External and internal motivation – where to look for the need for development?
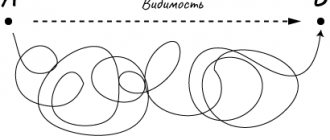
Life goes, but where? A person goes through life in a certain direction, and this direction is different from ordinary survival. There is an animal in everyone, driven by instinct. There are motor muscles, a nervous system that provides movement. Motivation helps to make a person’s actions meaningful, and to make him humanized and intelligent, interacting with his own kind.
This is movement from point A to B with a specific goal. Point B may be desirable because it is prestigious. You need to get to point B according to your inner command - “I can!” One point - two motives. Therefore, we should talk about the types of motivation and the sources of their occurrence.
What is motivation
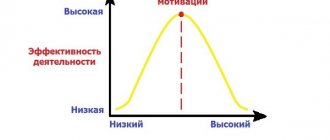
Psychology views motivation from the perspective of a need for something. Need, the feeling of discomfort associated with it, depends entirely on the situation - environment, mood. The state of “yesterday I wanted to, but today I don’t really want to” hardly motivates action.
Motivation is the thought of how good it would be if. In fact, it's a dream, but not every dream motivates you to get off the couch. This is the dream that makes her achieve it. Turns a person into a scientist who has created a hypothesis of his own satisfaction if certain conditions are achieved.
Any real scientist begins to think through a plan of action, conduct experiments, and move towards the goal step by step.
The starting point in motivation becomes internal discomfort, the discrepancy between the real and the desired. Motivation is what forces two factors to be correlated:
- I can or I can’t (opportunities);
- I want or don’t want (intentions).
A person’s capabilities depend on abilities, equipment and knowledge - competencies. This is how motivation can stimulate the internal development of abilities, learning, to lead to a goal. However, the absence of one of the elements will lead to the fact that volitional effort will not be formed, and lack of will will lead to disappointment and stress.
Signs of a motivating environment
When organizing any activity, it is important to consider several requirements. They are simply necessary to satisfy needs and form the right motivation:
- Activities should be creative and varied.
- Opportunity to develop while completing tasks.
- A sense of belonging to a group and recognition from it.
- The right to make decisions independently within one’s competence.
- Feeling of support and help.
- The presence of external attributes of success: praise, encouragement, compliment.
- The meaning of the required actions.
- The opportunity to express your own opinion, which will be taken into account.
- Availability and timeliness of information received.
- Feedback after the work done.
If all these signs (or at least the majority) are present in the organization of activities, then we can assume that the formation of internal motivation will be successful.
Main characteristics
Motivation consists of two parts:
- a person’s internal psychological attitude towards action or inaction;
- the ability to effectively correlate opportunities and abilities to achieve a goal.
It comes to a person in the form of specific experiences that are associated with positive emotions from achieving an object or realizing an idea. But the motive is realized only when it coincides with the ideals and cultural values of a person and society at a given moment in time.
The motif has several characteristics:
- gives energy for activity;
- directs actions to achieve goals;
- causes selectivity of attention;
- prepares for typical reaction scenarios.
The motive also necessarily includes the activity itself to achieve the goal. Motivation is not only how much a person wants to achieve a goal, but how much effort he is willing to put into it.
Types of motivation
A person goes towards something or leaves something.
In the first case, it is a positive motivation - movement “towards a goal”, in the second - negative - “from dissatisfaction (fear/poverty/poor self-esteem). But usually positive and negative motives are combined: if I quit smoking, I will become healthier, I will be able to play sports and earn more. “I’ll quit” in the context of a smoker is a negative attitude, but the ultimate goal is positive. Motivation makes you become better! External motivation is a call to action that can bring money, approval, or promotion. Doing something interesting for satisfaction and self-realization is internal motivation. External - can be determined by a motive from within - a view of the situation, the internal state of a person. As a result, external and internal motivation have blurred boundaries. Motive is what affects a person’s consciousness and depends on his picture of the world. Therefore, the need for movement necessarily includes characteristics of internal and external motives: by taking action, a person changes the world around him and his attitude towards it.
