Transactional analysis will answer the main question of your life: why can’t I do anything? Has it ever happened to you that you try, make efforts, but still cannot achieve what you want? You can blame anything. These could be circumstances, the people around you, the situation in the country and much more. But what if the problem is you? Transactional analysis will tell you about this. Its creator, Eric Berne, believed that our entire lives are programmed in childhood. Is it really?
The essence of transactional analysis according to Eric Berne
Transactional analysis (TA) in psychology is a technique that allows you to describe and analyze the behavior of an individual or group. Otherwise called transactional or transactional analysis. Used to treat complex psychological problems. Its author is psychotherapist Eric Berne.
Transactional analysis by E. Berne appeared in the 60s of the last century and immediately gained popularity. Partly because of its simplicity and accessibility.
TA has several goals:
- Find and eliminate stereotypes in behavior.
- Determine your values, learn to make decisions, taking into account your capabilities and needs.
- Understand your inner world.
- Understand relationships with people around you.
- Learn not to hide your feelings.
- Trust yourself.
It is interesting that Eric Berne’s transactional analysis can be carried out anywhere: at home, at school, at work. It is used in business and communication. But many psychologists believe that it is still better to consult with specialists. Without their help, it will not be possible to achieve significant improvements.
Technique 7. Working with worldview and its distortion
This technique uses interaction between group members who use rejecting or blocking transactions when talking to each other. A transaction is a communicative construct that is considered a unit of communication. The conversation involves people in three roles - client, lawyer and observer. The conversation between them should cover as many issues as possible. In one conversation, a person must maintain his role, that is, use either only blocking or rejecting transactions. Then you should switch roles.
How to determine what condition you are in
It is enough to observe the behavior a little. Each ego state has its own characteristic features:
- The “child” often says the following phrases: “I want,” “This makes me very angry,” “I don’t care about this.” Emotions are shown on his face. This could be a look somewhere at your feet, trembling lips, an expression of delight.
- “Parents” constantly prohibit something, point it out, and remind them of their sense of duty. They shake their heads, look menacing, and cross their arms over their chest.
And finally, “adults”. They look for benefits in everything, offer to calculate the benefits, discuss the appropriateness of this or that action or decision. They are constantly thinking about something.
Technique 11. Change contracts
The technique is aimed at concluding a contract with oneself for a particular change.
To do this, you mainly need to motivate your inner “child”. At the beginning, a person needs to set a goal, the formulation of which should not contain negative statements (do not smoke, do not be afraid, etc.). The goal statement should be positive. Then you should determine what you will have to sacrifice to achieve the goal and understand - is it safe, is it worth the expected result? After that, set yourself 5 intermediate goals and deadlines for their implementation. Be sure to communicate all this to other people and ask them to monitor the fulfillment of the goal. Psychological Training Center Orange Sun
Transactions
In modern transactional analysis, transactions are the process of interaction between the ego states of two people. They consist of 2 parts: stimulus and response. There are several types of transactions:
- Complementary or parallel. The stimulus from one person is complemented by the reaction of another. Communication takes place. Let's say you asked: “What time is it?” This is an incentive. The interlocutor answered you. This is a reaction. In such conditions, interaction lasts quite a long time. In this case, practically no conflict situations arise.
- Intersecting or crossing. This type of transaction is characterized by conflicts. One side sends a stimulus from the "adult" and the other responds from the "child" or "parent". For example, a husband asked his wife where his watch was. She, instead of answering the question, says that he always considers her to blame for everything. A quarrel begins with small reproaches. This will continue for a long time. The situation will change if the parties to the conflict consciously move into the “adult” ego state.
There is another type of transaction - hidden. They are very different from the other two. There are several ego states involved here. In short, a person says one thing and means another. Often he does not even realize what role he is in now.
Technique 4. Structuring time
Berne's theory suggests that there are six ways to structure time. During training in this technique, participants learn to interact with each other, using all six techniques in turn. For example, one conversation uses one time structuring technique, and another uses a second, third, etc. In addition, participants draw up a map of their day and note there how much time they spend on all these six structuring methods. This technique is directly related to the skills of planning and executing plans.
Stroking
In transactional analysis, this is another type of interaction between the ego states of the “child” and the “parent”. Children always seek approval from mom or dad. In psychology, these approvals are called strokes. They come in 3 types:
- Verbal. Manifested in compliments and praise.
- Non-verbal. This includes gestures, facial expressions, and winks.
