Many people develop a too frivolous attitude towards games: for most, it is nothing more than an entertainment event. Psychologists and psychotherapists look at them completely differently. They know that in professional hands, a game can become a diagnostic, educational, correctional and even therapeutic tool - not only for children, but also for adults.
It is able to illuminate the most hidden corners of the soul, reveal the causes of psychological trauma, and also form new, more useful skills of behavior and thinking. Game therapy, one of the leading areas of psychology and psychotherapy, deals with all this.
What it is
There are a huge number of definitions of this concept. To summarize them, game therapy is a method of psychological or psychotherapeutic influence on a person using games.
At the same time, experts clearly distinguish between two concepts:
- Play therapy is a psychological tool that only has the power to correct emotional and behavioral disorders.
- Play psychotherapy is a psychotherapy tool that deals with the treatment of borderline personality and behavior disorders.
Game therapy differs from ordinary play in that it is an organized play activity that has a therapeutic and corrective effect. It is carried out in specially created conditions under the close attention of a psychologist or psychotherapist and has clearly defined goals. The usual game is entertaining and occurs spontaneously, without outside interference.
You should also understand the difference between play therapy and role play. The latter can be presented in two forms.
- As one of the play therapy techniques
The specialist invites a group of patients to simulate events occurring under certain conditions. Participants must act according to their character's inner beliefs. At the same time, it is assumed that their actions will reflect their true motives, which they may, for one reason or another, hide in reality. Here, a role-playing game helps the play therapist understand what exactly is happening to his patient and in what direction to carry out further correction or treatment. She can also demonstrate one of the solutions to a problematic life situation.
- As an entertainment event
An ordinary role-playing game, outside the sphere of psychology and psychotherapy, although distinguished by a clear organization, is still entertaining in nature. All participants fulfill a specific goal set for their characters, the master’s task is to ensure that all the rules are followed, but nothing more.
Direction use
| Organizers |
More organizers 131
Coaches Alexander Pokryshkin (Moscow), Anastasia Ivelich (Moscow), Anna Zhuravleva (Moscow), Anna Nikitina (Moscow), Annetta Andreevna Barkevich (Moscow), Arsenia Valerievna Libon (Shklyaeva) (Moscow), Valentina Valerievna Mitrofanova (Moscow), Valery Akimov (Moscow), Victor Razuvaev (Moscow), Galina Popova (Moscow), Daria Vladislavovna Lapshina (Moscow), Daria Kondratova (Moscow), Deya Vladimirovna Leoran (Moscow), Dmitry Andreevich Lyubimov (Moscow), Evgenia Vavilova (Moscow), Ekaterina Danilina (Moscow), Ekaterina Ilyicheva (Moscow), Ekaterina Latskova (Moscow), Elena Altunina (Moscow), Elena Sergeevna Mokhova (Moscow).More trainers 346
Consultants Anastasia Ivelich (Moscow), Anna Zhuravleva (Moscow), Anna Nikitina (Moscow), Annetta Andreevna Barkevich (Moscow), Valentina Valerievna Mitrofanova (Moscow), Valery Akimov (Moscow), Viktor Razuvaev (Moscow), Galina Popova (Moscow) , Daria Kondratova (Moscow), Deya Vladimirovna Leoran (Moscow), Dmitry Andreevich Lyubimov (Moscow), Evgenia Vavilova (Moscow), Ekaterina Danilina (Moscow), Elena Altunina (Moscow), Elena Sergeevna Mokhova (Moscow), Elizaveta Vasina (Moscow) ), Irina Aleksandrovna Yusupova (Moscow), Irina Vadimovna Mokrousova (Moscow), Katerina Rabei (Moscow), Ksenia Radikovna Gareeva (Moscow).More consultants 268
Play therapy in other cities Tver, Kaluga, Tula, Nizhny Novgorod, Kursk, Voronezh, St. Petersburg, Kazan, Kiev, Volgograd, Rostov-on-Don, Kaliningrad, Perm, Ufa, Krasnodar, Black Sea coast, Stavropol, Poland, Magnitogorsk , Yekaterinburg, Chelyabinsk, Tyumen, Omsk, Novosibirsk, Tomsk, Barnaul, Kemerovo, Novokuznetsk, Krasnoyarsk.Thank you for your interest in the topic “what is Play Therapy”!
