The mental development of a preschooler is of great importance in the development of a bright and full-fledged person. The preschool period in the life of a modern person is only seven years. However, despite its short duration, it is one of the most important. At this time, the foundations of personality are formed.
Here it is very important to know the individual traits of a preschooler. They will help shape the child’s inclinations, which will then become the main foundation for entering the school education system. Parents should pay attention to the mental development of children of senior preschool age.
Features of the mental development of a child of senior preschool age
Psychology has an activity approach. It was studied by the Soviet psychologist and teacher Alexei Nikolaevich Leontiev, as well as his followers. They, relying on the works of Lev Semenovich Vygotsky, made a substantiation of the age structure. One of the main criteria for this structure is the so-called neoplasm.
Among the basics of neoplasm, we want to highlight 3 important factors:
- arbitrariness – the child’s will is formed, and he is already beginning to set goals and move towards them;
- visual-figurative thinking evolves - the child can already establish connections between images;
- The volume of memory increases - the preschooler independently sets himself the goal of retaining something in memory.
All these features indicate that it is simply necessary to study mental arithmetic. After all, classes using the methods of the “AMAKids Academy for the Development of Intelligence” are capable of developing memory and imaginative thinking (working with an imaginary abacus helps). Lessons speed up children's perception and processing of information significantly. In addition, they develop the necessary goal-setting qualities for an interest in self-development and learning new things. Classes at AMAKids are held in an interesting playful way, which is also important for developing a preschooler’s intelligence.
Psychologists and teachers highlight the formation of mathematical concepts as a separate and very important point. Mental arithmetic is a super exercise for the brain. If previously more hopes were placed on classical mathematics, now more and more on the development of the child with the help of mental calculation through the visualization of the abacus.
As an example, we can cite the mathematical abilities of mental arithmetic of AMAKids student Savva Tikhnenko, who is known for his participation in television programs. He amazed everyone with his mathematical abilities in Maxim Galkin’s show “Best of All.”
How to write a term paper on speech therapy
07.09.2010 244929
These guidelines are compiled to help students gain an understanding of the content and structure of coursework in speech therapy.
Logopedia of pedagogical science that studies anomalies of speech development with normal hearing, explores the manifestations, nature and mechanisms of speech disorders, develops the scientific basis for overcoming and preventing them means of special training and education.
The subject of speech therapy as a science is speech disorders and the process of training and education of persons with speech disorders.
The object of study is a person suffering from a speech disorder.
The main task of speech therapy as a science is the study, prevention and elimination of various types of speech disorders.
Coursework in speech therapy is a student's scientific and experimental research. This type of educational activity, provided for by the educational and professional program and curriculum, contributes to the acquisition of skills in working with literature, analyzing and summarizing literary sources in order to determine the range of insufficiently studied problems, determining the content and methods of experimental research, processing skills and qualitative analysis of the results obtained. The need to complete coursework in speech therapy is due to the updating of knowledge concerning the content, organization, principles, methods and techniques of speech therapy work.
As a rule, during their studies, students must write two term papers - theoretical and practical.
The first course work should be devoted to the analysis and synthesis of general and specialized literature on the chosen topic. Based on this analysis, it is necessary to justify and develop a method of ascertaining (diagnostic) experiment.
In the second course work, it is necessary to provide an analysis of the results obtained during the ascertaining experiment, as well as determine the directions and content of speech therapy work, and select adequate methods and techniques of correction.
So, let’s present the general requirements for the content and design of coursework in speech therapy.
The initial and most important stage of working on a course project is the choice of a topic, which is either proposed by the supervisor or chosen by the student independently from a list of topics that are consistent with the areas of scientific research of the department.
Each topic can be modified, considered in different aspects, but taking into account a theoretical and practical approach. Having chosen a topic, the student needs to think through in detail its specific content, areas of work, practical material, etc., which should be reflected both in the formulation of the topic and in the further construction of the study. It should be recalled that the chosen topic may not only have a purely theoretical orientation, for example: “Dysarthria. Characteristics of the defect”, “Classification of dysgraphia”, but also take into account the practical significance of the problem under consideration, for example: “Speech therapy work on speech correction for dysarthria”. It should also be taken into account that when formulating a topic, excessive detail should be avoided, for example: “Formation of prosodic components of speech in preschoolers of the sixth year of life attending a preschool institution for children with severe speech impairments.”
The course work includes such mandatory parts as: introduction, three chapters, conclusion, bibliography and appendix.
The text of the term paper begins with the title page . An example of its design can be seen here.
Then the content of the work is given, in which the names of chapters, paragraphs, and sections are formulated in strict accordance with the content of the thesis. An example of its design can be seen here.
In the text, each subsequent chapter and paragraph begins on a new page. At the end of each chapter, the materials are summarized and conclusions are formulated.
The introduction reveals the relevance of the problem under consideration in general and the topic being studied in particular; the problem, subject, object, and purpose of the study are defined. In accordance with the goal and hypothesis, objectives and a set of research methods aimed at achieving the objectives must be defined.
The relevance of the topic lies in reflecting the current level of pedagogical science and practice, meeting the requirements of novelty and usefulness.