- Physical. These are handshakes, pats on the shoulder.
You can “stroke” a person unconditionally (for what he is) and conditionally (for some actions). The message can be positive or negative.
Technique 8. Working with symbiosis
This technique is performed in pairs. First, people in a pair stand, leaning on each other, for example, on each other’s outstretched palms or simply leaning their backs. It is important that the balance is maintained by the other person (mutually). The second part of the exercise is a gradual transition to independent balancing, but without breaking physical contact. The third part - one of the partners stands motionless, and the second removes his hands or back. At each stage, the participant must feel his feelings and emotions. In most cases, there may be a little fear or uncertainty when breaking contact.
Analysis of psychological games according to Bern
What are games in psychoanalysis? This is an unconscious behavioral stereotype consisting of several parts. It's about weakness, trap, response, strike, payback and reward. Actions trigger feelings. Moreover, they intensify towards the end of the game. With each action comes the above-described stroking. Its intensity also increases.
Unlike ordinary entertainment and any rituals, games have hidden motives, winning, and conflict. They can be dishonest and dramatic.
According to Eric Berne, there are 6 types of psychological games. Each of them has its own subspecies:
- For 2, 3, 5 players. There may be more participants. Example – “Frigid Woman”, “Alcoholic”, “Why Don’t You”.
- Using words, money, body parts. These are “Psychiatry”, “Debtor”, “I need surgery” respectively.
- With different clinical types: hysterical, obsessive, paranoid, depressive. Examples are the games “Rape”, “Blubber”, “Why is it always like this with me”, “I’m back to my old ways again”.
- Depending on the zones. There are oral (“Alcoholic”), anal (“Blubber”), and phallic (“Fight”) games.
- Psychodynamic. They are divided into 3 subtypes: counterphobia (“if it weren’t for you”), projection (“Parental Committee”), introjection (“Psychiatry”).
- Characterized by instinctive drives. There are 3 subtypes: masochistic (“If it weren’t for you”), sadistic (“Blubber”), fetishistic (“Frigid Man”).
It is worth noting that games have 3 quality characteristics:
- Flexibility. Some games only use one type of material. Others show flexibility.
- Tenacity. Some people have no problem stopping the game. But there are also those who cannot refuse them.
- Intensity. Games can be light or hard. Players can also be different: relaxed, tense, aggressive.
Regardless of the type, games have a powerful impact on everyone's life.
Characteristics of games according to E. Bern
Let's take a closer look at some games from Eric Berne's transaction analysis. In psychotherapy they have a goal, role, dynamics, social and psychological paradigm, moves, benefits.
| "Alcoholic" | "Gotcha" | "Look what I did because of you" | |
| Target | Self-criticism, self-blame | Justification | As in the second case, justification |
| Role | Directly the Alcoholic, his Persecutor, Savior, Simpleton | Victim and Aggressor | |
| Dynamics | Oral deprivation (depriving a person of something important, leading to destruction) | The wrath of jealousy | The dynamics of the game can be soft and hard, coupled with anger |
| Social paradigm | One “adult” asks another to tell him the whole truth or help him overcome a bad habit. The second one promises to be frank | One “adult” points out to another his wrongdoing. The second agrees that he was wrong | |
| Psychological paradigm | A person in a “child” state plays catch-up, hopes that he will not be caught. The “parent” at this time gives good reasons why you need to stop drinking | The “adult” warns the “child” that he sees all his actions. The "child" realizes that he has been caught. The “adult” reports his dissatisfaction, punishment | Participants seek to avoid responsibility. They believe that there is simply nothing to blame them for |
| Moves | First comes provocation, then accusation and finally forgiveness. Or in another order: condescension-anger-disappointment | There are 3 options: provocation-accusation, defense-accusation and defense-punishment. | |
| Benefit | A person consoles himself, satisfies momentary desires. Alcohol is used as an opportunity to avoid various forms of intimacy. Often this is a challenge to people around: “Try to stop me” | This is an opportunity to justify your anger, some character flaws. This style of behavior allows two people (mostly of the same gender) to exchange angry tirades. Some people decide after playing this game that they can't trust anyone. | The threat of sexual intimacy speeds up the game. So-called “justified” anger helps to avoid it |
In other games, E. Bern identified only theses and antitheses. Take "Hit Me" for example. Usually its participants do not want this at all, but deliberately provoke other players. And often they achieve their goal. Such people include those who are not accepted in society, outcasts, women of easy virtue, as well as people who cannot find a permanent place of work. When they achieve the logical result of their behavior, they have only one question: “Why does this always happen to me?”