Tasks
The main game therapy function of the game is to identify and correct deviations in behavior and psyche in a relaxed environment. To implement it, depending on the specific problem, specialists solve several problems at once:
- restoration of trust in others, assistance in social adaptation, development of the communication sphere, optimization of relationships in the systems “child - parents”, “child - adults”, “child - other children” (similar schemes are being developed for adults);
- deactualization of phobic manifestations;
- demonstration of various ways to solve difficult life situations;
- correction of deformations in the formation of the “I-concept”;
- correction of negative character traits and behavioral deviations;
- treatment of borderline personality and behavior disorders;
- relief of psychological suffering;
- increasing self-esteem, getting rid of internal complexes;
- creating favorable conditions for the development of speech, thinking, memory and other cognitive abilities.
To summarize all these tasks, specialists using play therapy diagnose the problem and either correct it (in psychology), or treat it (in psychotherapy), and also teach.
Game therapy as a diagnostic tool:
- clarifies personality characteristics;
- clarifies relationships with the outside world in general and specific people in particular;
- reveals childhood psychotraumas at the sensorimotor level;
- demonstrates involuntary expression of oneself.
Game therapy as a means of developing cognitive processes:
- improves speech skills;
- develops memory (you need to remember the rules of the game, your goal in it, the names of the other characters);
- demonstrates how to solve difficult life situations;
- improves thought processes;
- broadens your horizons about the world around you;
- teaches social adaptation skills;
- forms an adequate mental response to events;
- develops the ability to arbitrarily regulate activities against the background of the need to obey a general system of rules.
Game therapy as a method of psychological correction:
- adjusts the system of social relationships;
- helps to overcome personal and cognitive egocentrism and decentration towards comprehension of one’s own “I” in the game;
- promotes understanding of such concepts as equality and partnership, cooperation and cooperation,
- provides the opportunity for personal development;
- organizes new methods of orientation in conflict situations;
- adjusts the system of life values and prioritization;
- corrects negative character traits and deviant behavior;
- eliminates psychological and behavioral barriers.
Game therapy as a method of psychocorrection and as a means of developing cognitive abilities is a tool of psychology. In psychotherapy it is used as one of the auxiliary treatment methods:
- eliminates bad habits;
- helps overcome worries and fears;
- relieves internal tension;
- solves severe psycho-emotional problems;
- effective in treating autism;
- increases frustration tolerance;
- gradually develops and strengthens disturbed mental processes.
Different games for different purposes
Unfortunately, there is no one universal game that would allow you to get rid of childhood problems. The choice of game depends on the source of the disorder and its depth. It is best if a psychologist selects suitable leisure time. But there is no harm from games, so you can use the recommendations described below.
Several conditions must be met for the game to be successful.
- Such a pastime should be interesting not only for a child, but also for an adult. Children always sense insincerity. And if they know that their parents play with them because they have to, and not because they want to, then the entire therapeutic effect may come to naught. The sincere pleasure of all participants is the key to success.
- The game should be spontaneous. For kids this is of particular importance. If a child plays according to some schedule, then for him it will not be entertainment, but work.
- The game must be voluntary. In general, this is obvious from the previous paragraphs. Entertainment under pressure is no longer such.
Games to improve psychological well-being
Children feel calm when they know that someone needs them and is interesting. The easiest way to show this is through the following well-known games:
- blind man's buff;
- tag;
- hide and seek;
- obstacle course.
In all games, it is important to give in a little, if it is clear that the baby is not coping, encourage and praise for success
Games that help correct aggression
For children who show aggression, it is important to show in contrast that there is another model of behavior, and also that any dispute should end on a positive note. These games can be played from the age of two
- War game. A child and an adult throw various safe objects at each other: pillows, wads of paper, plush toys, using shields and shelters. And they end the fight with a draw and hugs.
- Cats. The baby and the adult take turns turning together, either into kind, purring and caressing cats, or into angry and hissing ones. Instead of cats there can be dogs, hedgehogs and any other animals.
Games aimed at relieving tension and relaxation
The main goal of eliminating these parameters is a change in brain activity and physical calm.
- The sea is agitated once. The well-known game works great for distraction and relaxation. The adult says: the sea worries once, the sea worries two, the sea worries three, the sea (terrestrial, vegetable, any other) figure freeze! While voicing the phrase, the child sways as if on the waves and freezes at the last word in some position until the presenter guesses what kind of figure it is. Then the players change roles, or do the same thing again. This entertainment is suitable for children from three years old.
