Adaptation is the adaptation of the body to the circumstances and conditions of the world. Adaptation of a person is carried out through his genetic, physiological, behavioral and personal characteristics. With adaptation, human behavior is regulated according to the parameters of the external environment.
The peculiarities of human adaptation lie in the fact that he must achieve simultaneous balance with environmental conditions, achieve harmony in the “man-environment” relationship, and adapt to other individuals who are also trying to adapt to the environment and its inhabitants.
Adaptation concept. There are two approaches to analyzing the phenomenon of adaptation. According to the first approach, adaptation is a property of a living self-regulating organism, which ensures the constancy of characteristics under the influence of environmental conditions, which is achieved by developed adaptive abilities.
According to the second approach, adaptation is a dynamic formation, the process of an individual getting used to environmental circumstances.
Since man is a biosocial system, the problem of adaptation should be analyzed according to three levels: physiological, psychological and social. All three levels have a connection with each other, influence each other, and establish an integral characteristic of the overall functioning of the body’s systems. Such an integral characteristic manifests itself as a dynamic formation and is defined as the functional state of the organism. Without the term “functional state” it is impossible to talk about the phenomenon of adaptation.
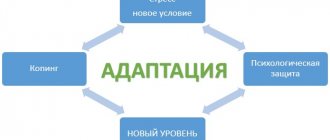
Adaptability in situations in which there are no barriers to success is achieved through constructive mechanisms. These mechanisms include cognitive processes, goal setting, and conformist behavior. When the situation is problematic and saturated with external and internal barriers, the adaptation process occurs through the defense mechanisms of the individual. Thanks to constructive mechanisms, a person can show an adequate response to changes in social life circumstances, taking advantage of the opportunity to assess the situation, analyze, synthesize and predict possible events.
The following mechanisms of human adaptation are distinguished: social intelligence - the ability to discern complex relationships, dependencies between objects of the social environment; social imagination - the ability to understand experience, mentally determine fate, realizing oneself now, one’s resources and capabilities, placing oneself within the framework of the current stage of society; realistic aspiration of consciousness.
Personality adaptation consists of a system of defense mechanisms, thanks to which anxiety is reduced, the unity of the “I-concept” and the stability of self-esteem are ensured, and the correspondence between ideas about the world and about the person himself in particular is maintained.
The following psychological defense mechanisms are distinguished: denial - ignoring unwanted information or traumatic episodes; regression – a person’s manifestation of infantile behavior strategies; formation of a reaction - changing irrational impulses, emotional states to the opposite; repression – “erasing” painful memories from memory and consciousness; suppression is almost the same repression, but more conscious.
The above-described basic protective mechanisms during personality adaptation are still additional, they are considered more mature: projection - attributing to someone qualities and actions that are inherent in the personality itself, but she is not aware of them; identification - identifying oneself with some real or imagined character, attributing to oneself his qualities; rationalization - the desire to explain an action, interpreting events in such a way as to reduce its traumatic impact on the individual; sublimation – transformation of instinctive energy into socially acceptable forms of behavior and activity; humor is the desire to reduce psychological stress by using humorous expressions or stories.
In psychology, there is the concept of an adaptation barrier; it means a kind of boundary in the parameters of the external environment, beyond which personal adaptation will no longer be adequate. The properties of the adaptation barrier are expressed individually. They are influenced by biological environmental factors, constitutional personality type, social factors, individual psychological factors of a person that determine the adaptive capabilities of the individual. Such personal properties are self-esteem, value system, volitional sphere and others.
The success of adaptation is determined by the full functioning of the physiological and mental level of the individual. These systems are located and function in interconnection. There is a component that ensures this relationship between the two levels and carries out the normal functioning of the individual. Such a component may have a dual structure: a mental and physiological element. This component in the regulation of human adaptation is emotions.
Biological and psychological adaptation
Biological adaptation is a phenomenon that unites humans and non-intelligent life. The term usually refers to the ability to adapt to changing external conditions. They take into account climate, internal changes in the body, light levels and environmental pressure indicators, humidity levels, and forced limitations in the implementation of certain functions. Internal changes to which one has to adapt are also various diseases.