“Intrinsic motivation” is a term that was introduced by R. Woodworth: a person is born with the goal of mastering the world through behavior - effective interaction with surrounding objects. Other types of internal motivation are considered by R. White, such as the search for a “sense of effectiveness,” when a person acts for the sake of the need for efficiency, competence and mastery.
Classification of motivation by other factors
In psychology, people are divided depending on their motivation to succeed or the desire to avoid failure, which is determined by developed tests. However, people who are motivated to succeed, in case of failure, look for those to blame. People who strive to avoid failures, on the contrary, look for the cause of failure within themselves, therefore they are always ready to find reserves to increase the efficiency of their activities.
Variety of theories of human motivation
Theories of motivation are studied in psychology in order to better understand what motivates a person to act and how his behavior is formed. Such famous psychologists as Maslow, Alderfer, Herzberg, Adams, Vroom and many others worked on theories of motivation. A detailed analysis of human needs made it possible to identify two main directions in the field of theories of motivation:
- Procedural;
- Contentful;
Each of these theories of motivation has attracted many adherents. By studying the basic theories, you can better understand the types of personal motivation and analyze the nature of a person’s actions in different life situations.
Extrinsic versus intrinsic motivation: which is stronger?
One side of motivation supports the other. Praise, gratitude or feedback from a client evokes a sense of professionalism and competence, which increases internal motivation. Then, for the sake of approval from outside, you want to increase your skills, efficiency, and develop as a person. Falling in love with work and being inspired by the activity appears.
The relationship between internal and external is shown in the types of motivation that express the desire for success, popularity, recognition of significance, overcoming and self-overcoming (improvement), and vocation. These types are presented in the form of a ladder of human self-development. They show how a focus on external success creates people who are satisfied with their work.
Why do employees perform poorly?
According to statistics, only a small proportion of bosses are satisfied with their employees and the results of their work. Any company, even the most successful, always has something to strive for. There are several main reasons why employees do not fulfill their obligations in good faith:
- Lack of interest in the work itself, as a result of work activity, there is no desire to go to work in the mood and give 100 percent; and most importantly, the employee does not feel his importance in the team;
- There is no clear understanding of how wages work out, how bonuses are calculated, and what indicators the additional bonus depends on;
- Lack of professionalism in the team (employees need to undergo training and learn communication skills with clients). So, after the manager has figured out the reasons why the team is not working intensively, a motivation system should be introduced. And it’s no secret that the most effective is monetary motivation.
Factors that determine the level of motivation
The power of motivation consists of the factors that make it up:
- internal motive - the need for action, development, change forms the reason for movement. The goal or desired object (result of action) - must be so significant as to influence the picture of the world, capture consciousness and attention.
- The possibilities of satisfying a need are sometimes much smaller than the circumstances that have to be overcome. Therefore, a sober assessment of strengths and weaknesses is important.
- Ability to plan – a plan does not have to be on paper, but only in your head. To perform an action, you need to have knowledge and instructions for completing it. Lack of knowledge may be the reason for low levels of motivation.
- Self-control and implementation of the plan depends on what you have to sacrifice to achieve the goal. Insufficient reward can disappoint - that’s why motivation always consists of internal and external factors.
The vector of effort, the direction - it is important that a person is attracted to the external aspects of the process or result. It is the internal motive - the need for action, development, change that forms the reason for movement.
Methods (ways) of motivation
The methods of motivation depend on the object of effort. The term motivation is used to force a person to act in a certain way. To be more precise, motivation increases the effectiveness of a person’s activities in any field. Methods of exposure depend on the area of application.
Staff motivation
Personnel motivation refers to measures taken to increase labor efficiency. Depending on the goals and principles of management, the organization uses:
- financial incentives;
- organizational and administrative (fines, regulations, coercion, negative incentives);
- socio-psychological (addressed to internal motivation - involvement in something).
The choice of a motivational method in management depends on the manager’s skill and ability to find an individual approach to subordinates.
Student motivation
Teachers must take into account age-related characteristics of attention, thinking and memory in order to organize the cognitive activity of children of different ages. The most commonly used are classic
- verbal – a vivid, emotional story;
- visual and practical aids - cards with tasks, laboratory exercises that open up a desire to experiment in children;
- reproductive and search - methods of problem situations aimed at developing creative potential;
- independent work - preparing abstracts from a group or student, conducting observations that connect theory with practice.