- Doll. The presenter tells the child to imagine that he is turning into a doll. Lists all the parts of the body that should become stiff, while pressing on them. The child freezes in one position, trying to tense all his muscles until the adult says that the baby has become a human again. He becomes glorified and softens. This game can be played from the age of four.
Games that help correct fears
If a child is worried about internal experiences and fears, it is important to show him that in any situation you can find a way out and be saved.
- Cat and mouse. An adult and a child take turns taking on the role of a cat or a mouse. The cat is sleeping, and the mouse is running around him and squeaking. He wakes up, starts hunting for the mouse, she runs away and saves herself in her hole. This game can be played from two years old.
- Bringing. One of the players puts on a sheet and becomes a ghost. With a frightening “UUU” sound, he begins to run after the other participant and if he catches them, they change roles. This type of entertainment can be used from the age of three.
Main types and forms of play therapy
Depending on the degree of intervention in the game by a specialist
- Directive
The play therapist is the organizer and leader of the entire game process. He takes an active part in it, asks questions, directs, and plays a character himself. He takes responsibility for achieving his goals.
- Non-directive
The play therapist is an observer from the outside. Only at the very beginning does he determine the rules of the game, and then does not interfere in the process and watches how the participants behave. Only the most general goals are set (to help restore mental balance, overcome fear, learn socialization skills), but not specific ones. This is explained by the fact that it is unknown how this or that character will behave and what he will come to by the end of the game.
Depending on the theoretical model
- Psychoanalytic (psychodynamic)
Founders: A. Freud, D. W. Winnicott, M. Klein. In psychoanalysis, spontaneous play activity is the direct and surest path to the unconscious, a way of processing the experience of early psychotraumas and conflicts. Recently, sand play therapy has gained great popularity within the Jungian school of psychoanalysis.
According to research, sand play therapy stabilizes the emotional state, helps express emotional experiences, relieves fears, and relieves psychological stress. You can draw anything on the sand and not be afraid to make a mistake, because everything can be easily and repeatedly corrected with one movement of the hand.
- Humanistic/centered
Founders: V. Exline, K. R. Rogers, G. L. Landreth. Refers to non-directive play therapy. The main condition is spontaneity.
- Behavioral
Founders: B.F. Skinner, A. Bandura. The main function is performed by a play therapist - teaching how to correctly play social roles.
- Liberating
Founder: D. M. Levy. Creating gaming conditions that provide the opportunity to relive a conflict, traumatic situation, but in a calmer and safer environment. This allows you to free yourself from tension and fears.
- Structured
Founder: G. Hembridge. Creating a clearly structured game situation that allows you to solve specific problems.
- Relationship building
Founders: O. Rank, Taft, F. Allen. The relationship between the play therapist and the client is built on the “here and now” principle, without references to past experience and a return to childhood.
- Primitive
Promotes children's intellectual, emotional, physical and social development through appropriate learning opportunities.
- Integrative-eclectic
Harmoniously includes elements of all previous directions.
Depending on the material used
- Unstructured
Involves the use of outdoor games (jumping, climbing), exercises and tasks with water, clay, plasticine, sand, and art therapy. With all this unstructured material you can express your hidden desires. He develops sublimation.
- Structured
Involves the use of family games, with puppets, dolls, construction, aggressive (using toy weapons). Helps to see a person’s constructive and destructive intentions.
Depending on the duration of the course
- Short-term - from 2-3 lessons to 1 month;
- long-term - from 1 month to 1.5 years.
Depending on the number of people
- Individual - work with one client;
- group - for children 4-5 years old, a group of no more than 4 people is created; for 5-11 years old - 6, for 11-14 - 8, starting from 15 - 10.
Specialists must be clearly aware that there is only one contraindication for individual play therapy - a deep degree of MR. For a group there are quite a lot of them:
- pathological jealousy;
- competition with siblings;
- antisocial behavior, when a person (child) may pose a threat to other group members;
- early or accelerated sexual development;
- excessive aggressiveness;
- aggravated stress state.
What is not a contraindication for group play therapy:
- need for communication;
- the desire to earn approval from others;
- desire for high social status;
- minor deviations in behavior due to the lack of basic social skills;
- lack of love;
- internal complexes, low self-esteem.
Group play therapy is organized only if the child has developed a system of basic social skills and communicative orientation.
How is play therapy carried out?