Adaptation
Psychological adaptation is the process of adjusting an individual to social requirements, the needs of oneself, and an individual set of interests. Social adaptation involves the assimilation of norms and values that are relevant to the community in which a person finds himself. This applies not only to a large community, but also to small social formations, for example a family.
Stages, levels, stages
Scientists distinguish three stages of adaptation:
- There is a destruction of the existing program of homeostasis and stability of physiological functions to the maximum limit (i.e., not below the limit of minimal support for life).
New programs have not yet passed the implementation stage or have not been created, but old programs have already been destroyed. Therefore, the body goes into “temporary adaptation” mode in order to survive the critical period. Individual behavior comes down to defense. - Creation and implementation of a new program that forms the structure of homeostatic regulation.
- The body’s activity goes into a stable mode and new protocols “optimize the life” of the individual.
Levels of adaptation:
- physiological adaptation (reaction of compensatory systems that support vital functions in extreme conditions),
- social adaptation,
- psychological (development of new neural connections that control the intensity and sequence of the individual’s reactions),
- work adaptation,
- anatomical adaptation.
stages :
- before adaptation begins,
- introductory stage (situation assessment),
- familiarization (study of the situation and its accompanying conditions),
- entry (integration into the current situation),
- action (a dynamic process in which changes occur and a protocol of behavior/reactions is formed),
- functioning (following a new protocol of behavior/reactions),
- completion (fixing the new protocol as a base one).
Social adaptation
Social adaptation is a phenomenon that can be observed by tracking the evolution of interactions between a person and the individuals around him. To assess the ability to adapt, it is necessary to observe the active activity of the individual. The social aspect of the phenomenon under consideration presupposes the ability to study, work, create relationships with other people and adjust behavior, taking into account the expectations and requirements of other participants in society.
Any organism during its existence adapts to external conditions. This process is continuous and occurs from the moment of the beginning of existence until biological death. One aspect of the onboarding program is training. Within it there are three subtypes: reactive, operant, cognitive.
Reactive, operant, cognitive
Features of reactive type adaptation are explained by the body’s ability to respond to external factors. During the interaction, gradual habituation occurs.
Operant adaptation is much more complex than the reactive method described above. It is realizable when an individual has the opportunity to interact and experiment, during which a response from the surrounding space is observed. This makes it possible to identify cause-and-effect relationships. The widespread trial and error method is a classic example of this type of adaptation. This also includes observations and the formation of responses.
Human adaptation through cognitive learning involves identifying a cause-and-effect relationship between situations with a subsequent assessment of what is happening. To do this, you need to be able to analyze previously gained experience, as well as learn to anticipate the possible consequences of actions. Cognitive learning includes latency, insight, reasoning and the formation of psychomotor skills.
Impact of climate
An important factor is temperature and its effect on the body. Population densities around the world vary depending on air temperature. Due to thermoregulation of the body, a person adapts to seasonal temperature changes. Therefore, the smaller the difference in seasonal temperature changes, the more favorable the living conditions and the population growth.
Solar activity affects a person’s performance and health; orientation in space also depends on sunlight and increases brain activity. Due to a lack of vitamin D, diseases such as rickets develop.
Adaptive types of humans in different climatic zones differ in skin color and muscles.
Atmospheric pressure also affects physiological parameters. In the north of Eurasia, Canada, and Alaska there is a cold zone. The growing season lasts no more than two months. Low temperatures prevent active farming.
In the latitudes of Eurasia there is a cool zone, as well as in the north and south of America, in the Andes. The warm regions of this belt are distinguished by the development of agriculture.
On the territory of Europe there is a temperate zone, not including the southern islands, the Russian Plain, Kazakhstan, Southern Siberia and the East, Mongolia, Tibet, Northeast China, the southern part of Canada, and the northern regions of the USA.
The warm zone occupies the Eurasian Mediterranean, southern China, most of the USA and Mexico, Chile and Argentina, southern Africa and Australia.
The hot-type belt occupies the predominant area of Africa, South America, South Asia, the Arabian Peninsula, and Central America. Also, agroclimatic zoning of the world is carried out depending on the degree of moisture.
Training: what is it like?
A classic example of adaptation is learning through trial and error. It is common in both human society and animals. The object, when encountering an obstacle for the first time, tries to cope with it. Ineffective actions are discarded, and sooner or later the optimal solution is identified.