Three elements of personality
The described method divides a person's life into three states: Child, Parent and Adult. Let's look at each of them in more detail:
Ego state Child
This condition is represented by behavioral norms formed in childhood. Therefore, the behavior, thoughts and feelings of a person in the Child state are similar to those of a child; such an individual is childish, he is prone to rebellion, fear, and often seeks the support of other people or requires increased attention.
Psychologists divide this ego state into the following parts:
- Free Child , whose main features are emotionality, spontaneity, a penchant for games and creative activity. This state represents a kind of “free” principle in any person, capable of immediate joyful experiences and feelings, spontaneity and childish curiosity. An individual in the Free Child state can make quick, feeling-based decisions and is drawn to self-expression and creativity, while being guided by his own desires.
- The main characteristics of the Adaptive Child are obedience, obedience and the ability to adapt to the requirements of the people around him. An individual in such an ego state tries to live up to the expectations placed on him, to receive positive feedback from superiors, he avoids criticism, and obeys the rules and norms established by his superiors.
- Characteristics of the Rebellious Child include protesting against the established order, fighting against control, and arguing with superiors. In this ego state, the individual rebels against any attempts to establish control over him, sabotages the responsibilities assigned to him and does not complete assigned tasks.
Parent
This state reflects the traits of a personality that was significant for the individual in his early years; in general, this ego state is characterized by the behavior of the guardian, also gleaned by the person from childhood. In addition, in the described state there are two types:
- The dominant features of the Critical (or Controlling) Parent are severity and criticality, the requirement for obedience and submission to established rules. In such an ego state, a person begins to point out to others their mistakes and teach them about life, criticizes their behavior, demanding that others conform to standards acceptable to him.
- in contrast to the Criticizing, the Nurturing (or Caring) Parent tends to empathize, reassure and protect others. A person in such a state wants to support loved ones in word and deed, he strives to help them and take care of them.
Adult
An adult is responsible for the logic and rationalism of our behavior, for making responsible decisions and for a person’s actions in a certain life situation. This state is the only one of all human ego states that lives only in the present time, there is no place in it for the individual’s childhood experience, nor for the infantility and spontaneity characteristic of a Child, and therefore only it represents an excellent support for making important decisions.
It is worth noting another important aspect - in different life situations people are in different ego states. For example, when communicating with high-ranking individuals, an individual becomes an Adaptive Child, and the same person appears in the image of a Controlling Parent to his own subordinates.
In addition, the ego state from which a person communicates with his interlocutor has a direct impact on this interlocutor, for example, when talking with someone from the position of a Controlling Parent, we ourselves push him to react either as a Rebellious or an Adaptive Child. Thus, knowledge and understanding of the concept of transactional analysis allows people to effectively and correctly build friendly, personal and family, as well as professional relationships, while simultaneously avoiding a huge number of unnecessary conflicts.
About the concept of “life scenario”
In the method of transactional analysis there is the concept of “life script”. Byrne writes about him in his book “People Who Play Games.” According to the author, the life program of people is formed in preschool age. In the Middle Ages, teachers and priests adhered to this rule. They even offered to take the child away for education and give him back to his parents after 6 years.
Berne said that a script is a life plan stored deep in the subconscious. Its formation is influenced primarily by the mother and father. According to him, a person is driven to action by some inner force. And no matter how hard he tries to defeat her, the ending often differs from what he wanted. For example, many people strive to earn a lot of money, but continue to lose it. Others achieve success at this time.
It is interesting that for the first 2 years the child’s scenario largely depends on the mother. The program she laid down in psychotherapy is considered its primary protocol, life position.
During the first year after birth, either trust or distrust in the world around us is formed in the child’s mind. He develops certain beliefs about himself and those around him. He understands that he is good, everything is fine with him, or vice versa.
The same is true for other people. They are good, everything is fine with them, or they are bad and not everything is fine with them. These are life positions. Let's call them I and You. “Everything is fine” - “+”, “not everything is fine” - “-”. The combination of these positions is the basis of the life scenario of each person. Let's take a closer look:
- I+, You+. This is an unconditional success. A sign of a healthy personality who confidently moves towards victory. This attitude can be learned in early childhood or achieved through hard work on yourself.