When defining the research problem, it is important to indicate what practical tasks it will help to implement in training and educating people with speech pathology.
The object of research is understood as certain aspects of pedagogical reality, perceived through a system of theoretical and practical knowledge. The ultimate goal of any research is to improve this object.
The subject of research is some part, property, element of an object, i.e. the subject of research always indicates a specific aspect of the object that is to be studied and about which the researcher wants to gain new knowledge. An object is a part of an object.
You can give an example of the formulation of the object, subject and problem of research:
– The object of the study is the speech activity of preschool children with phonetic-phonemic speech disorders.
– The subject of the study is the features of intonation speech of children with phonetic-phonemic speech disorders.
– The research problem is to determine effective directions for speech therapy work on the formation of intonation expressiveness of speech in the system of correctional intervention.
The purpose of the study contributes to the specification of the object being studied. The goal of any research is to solve a specific problem. The goal is specified in tasks taking into account the subject of research.
The research objectives are formulated in a certain sequence, which determines the logic of the research. The research objectives are set on the basis of a theoretical analysis of the problem and an assessment of the state of its solution in practice.
The first chapter is an analysis of literary sources, which examines the state of this problem in historical and modern aspects, and presents the most important theoretical principles that formed the basis of the study.
When writing the first chapter, you should pay attention to the fact that the text of the course work must be written in a scientific style. When presenting scientific material, it is necessary to comply with the following requirements:
– Specificity – a review of only those sources that are necessary to disclose only a given topic or solve only a given problem;
– Clarity – which is characterized by semantic coherence and integrity of individual parts of the text;
– Logicality – which provides for a certain structure of presentation of the material;
– Reasoning – evidence of thoughts (why this and not otherwise);
– Precision of wording, excluding ambiguous interpretation of the authors’ statements.
A literary review of the state of the problem being studied should not be reduced to a consistent presentation of literary sources. It should present a generalized description of the literature: highlight the main directions (currents, concepts, points of view), analyze in detail and evaluate the most fundamental works of representatives of these directions.
When writing a work, the student must correctly use literary materials, make references to the authors and sources from which the results of scientific research are borrowed. Failure to provide required references will reduce your coursework grade.
As a rule, in coursework on speech therapy, references to literary sources are formatted as follows: the number of the cited source in the general list of references is placed in square brackets. For example: General speech underdevelopment is a speech pathology in which there is a persistent lag in the formation of all components of the language system: phonetics, vocabulary and grammar [17].
When using quotations, in square brackets, in addition to indicating the source number, the page number from which this excerpt is taken is indicated, for example: Speech rhythm is based on a physiological and intellectual basis, since, firstly, it is directly related to the rhythm of breathing. Secondly, being an element that performs a communicative function, “correlates with meaning, i.e. controlled intellectually” [23, P.40].
However, course work should not be of a purely abstract nature, so you should not abuse the unreasonable abundance of citations. Quoting should be logically justified, convincing and used only when really necessary.
In the second chapter , devoted to experimental research, the organization should be described and the program of the ascertaining experiment should be presented. The survey methodology, as a rule, consists of a description of several series of tasks, with detailed instructions, visual and lexical material, the procedure for completing tasks by experiment participants, and scoring criteria. This chapter also provides a qualitative and quantitative analysis of the results obtained.
When analyzing the results of an experiment, it is necessary to use a scoring system. Examples of various criteria for quantitative and qualitative assessment are presented in the following works:
– Glukhov V.P. Formation of coherent speech in preschool children with general speech underdevelopment. - M.: Arkti, 2002. - 144 p.
– Fotekova T.A. Test methodology for diagnosing oral speech of primary schoolchildren. - M.: Arkti, 2000. - 56 p.
– Levchenko I.Yu. Pathopsychology: Theory and practice. - M.: Academy, 2000. - 232 p.
In order to visually present the results obtained during the experimental study, it is recommended to use tables, graphs, diagrams, etc. Histograms can be used in a variety of ways - columnar, cylindrical, planar, volumetric, etc. An example of the design of tables, figures, and histograms can be found here.
The third chapter provides a rationale for the proposed methods and techniques and reveals the content of the main stages of correctional work.
The conclusion contains a summary of the material presented and the main conclusions formulated by the author.
The bibliography must contain at least 25 sources. The list includes bibliographic information about the sources used in preparing the work. An example of its design can be seen here.
In the application you can present bulky tables or illustrations, examination protocols, observation records, products of activity (drawings, written works of children), notes from speech therapy classes, etc.
The volume of one course work must be at least 30 pages of typewritten text.
In general, coursework in speech therapy is the basis for a future thesis, in which the study of the begun problem can be continued, but from the standpoint of a different approach or a comparative analysis of the disorders being studied in different age categories of people with different types of speech disorders.
The content and format of theses in speech therapy can be found here.
Literature:
1. How to write a term paper on speech therapy: Methodological recommendations. Educational and methodological manual / Comp. Artemova E.E., Tishina L.A. / Ed. Orlova O.S. – M.: MGOPU, 2008. – 35 p.