Forming a reaction is to some extent training. This adaptation involves a reward for an adequate response. The reward can be physical or emotional. Some psychologists are firmly convinced that children's adaptation is most effective in this way. As soon as the baby learns to pronounce sounds, those around him are delighted with his babble. This is especially pronounced in the mother, who thinks that the child is calling her.
Observation is another way of learning. Social human activity is largely organized in this way - the individual observes how those around them behave. By imitating them, a person learns. The peculiarity is that understanding the meaning of actions and their sequences is not assumed.
Alpine adaptive type
This type of latitude is characterized by low average annual temperatures and lack of oxygen. People of this type are distinguished by a massive skeleton, a cylindrical chest, and a high content of hemoglobin and red blood cells in the blood. The thyroid gland is less developed. Metabolism is intense compared to the types described above.
The intensity of development is low, as is growth, but life expectancy is significantly higher than in other regions.
Vicarious and latent adaptation
Vicarious adaptation presupposes the assimilation of a certain model of behavior, an understanding of its relevance and the consequences of the actions taken. Typically, such adaptation is observed after becoming familiar with the behavior patterns of famous and famous, successful individuals. Some imitate movie characters or their friends.
Latent adaptation is based on receiving signals from the surrounding space. Some of them are conscious, others are not clearly perceived, and others are not perceived by consciousness at all. The brain forms a cognitive map of the world in which the individual is forced to survive, and determines what response to the situation in the new environment will be optimal. This development of adaptation was confirmed by conducting excrement experiments with rats that were able to detect their way to food through a maze. In particular, scientists first taught the road, then filled the labyrinth with water. The animal still got to food, although it was forced to use other motor reactions to do this.
Adaptations to extreme living conditions
Plants and animals living in deserts and polar regions of the Earth also acquire a number of specific adaptations. In cacti, the leaves have transformed into spines (reducing evaporation and protecting them from being eaten by animals), and the stem has turned into a photosynthetic organ and water reservoir. Desert plants have long root systems that allow them to obtain water from great depths. Desert lizards can survive without water by eating insects and obtaining water by hydrolyzing their fats. In addition to thick fur, northern animals also have a large supply of subcutaneous fat, which reduces body cooling.
Insight and reasoning
One of the learning methods within adaptation is insight. The term usually refers to a situation where an individual receives data at different points in time, which is then formed into a single picture. The resulting card is used when it is necessary to survive under conditions of adaptation, that is, in a situation completely new to the individual. Insight is, to some extent, a creative process. The solution, as a rule, appears unpredictably, spontaneously, and is original.
Reasoning is another relevant method of adaptation. They resort to it when there is no ready-made solution; trials with the possibility of making mistakes seem to be an ineffective option. The result that the reasoning individual receives is used in the future to get out of various situations.
We work in a team: features
For any company manager, an extremely important aspect of internal policy is personnel adaptation. With an irresponsible attitude towards this issue, staff turnover becomes high, and the active development of the company is almost impossible. The manager may not always deal with new employees - this approach is applicable only in small-scale businesses. Instead, it is necessary to develop standard optimal procedures to help a new person integrate into the work process of the enterprise.
Adaptation represents an individual’s acquaintance with the internal organization and corporate culture. The new employee must adapt to the voiced requirements and integrate into the team.
Personnel adaptation is the adaptation of new people to the conditions of the work process and the content of work, to the social environment in the workplace. To make the process easier, you need to think about how to make the process of getting to know your colleagues and responsibilities easier. Adaptation involves conveying the stereotypes of behavior accepted in the team. The responsibility of the new employee is to assimilate, adapt to the environment and begin to identify common goals and personal interests.
Arid type of adaptability
This type includes people living in desert areas. These latitudes are characterized by rare precipitation and a hot climate.
Features of the physique of an arid adaptive type of person: linear physique, flat chest, poorly developed muscles, small fat component, slow metabolic process in the body. Less sensitive to changes in environmental temperature.