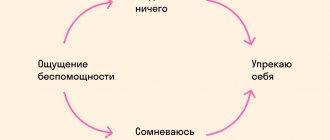
- I+, You-. Consciously or unconsciously, a person plays the psychological game “You are to blame.” He sees those around him as enemies. Moreover, he seeks to get rid of them. This applies not only to strangers, but also to relatives, friends, even children. In particularly serious situations, a person with this position becomes a killer.
- I-, You+. Position of depression. Man is engaged in self-destruction. And, worst of all, he passes this scenario on to children. Such people are mostly melancholic, losers who spend their whole lives alone.
- I, you-. Complete hopelessness. As in the previous case, this is a loser's scenario.
It is very difficult to give up your life position and change your life scenario. It's like trying to pull out a foundation without destroying a house. But such a possibility still exists. An experienced psychologist or psychotherapist will provide assistance.
It is worth saying that how relationships with other people will develop depends on your life position. The position of the interlocutor is striking even at the first meeting. And like, as you know, attracts like. If you are a happy, cheerful person, then your social circle is the same. It is unlikely that you will want to communicate with eternal whiners.
conclusions
Thus, a transactional analysis session conducted by an experienced specialist will help a person understand the essence of the reasons why his life is not turning out the way he would like. The basis of this concept was the assertion that the postulates embedded in the subconscious of an individual in childhood determine his entire future life. However, transactional analysis allows you to identify and eliminate these problems, and therefore you should not be afraid of a visit to a psychotherapist, because he can literally change the scenario of your future life path for the better.
Literature on Transactional Analysis
Specialized literature will help you better understand the basics and advantages of transactional analysis in psychotherapy:
- "Transactional Analysis and Psychotherapy", Eric Berne.
- "Games People Play. Psychology of Human Relationships”, Eric Berne.
- "Games People Play. People Who Play Games by Eric Berne.
- “Games that successful people play. Master class on practical psychology”, Pia Bylund, Kåre Christiansen.
- “Techniques of transactional analysis and psychosynthesis”, Irina Malkina-Pykh.
These books may seem difficult at first. But reading them is a great opportunity to look inside yourself.
Theories
The main cornerstone of transactional analysis is script theory. Its creator is Eric Berne. Over time it was improved by Claude Steiner. Elements of the theory:
- A counter-script is a set of actions performed in a certain sequence. Allows you to move away from the original scenario. It begins to take root in a third-party ego state. If, according to the standard scenario, a person must suffer, then according to the counter-scenario he becomes happy.
- A script is a life plan that has been drawn up since childhood. It is chosen by children depending on the foundations that those around them, their parents, lay in it. The choice of scenario depends on the will of the child and the influence of external factors.
- Anti-script - formed when a person cannot live according to the script drawn up in childhood. At the same time, the subject cannot forget about the main scenario. So he continues to act according to it.
A scenario refers to the fate of an individual, and an anti-scenario refers to a lifestyle.
Examples of role mismatch
In life, role discrepancies are not uncommon, which is why conflicts arise. Here's what it might look like in different areas.
Family
The husband, from the position of an adult, asks: “Darling, do you know where my tie is?” The wife, from the position of a parent, replies: “Where you left him. How small! "
In sales
The buyer, from the perspective of an adult, asks: “How much does this dress cost?” The seller answers irritably from the position of a parent: “You don’t have eyes, can’t you see it yourself?”
At work
A young specialist turns to a colleague or manager for help from the position of an adult: “Could you tell me which algorithm and program is best to use to solve this problem?” And in response he hears an irritated parent: “It’s high time to understand and know this yourself.”
Parent
Parent – “should”, “shouldn’t”. When the parent awakens in us, we take a “hands on hips” pose, point a finger, express contempt or condescension with a smile. The gaze is heavy and directed downward. The sitting position is relaxed, the body is slightly tilted back. The parent always defends his position, teaches others, and considers only himself right. In the vocabulary of such a person there are expressions:
- I won't stand for this.
- You are completely wrong.
- Do as I say.
- You are required.
- It is forbidden.
- A fool understands.
- You can't really do anything.
The parent always strives to catch the opponent, identify contradictions in his judgments, and prove the speaker wrong. It relies on the information that was received in childhood from the family and social environment: norms, requirements, prohibitions. “Do as I do or do not as I do, but as I say,” is the position of the parent. He controls and cares. When a parent is completely blocked, the person becomes unprincipled and forgets about morality and rules of behavior.