2. Research work of students in the system of higher professional pedagogical education (specialty 031800 - Speech therapy). Methodological recommendations for completing the thesis / Compiled by. L.V. Lopatina, V.I. Lipakova, G.G. Golubeva. - St. Petersburg: Publishing house of the Russian State Pedagogical University named after. A. I. Herzen, 2002. - 140 p.
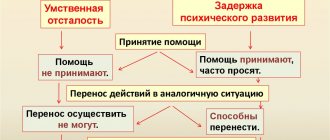
Difficulties in the mental development of preschool children
The psychological characteristics of older preschoolers are that due to rapid growth, contradictions appear that affect the child’s emotions and actions. The main driving forces for the development of children under 7 years of age are the following factors:
- the world;
- new opportunities;
- greater physical activity;
- desire to communicate with friends and strangers.
Due to some difficulties, this development may be delayed. Here we list a number of these problems:
- problems related to emotions or personality (temper, melancholy and sadness, fear of something);
- slow formation of the cognitive process, which includes poor memory, a small vocabulary, lack of understanding of what is happening, lack of attention;
- behavior problems (the child tells lies, is rude, is rude, is arrogant);
- problems associated with neurology (restless sleep, excessive fatigue);
- problems related to communication (excessive resentment towards others, isolation in one’s own little world).
Social development situation
The social situation of development of an older preschooler can be called “child – social adult.” It remains unchanged from the primary school period and is characterized by close interaction with the world of adults. However, in older preschool age this interaction becomes more active; it is aimed not only at parents and immediate relatives, but also outside the family. The child is interested in communicating with people he is interested in, so he gains the interaction experience necessary for successful socialization.
Indicators of neuropsychic development of senior preschool age
Communication is characterized as non-situational - personal, with activity on both sides. The purpose of such communication is not to understand the objective world, but to directly communicate with the interlocutor.
Advice to parents: do not deprive your child of the opportunity to attend kindergarten. It is there that he will receive his first communication skills, learn independence, discipline and will develop comprehensively together with his peers.
Recommendations for parents
- Involve your son or daughter in the household chores and give your child simple, age-appropriate tasks. Thanks to them, he will feel important and significant, and will understand that he is valued.
- If a child is too shy, do not stop praising him, support all his endeavors, rejoice at any, even minor, successes.
- Compliments and punishments must correspond to how old the child is and what he has done.
- There is no need to compare your son/daughter with yourself or with the neighbor's child. It’s better to compare your child with yourself or who he was in the past and who he is now.
- Encourage active and proactive actions coming from the child.
- Form the correct perception of failures and losses. A preschooler must be able to recognize his shortcomings and shortcomings.
- Accept your child as he was born, that is, with all his pros and cons. After all, he is a part of you.
- Surround your son or daughter with love and care. The child should feel your protection. He must understand that you will support him and will always be on his side. Don’t forget about tactile contact: kiss, stroke your child’s head and hug him often.
Age crisis
Senior preschool age ends the seven-year crisis, which marks the transition of the preschooler to the age period of the junior schoolchild. The child loses his former spontaneity, this is due to the fact that he begins to act not only emotionally, but at a certain moment includes an intellectual component. Starting to get angry, he realizes that he is angry; starting to cry, he realizes that he is upset. Perception moves from the realm of the sensory to the realm of the conscious, that is, the child can perceive and at the same time generalize what is happening, that is, call an object by a word.
An older preschooler begins to imitate adults and try on different roles, and this is not always appropriate.
Parents may regard this as pampering or even clowning around. Child-parent relationships become strained during this period; the preschooler insists on his own position and does not listen to the opinions of adults. Wanting to look more mature, the child tries to act in accordance with the status of an adult: he takes on new responsibilities, acts differently in familiar situations, in a word, he tries to destroy the opinion of himself as a small child. The psyche of a child during a period of age crisis is unstable, so it is important for parents to remain calm.
Advice to parents: Do not perceive the 7-year crisis as an illness from which you need to protect your child.
Give him more freedom and do not limit him in anything, just carefully control him and guide him in the right direction. It is best to show parental care with the help of advice that the child seeks himself, and not by being overprotective.
Game as a way of development
Preschool psychology defines play as a leading activity in the development of children of this age. What does "leading activity" mean? This means that it is this activity that has the main influence on the development of the child’s personality and all his mental processes.
During the game, the child learns to control his behavior according to the chosen role. This is how his voluntary behavior is formed. But you should not think that the game for the baby is just a fantasy, a pretense. No. For him, a game is an emotionally rich and absolutely real activity, where he can become anyone: a doctor, a salesman, a teacher, a knight or a princess.
Playing together helps children develop communication skills and also contributes to the emergence of social motives (achieving success, leadership).
During the process of role-playing play, the preschooler develops the following new formations:
- subordination of motives, that is, the ability to subordinate one’s personal desires to the rules of the game;
- learning the ability to communicate with other children. He masters the skills of interacting with peers, gaining both positive communication experiences (friendship, shared toys) and negative ones (grievances, quarrels);
- mastering the word “MUST”, and understanding that it is much stronger than the word “WANT”.