Theory…
The conditions of adaptation, the rules of this process and the features regulating its course have more than once become the object of study by prominent minds of our world. Abroad, Eysenck's definition is currently most widely used, as well as expanded versions formed by his followers. This approach involves treating adaptation as a state of satisfying the needs of an object and the environment, as well as the process during which such harmony is achieved. Thus, adaptation presupposes a harmonious balance between nature and man, the individual and the environment.
There is an opinion that psychological adaptation in the workplace involves changing the process of familiarizing a new employee with his obligations and with the company as a whole. The process must be subject to environmental requirements.
Personnel adaptation, if we follow from the conclusions in Egorshin’s works, is the adaptation of the team to environmental conditions outside and inside the enterprise. Employee adaptation, accordingly, is the result of the process of adapting a person to colleagues and the workplace.
Tropical type of adaptability
At these latitudes there is high solar activity, tropical storms, etc. The environment plays an important role in the formation of adaptive types of humans.
This type includes people living in warm and humid areas. They differ in the following characteristics: elongated body shape, dolichomorphy - long arms and legs, combined with a short body. Relatively large body surface. There are many sweat glands, which contributes to intense sweat production.
The metabolic rate is average, the synthesis of endogenous fat and cholesterol from the liver is low, which affects human health in these areas. There is a reduced content of minerals in the bones. The phenomenon of low protein is common, and endemic diseases associated with increased or decreased levels of one or another chemical substance in the habitat area have also found their place.
All these signs were acquired due to exposure to a hot climate with high humidity.
...And practice
It so happens that in our country adaptation is often equated to a probationary period, but in fact these concepts are different. Adaptation for an employee lasts 1-6 months. The probationary period is a quarter of a year. An adaptation period is necessary for any person, but a test for employment is not always necessary.
During the test, special attention is paid to the professionalism of the employee and his ability to fulfill obligations. Adaptation consists of two components: professionalization and inclusion in the microsociety.
Although adaptation and probation are not identical concepts, they cannot be called incompatible either. If, during employment, the contract stipulates the need for a probationary period, testing and adaptation overlap each other.
Coming to a new workplace, a person tries to enter into internal relationships characteristic of the company. At the same time, he has to take different positions, which have characteristic rules of behavior. A new employee is a colleague, a subordinate, for some, perhaps a leader, as well as a participant in a public formation. It is necessary to be able to behave as required by a specific position. At the same time, the new employee must follow his own goals and take into account the admissibility of this or that behavior from the point of view of personal priorities. We can talk about the relationship between adaptation, working conditions, and motivation.
Continental type of adaptability
The population of this zone is characterized by the following characteristics: a flat chest, a tendency to be overweight, and a lower than normal content of substances of mineral origin in the skeleton.
The chest type of body type is common, which is characterized by weak muscle development, stooping, and a hollow in the abdominal area. The abdominal type has also become widespread, the distinctive features of which are: a conical chest, a convex belly, and a regular (wavy) or stooped back.
In the taiga zone, the signs are similar, but the distinguishing feature is the miniature physique.
Nuances of the question
Adaptation is more successful the more the values and norms that are relevant for the individual and the team correspond to each other. This allows the individual to quickly accept and better understand and assimilate the features of a new environment for him.
As scientists say, in order to start working to the best of your abilities and capabilities, you need to spend at least 8 weeks getting used to new conditions. For mid-level workers, 20 weeks are required, and for management, 26 weeks or more. When choosing the length of the adaptation period within an enterprise, you should be aware that a quarter of a year is a fairly long period of time. If during this period there is no return from the person hired, it is unlikely that he is suitable for the enterprise.
At the same time, we must remember that a quarter of the year is a period that for many is not enough to successfully socialize. This lies in the difficulty of assimilating the values and rules of behavior adopted at the enterprise. Consequently, it is difficult for a person to become a full-fledged member of the team. The main task of the leader is to distinguish between adaptation and testing and to realize that the process of adaptation cannot occur instantly. It consists of successive stages and stretches over a long time.
By the way, the relevance of adaptation in the workplace is well proven by statistical data. As researchers have found, up to 80% of workers who quit in the first half of the year after employment make this decision within the first 14 days from taking office.
Arctic type
The adaptive type of man was formed as a result of the influence of cold and food, mainly of animal origin. The population of this type is distinguished by powerful muscles, a massive skeleton, a fat complex, the chest is large and has the shape of a cylinder.