Play therapists use several techniques to treat children, either physically or cognitively, who have difficulty playing. Many of the methods are rooted in psychotherapy and psychology. Some are designed to enable the child to adapt to physical impairments using step-by-step processes, modified processes, adaptive equipment, or assistive technologies.
The act of playing itself is often therapeutic for children. Activities such as playing games, drawing or stringing beads help children develop flexibility and dexterity while experiencing control over their environment. Interacting with other children, or an animal, can help a child communicate; thereby eliminating the feeling of isolation.
There are three forms of play therapy:
- Number directed play occurs when the child is encouraged to continue playing whatever she or she wishes. This gives the therapist a snapshot of how the child is feeling and what issues may be preventing the child from fully expressing him or herself in other situations.
- Directed play occurs when the therapist determines how the play will proceed.
- Play indications are when the therapist teaches the child adapted play techniques.
Play therapy can be done on a one-on-one basis between therapist and child, or in a group—or both. In addition, play therapy covers many types of play, from physical activities that require movement, to using toys in groups or alone, to passive activities like listening to a story.
During play therapy, children will learn:
- Advantages of the game
- How to have fun
- How to make friends
- How to channel the momentum to play the action
- How to play and together with others
- How to Thrive in a Group Setting
- How to minimize physical limitations
- How to physically manipulate toys and objects
- How to comply with socially accepted norms of the game
Techniques used in play therapy include:
- Talk therapy
- Conversation to engage with a child
- History time featuring books that support positive messages
- Animal interaction
- Human interaction with children and colleagues or adults with authority
- Time for family
Play with purpose often and have fun. Toys are exciting, exploitative and manipulative. Arts and crafts promote exchange and openness. Large art projects created with others provide a sense of partnership. Dramatic dance or musical performances engage the senses.
It's easy to understand why children embrace play therapy compared to other treatments; they often do not perceive play in a negative light; difficult or painful.
Principles, methods, techniques
Basic principles of play therapy:
- gaming activity is not an entertainment event, but a means of diagnosis, correction, training and auxiliary treatment;
- the topic of the game is significant for the play therapist and interesting for the client;
- activation of independent initiative of participants;
- directive and non-directive game components complement each other;
- the relationship between spontaneity and specific focus is determined not by the age of the participants, but by the characteristics of their psyche;
- gameplay can be directed, but not commented on by adults;
- psychological and psychotherapeutic influence is carried out through the characters.
Basic methods:
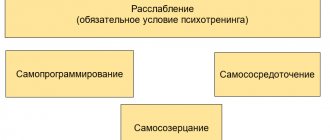
- suggestion in reality;
- auto-training;
- imagotherapy;
- independent and role-playing games;
- improvisation.
Main directions:
- sand play therapy;
- fairytale therapy;
- puppet therapy;
- chess;
- musical;
- motor;
- role-playing;
- dramatic.
Depending on the directions, the techniques used are determined:
- sand drawing;
- writing and playing fairy tales;
- sculpture and design using clay, alabaster, wax, soap, wood, wire, metal, paper, boxes and even garbage;
- games with dolls;
- chess helps to realize and fulfill life's tasks (according to Gestalt therapy, each chess piece, creating its own tactics and each move demonstrates some new aspect of personality);
- games involving music and dancing are a new method of adaptive education for preschoolers with mental retardation;
- stage productions, when the character of the hero reveals the actor himself, his fears, experiences, and complexes.
Depending on the problem at hand, a play therapist can choose one technique to work with a person. For example, for children with mental retardation, the most effective option would be music and dance games. But most often, specialists combine methods, directions and techniques to achieve a more comprehensive result.
Who is better for a child to play with?
It is impossible to answer this question unambiguously. It all depends on the goals described above. If it is necessary to reveal potential or slightly correct behavior, then it will be comfortable and adaptive to do this with parents. After all, they are the ones who know their baby better than anyone else and will find an approach to him. And the child will be more comfortable playing with relatives. Regular trips to the office with a “Psychologist” sign can themselves cause stress, which is unnecessary if the baby is just a little capricious, for example.
Parents cannot always cope with psychological disorders on their own due to many factors: subjectivity, lack of appropriate education, time, desire, and others. Therefore, in such cases, it is better to contact a play therapist who, if necessary, will involve both mom and dad in the game or teach them how to play at home.
On practice
For preschoolers
For young children, play activity is the leading one. Therefore, most activities in kindergarten are based on it.