Self-motivation
Self-motivation is based on external and internal motivation for cognitive activity. A person becomes active only when the direction of activity coincides with the vector of personal development.
The work is not inspiring because it is boring, routine, boring. Work, as an activity, in such cases is not an end in itself. The result is financial incentives.
We need to remember that work provides an opportunity for something more and serves as a financial source. What do you need? Find activities that provide energy for action and routine responsibilities. Use negative motivation, among other things. Look for yourself in other areas where the result of your activity will coincide with your internal motive.
Affirmations
Affirmations are used to overwrite negative attitudes. Instead of “I won’t succeed,” say: “I try new things with ease. I like to try new things."
Instead of “I’m afraid of my boss’s screams,” repeat: “I listen to any criticism calmly. I accept only constructive suggestions."
Self-hypnosis
Self-hypnosis is a method of forced smiling, which triggers chemical reactions in the brain. Of course, after a sleepless night there is no point in saying “I’m full of strength!”, but you just need to get some sleep. Settings must be specific and realistic. Before an important conversation: “I am confident, I am calm.” During a quarrel, “It’s hard to make me angry.” In times of doubt - “I am ready to work and act.”
Biographies of famous personalities
The time for stories has come. Nowadays, everyone can create their own legend with the help of social networks and find fans who will motivate them. F. M. Dostoevsky outlined the story of his own dependence in the novel “The Gambler” and turned collapse into triumph. Turning weaknesses into strengths - finding opportunities - is within the power of everyone. A thorough analysis and study of analogies is needed.
Visualization
Method of attunement with the goal. This is not a magical device that subdues the twists of fate, but the very oasis that makes you go forward to get drunk. Don’t think that thinking about a chic office will make it one without difficulty. A dream makes the heart beat faster, produces endorphins, and stimulates brain activity.
The right choice of personnel incentives
It is important for any management to understand in a timely manner what incentives motivate this or that employee. Therefore, when building a motivation system, it is so important to navigate the team and understand each employee. The boss needs to study the reasons for the staff’s lack of interest in work using a questionnaire or survey. The results obtained will help to understand which bonus principles are suitable for stimulating these workers. Different goals and plans of people, level of education and aspirations of the employee determine the use of different types of personnel motivation:
- Material incentive;
- Non-material motivation of personnel;
- Motivating the team leader. \
The first thing you need to do is formulate a goal that may be slightly overestimated, but is quite achievable by the employee. In addition, there are now many books on the effectiveness of personnel management on store shelves. The specialized literature contains tips and methods that, after application, will bring about some changes in the company.
Scope of application of the concept
Motivation is a broad concept, but in general it reflects the reasons for human behavior. In various scientific fields, a person is an object of research in various directions. Therefore, different types of motivation are considered. In psychology, it is a carrier of consciousness; in economics, it is a subject of economic activity with needs; and in management, it is an employee whose activities are subordinated to the company’s goals. Teachers motivate by increasing the activity of cognitive activity in schoolchildren and students. The term is used in marketing when a person with needs, motives and judgments makes a decision to purchase a product.
In psychology
Psychology seeks answers to two questions:
- How does human behavior differ from that of animals?
- How can behavior be regulated to solve the problems of training, education, and activity management?
Therefore, in the broad sense of the word, motivation includes:
- psychological and physiological characteristics of a person;
- environmental factors influencing behavior.
In the narrow sense of the word, these are psychological changes that shape, direct and support human behavior. These are reasons that explain why a person did what he did in a particular situation. Why? For what purpose? For what?
Psychology of motivation studies three aspects:
- biological and physiological mechanisms associated with the satisfaction of basic needs;
- behavioral or non-psychological stimuli from the internal and external environment - conditioned reflexes;
- psychological – psychological factors are considered (unconscious, internal and external stimuli, social factors, humanistic – human consciousness).
There are various branches of psychology that have studied aspects of behavior.
In management
In management, motivation is the process of stimulating one or more people to activities that are aimed at achieving the goals of the enterprise. It's a way to get work done efficiently.