The hemoglobin level in the Arctic adaptive type of person is high compared to other types. The bone marrow reaches large sizes, the bones are rich in minerals, cholesterol and protein in the blood of such people are at a high level. At the same time, immunity is average.
Children: special age, special attitude
Childhood adaptation is a particularly sensitive issue. As a rule, problems first arise when the child needs to be sent to a nursery or kindergarten. Over time, the time comes to get the child ready for school, and parents and children again face adaptation problems. The first days are the hardest. To facilitate this stage, it is necessary to take into account the characteristics of the baby’s age. Psychologists who specialize in the problems of children’s adaptation to educational institutions come to the aid of parents.
A special feature of adaptation in kindergarten is the abundance of negative emotions at first. Babies tend to be capricious and cry, whine. For some, the negative state is expressed in fear - the child is afraid of the unknown, new people, especially adults. Stress can trigger anger. It is possible to show aggression towards anyone and anything. During the adaptation period, some children exhibit depression, lethargy, and lethargy.
To somewhat smooth out the transition, positive emotions should be provided, and they should be associated for the child with the new place. An abundant option is a selection of incentives, games, and rewards that the baby receives for adequate behavior. Over time, negative emotions will completely give way to positive ones. Parents should be prepared for the fact that the child will have trouble sleeping for the first time after starting to attend a child care facility, even if such difficulties have not previously been observed. Restless sleep, waking up in tears or screaming is a problem that ends on its own by the time the adaptation stage is completed.
Study by Luscher method
Maxi Luscher is a specialist in sociology, philosophy, law, religion and clinical psychiatry.
Using the Luscher technique, you can determine the emotional status of a child, his emotions during the educational process and situations related to school, and self-esteem.
Psychodiagnostics is carried out using a color test. The short version of the test consists of 8 colors (gray, dark blue, blue-green, red-yellow, yellow-red, red-blue, brown, black). The extended version includes seven color simulation tables.
The child assigns each color its own serial number based on personal subjective feelings (how pleasing each color is to the eye).
Then the specialist conducts an additional survey, covering the colors according to a special scheme. The finished results are interpreted in accordance with the standards established by Luscher.
The author of the technique selected shades experimentally , selecting stimulus signals from 4500 potential options.
Features of the adaptation period
Social adaptation of children when they begin attending an educational institution usually involves a deterioration in appetite. Psychologists explain this by the atypical, unusual taste of food, and a new diet. Stress leads to disruption of the receptors responsible for the perception of taste. If your appetite returns to normal, you can confidently talk about successful adaptation to a new place.
Sometimes parents note that in childhood adaptation is accompanied by a temporary deterioration in vocabulary. Psychologists explain this by a person’s tendency to use the simplest possible verbal structures in a complex stressful situation, when it is necessary to get used to a new environment. To some extent this is a defense mechanism. There is no need to panic: if adaptation proceeds normally, over time the vocabulary will increase again, and the functionality of speech will be completely restored.
Another manifestation of adaptation is a weakening of activity, the desire to learn, and a decrease in curiosity. The inhibited state is replaced by normal activity towards the end of the habituation period. In addition, the first month of visiting a new facility is usually accompanied by a deterioration in the immune system. Many people are susceptible to colds. The causes of the disease are psychological, much less often physiological. Under the influence of stress, the body's defenses weaken and the ability to resist aggressive factors decreases. As soon as emotional stability is achieved, the tendency to get sick goes away.
Benefits and harms
You should not send your child to an educational institution too early. Even if the child can cope with the adaptation normally, being separated from the mother too quickly does not bring anything good. Scientists have found that attending kindergarten at the age of two is guaranteed to cause severe stress, affecting the baby’s physiology and psyche. This practice can lead to neurotic reactions, because the age is still too young for separation from the mother to be painless. Consequently, the baby develops slowly, and the quality of the skills acquired also becomes lower.
The child cannot adequately contact and trust his parents, since the connection was broken too early, without strengthening. Over the years, the problems only get worse, and kids face problems interacting with peers. By the age of four, children form groups to play, and until this point it is preferable to play alone. If a child finds himself in a group setting too early, he cannot develop adequately. This often has a negative effect on speech functions.