What kind of games and exercises can be used for preschool children aged 3-4 years:
If at 3-4 years the main task of play therapy is training and development (of the same cognitive abilities), then at 6-7 years it acquires a more diagnostic and corrective nature, allowing the correction of psychological problems.
For children 6-7 years old:
For problem children
Play therapy in childhood can effectively treat all kinds of personality and behavior disorders.
For children with disabilities
Play for children with disabilities often remains the only way to express themselves due to their specific characteristics. At the same time, it allows specialists to help treat the underlying disease and develop the child as much as possible.
Recommended: finger (Bird, Horned Goat, Bell), with waste material (laces, clothespins, beads, buttons), educational (construction set, mosaic, puzzles).
With anxious children
Research shows that play therapy has a harmonizing and corrective effect on the level of anxiety in children and on their mental state in general.
Relaxation and breathing exercises: Fight, Balloon, Gift under the tree, Piper, Barbell. For relaxation: Dancing hands, Waterfall. To develop a sense of trust and self-confidence: Bunnies and elephants, Change of rhythms and many others.
For preschoolers with aggression
Children become aggressive because they have nowhere to throw out the negative energy accumulated as a result of psychological trauma. Play therapy helps them with this.
To relieve muscle tension: Ball, Circus, Chase away Baba Yaga, Caricature, Let's make a fairy tale, Glue rain. For such children, outdoor play activities will also be useful: Two rams, Tukh-tibi-duh, Ask for a toy (in verbal and non-verbal versions).
Board games
Activities with children can be not only active. It is also possible to use board games. As art therapy, they contribute to the development of the child’s abilities and personal qualities. In addition, they combine play with learning. That is why conducting such classes can become a wonderful educational tool for preschoolers.
Board game therapy develops a child’s attention and visual memory, logic and intelligence, imaginative thinking and imagination. As a rule, several people should take part in such classes at once.
In this case, art therapy games promote interaction between children. By obeying the proposed rules, preschoolers learn proper communication with each other, patience while waiting for their turn to make a move, empathy for their opponents, as well as accepting with dignity not only victories, but also defeats. Thus, board games in art therapy allow you to correctly form a child’s personal qualities.
Among the main advantages of such activities is the lack of need for playgrounds and complex equipment. For them you only need a table and all the necessary items (cubes, chips, cards, etc.). Such games have the following advantages:
teach preschoolers to recognize and then remember a wide variety of phenomena and objects, develop the child’s attention and expand their vocabulary, doing this in an interesting and colorful way; prepare the baby for life by offering him certain problems, solving which the baby develops his skills and abilities, gaining life experience; help improve reaction speed, dexterity, coordination and eye. For example, the board game “Shopping Therapy”
It is intended for girls. Her goal is to make as many purchases as possible while spending as little money as possible. During the game, the participants will have to take turns making moves. This will allow them to enter the boutiques of the shopping center. It has two floors. At the first of them, you are offered to buy various outfits, as well as choose accessories to go with them. The second floor is the entertainment area. You can get here by going to the “elevator” field. The participant who finds herself on the second floor must skip one lap. Here, when entering the fields of restaurants and bars, she will have to pay a certain amount. The one who is lucky finds himself in the field of luck. Here you can win a certain amount of prize money. The winner is the participant who managed to buy the most goods while spending the least money on them.
For example, the board game “Shopping Therapy”. It is intended for girls. Her goal is to make as many purchases as possible while spending as little money as possible. During the game, the participants will have to take turns making moves. This will allow them to enter the boutiques of the shopping center. It has two floors. At the first of them, you are offered to buy various outfits, as well as choose accessories to go with them. The second floor is the entertainment area. You can get here by going to the “elevator” field. The participant who finds herself on the second floor must skip one lap. Here, when entering the fields of restaurants and bars, she will have to pay a certain amount. The one who is lucky finds himself in the field of luck. Here you can win a certain amount of prize money. The winner is the participant who managed to buy the most goods while spending the least money on them.
Thus, "Shopping Therapy" is a game that is an interesting and exciting entertainment. Here, each of the participants will feel as if she was in a real shopping center, where she is offered to buy everything she wants for money.
The game package includes the playing field itself, as well as 60 red and 24 yellow tokens. They come with 4 passports, 60 banknotes, a move die, 72 cards, and 20 Excursion cards. The game rules are also included.