The types of motivation considered in management are based on structuring people's needs. Maslow identified five groups of needs, which differ significantly depending on the level of development of the country, culture, and society. McClelland introduced the following types of needs: power, success and belonging. Herzberg proposed taking into account factors influencing the satisfaction of needs in the process of work. Working conditions, pay, relationships in the team - hygiene factors - are things that can cause dissatisfaction, but their improvement will not lead to satisfaction of needs. Herzberg calls motivating factors a feeling of success in career growth, expanded opportunities, recognition from colleagues and superiors.
According to expectancy theory, motivation arises if a person is confident that his efforts will help him achieve his goal and receive a reward. Equity theory states that a person subjectively compares the size of reward and effort. Drive occurs when work is overvalued and provides an incentive to exert more effort.
In economics
The economic interests of society depend on the financial situation of people and class differences. Each person has everyday interests, which also influence work behavior and attitude towards work.
Interests are reflected in the motives for work. This is a conscious inner urge to work to satisfy needs. Motive predetermines a person’s behavior, choice of activity, building knowledge and skills to achieve goals. Motivation is a set of related motives.
In economics, a motivational core is distinguished: the motives of vocation, security and prestige - self-realization, wealth, social status. The degree of satisfaction of these motives influences how a person evaluates working conditions and forms an attitude towards it.
To strengthen motives, management uses material and non-material incentives - a board of honor, gratitude or cash bonuses. At the intersection of meeting needs, developing motives and incentives, a system of motivation in economic activity is born.
Human motivation: procedural direction
The following theories of human motivation analyze not only needs, but also efforts and the nature of activity aimed at achieving the desired goal. The most famous procedural theories include:
- Vroom's expectancy theory. The level of motivation for a particular person depends not only on the presence of needs, but also on how hard he is willing to try to satisfy these needs. You need to be firmly confident that the approach you choose will be effective and help you achieve your goal;
- Adams' theory of equality. The essence of this theory of motivation for a person is that he tends to compare the result of certain actions with the result of other people who find themselves in similar life circumstances. Since this theory of human motivation is subjective, in addition to a fair assessment, a person can underestimate or overestimate the result obtained by others;
- Porter-Lawler model. This theory of human motivation combines elements of the work of Vroom and Adams;
Why do you need motivation?
Who needs it?
Motivation is an instruction for behavior. When a person wants something, the brain independently finds clues to achieve success. A guy seeks a girl's attention, a child finds gifts from Santa Claus, a woman loses weight after giving birth. They are motivated because they know exactly what they want. The search for motivation is carried out by those who are not sure of the goal. A person who gets paid to work for survival will crawl to work. His ego will scream that it is better to sleep, but to sleep he will want to eat, and food is bought with money. And again we need to work! Motivation is a struggle against one’s own habits and foundations. Therefore, trainers and motivators warn - get ready to change your life completely. Trying on someone else’s experience is being motivated by someone else’s success. This reveals the line between how external and internal motivation works - the difference between an imposed goal and determination.
Signs of Motivated People
The main signs of people who are charged and motivated to work include:
- optimism - motivated people are confident in advance that their plan will be fulfilled and the result will be excellent;
- perseverance - obstacles do not become an insurmountable task for them;
- activity - a lot of enthusiasm, which helps not to stop on the path to the goal;
- concentration - people are not distracted by trifles, moving towards the goal;
- confidence - such people understand themselves as a whole person with problems and shortcomings, they know how to use their strengths and work on their weaknesses.
In psychology
Psychology is a science that studies the influence of motivation on the desires, needs and state of a person. There are different concepts in psychology about the emergence of motivation. For example, behaviorism says that a need arises when the organism deviates from the ideal. If a person is hungry, he becomes motivated to return to the ideal, that is, to satiety, and in this case, his main driving force is the desire to eat.
Practical advice
Motivation is needed by those who want to force a person to fulfill demands and obey. Therefore, they manage children, subordinates, consumers - buyers of goods and services. Even the desire to have a slim body is an imposed motive. To avoid needing motivation, you need:
- determine the type of activity you like;
- identify the goal that can be achieved in this activity;
- to have, as a result of achieving the goal, satisfaction of the financial and internal goals - gratitude, self-esteem, recognition of mastery.
That's when there will be no need for motivation. The purpose of the activity motivates itself.