, cars, special ones. - Air
means airplanes and helicopters. - Water
- it consists of ships, barges, boats, boats.
Rice. 3. Mozhaisk interchange of the Moscow Ring Road
Material activity
Associated with changes in real objects of the surrounding world that can be seen or felt. The results have meaning for one person or a large group of people.
This includes:
- agriculture;
- production of parts in factories;
- cooking.
Creativity also has a material side, as artists can create paintings or sculptures.
Services sector
All three areas of activity mentioned below are combined into one group, which is called the service sector. In themselves, they are not human economic activity as such, but contribute to its active development.
The science
Science in the state is a fundamental part that allows regulating not only processes within the country, but also providing the country with innovative technologies, providing the most advanced developments, discoveries, and facts. Science includes all possible areas of human activity.
In its essence, science is a certain set of knowledge in a specific environment, which is characterized by a wide range of concepts, terms, and patterns. Thanks to scientific discoveries, any country can take a leading position in the world rankings. Science helps the state develop.
Education
Education is the state’s guarantee for a bright future. Time flows mercilessly forward, and with it the years of life. The old generation is being replaced by a new one. But in order for it to ensure a decent existence and development for itself, its family and the Motherland, it is necessary to teach young people how to do this correctly, how to correctly assess the situation. Education in the Russian Federation consists of three main stages:
Each stage is divided into several stages, and they, in turn, are characterized by a certain set of knowledge and skills. Only after receiving a sufficient level of knowledge will a person be able to apply it in his life and engage in a specific type of economic activity.
Rice. 4. Service workers
Arts and culture
Art has always played a significant role in the development of the country. It was this that helped not only to sensibly assess the situation, but also to compare reality with fantasy. Art is a fairly broad concept that includes such areas as painting and literature. Providing spiritual good is the true goal pursued by culture. Cultural wealth, heritage is something that will never be forgotten. It has been preserved for many thousands of years, passed down from generation to generation. Traditions are what a nation values, which shows not only customs, but also the moral state of each person. For every citizen, culture is part of the soul. It is impossible not to take part in industrial activity - perhaps not to take part in cultural development.
Education
This is another important type of human activity. The social studies topic devoted to activity is interesting because it examines its various types and allows us to consider the whole variety of types of human activity. Despite the fact that the human learning process begins in the womb, at a certain period of time this type of activity becomes purposeful.
For example, in the 50s of the last century, children began to be taught at the age of 7-8 years; in the 90s, mass education was introduced in schools from the age of six. However, even before the start of targeted learning, the child absorbs a huge amount of information from the world around him. The great Russian writer L.N. Tolstoy emphasized that at the age of 5 years a small person learns much more than in the rest of his life. Of course, one can argue with this statement, but there is a fair amount of truth in it.
Knowledge, abilities, skills, habits
Knowledge, abilities, skills, or KUN – the basis responsible for organizing and managing practical activities.
Knowledge
These are images of sensations and perceptions, later processed into ideas and concepts. Without them, conscious, purposeful activity is impossible. Knowledge increases the effectiveness of actions.
Skills
This is mastery of a method of performing an action that does not require reinforcement with exercises. Conscious individual control is the main difference between skills. They are closely related to thinking and are impossible without active intellectual activity. Skills allow you to find a way out of non-standard situations and respond to changes in external conditions.
Skills
Skills are actions brought to automaticity. The success of an activity depends on skills. Skills are formed through exercise - repeated repetition of a specific action (actions). The skill is based on a dynamic stereotype, that is, a neural connection between the elements of the action. This happens uncontrollably, but if any inaccuracy occurs, the person immediately notices it. The stronger the nerve connection, the faster and better the action.
Skills can be motor, thinking, sensory, behavioral. The skill is formed in several stages:
- introductory (comprehension of actions, familiarization with implementation techniques);
- preparatory (conscious but inept execution of an action);
- standardizing (unity and automaticity of actions);
- situational (mastery of arbitrariness of action).
Learning new skills is always influenced by old ones. Sometimes this helps, and sometimes it hinders. In the first case we are talking about coordination of skills, in the second – about interference (contradiction). Skills are aligned when:
- the movement system of one skill coincides with the movement system of another;
- one skill is a means of better mastering another;
- the end of one skill is the beginning of another and vice versa.
Accordingly, interference occurs under the opposite conditions.
Habits
A habit is an action that has become a need. Habits can be positive and negative. Habits, like skills, are based on dynamic stereotypes. Habits are formed through:
- imitation;
- multiple random repetitions;
- conscious, goal-directed learning.
They can be a driving force or a braking factor when performing an activity.