Updated July 23, 2021 772 Author: Dmitry Petrov
Hello, dear readers of the KtoNaNovenkogo.ru blog. From birth we experience different needs (for food, sleep, air, care).
Over time, they change, are supplemented, and strengthened. But it is their satisfaction that makes us act, move forward, go towards the goal.
Today we will talk about what it is, find out what needs are inherent in each person, what types they are divided into, and also take a detailed look at the pyramid of human needs from the famous American psychologist Abraham Maslow.
What are needs
The key word in defining the concept of need is “need”.
Need
- this is the need for certain things, objects of the material world, objects, people, social indicators, in the absence of which a person feels uncomfortable.
Taking into account this definition, neediness, in order to become a need, must meet the following criteria:
- A lack of need causes a feeling of dissatisfaction. A need is something desired, a good.
- Accompanying with emotions: from negative at the first stage to joyful after the need is fulfilled. When we really want something, we get nervous and anxious; when we get what we want, we relax.
- Fixation on the subject of need. Consciousness snatches from reality those things that can satisfy us. For example, if we are hungry, we will focus on the food and the smell of food.
The system of needs is also formed according to special rules:
- Need is common to all living beings on the planet. But the more developed the species, the higher the level of needs. The tree has enough nutrients from the soil, sunlight, and rain watering. Man, as a highly developed animal, needs much more.
- The older the person, the more extensive the list of what is required. A baby can do without things that an adult needs.
- Needs are a strictly hierarchical structure, some are primary, others are secondary.
People's actions are dictated by the presence of a certain need, which is the main motivator of activity. Motivation to get what you want moves a person forward and forces him to act. Everything that has been created by people throughout the history of mankind in politics, economics, art, science is the result of activities to satisfy needs.
The inability to fulfill needs can lead to dependence on their importance for the individual and to the following various consequences:
- Physical death of a person
. If the need for food, sleep, water, air, safety, etc. is not satisfied. - Frustration
is a long-term experience associated with a nervous disorder and can lead to serious psychological problems. An example is the lack of recognition of a person’s merits by society. - Sublimation
- the transition of the energy of dissatisfaction into creation, creativity. For example, the absence of sex is replaced by heavy sports activities.
Thus, needs should be listened to and efforts should be made to realize them.
Appearance
As some needs are satisfied, a person develops other needs, which suggests that needs are limitless. Needs are associated with a person’s feeling of dissatisfaction when a person lacks what is required. The presence of a need is accompanied by emotions: first, as the need intensifies, negative, and then, if it is satisfied, positive. Needs determine the selectivity of perception of the world, fixing a person’s attention primarily on those objects that can satisfy his needs. Throughout life, a person's needs change and increase.
The presence of unsatisfied needs in a person is associated with tension and discomfort, a discrepancy between the internal (desired) and external (real) [2], which are the stimulants and motivation of human activity. The presence of unmet vital needs can lead to death. A need can be understood as a certain hypothetical variable, which, depending on the circumstances, manifests itself either as a motive or as a trait. In the latter case, the needs are stable and become qualities of a person’s character.
What needs does a person have?
Man is one of the representatives of the animal world, with instincts and needs inherent in other species. At the same time, we have higher intelligence, feelings, and strong-willed qualities. This combination causes the presence of needs at two levels: basic and additional (primary and secondary).
Basic Needs
This group is vital for humans as a biological species. Basic needs are divided into two groups.
| Physiological | Existential |
| Breathing, nutrition, thirst, sleep, rest, procreation, housing. | Comfort, social and legal security, availability of employment, etc. |
Physiological basic needs must be satisfied first, since without them existence itself is impossible. The listed things and phenomena have been inherent in man since primitive times.
A person tries to make the process of satisfying basic needs more comfortable. If at the initial stage of the development of the human race animal skins served as clothing, today a whole industry is working to clothe us.
Basic needs can change with age in favor of the predominance of some over others. Sleep, for example, is more important for young children and older people, but in our youth we are able to get by with minimal hours of rest and still feel alert. Sex, as a primary need, can also, for a number of reasons, lose priority with age, but in adolescence it is a priority.
Questions often arise about security as a necessity for existence. Man has always experienced danger from phenomena in the surrounding world or from other people. A tsunami, a collapse of glaciers, an attack by wild animals or other tribes - all this forced a person to defend himself or run away. Over time, entire institutions were formed that were supposed to protect the individual from external incursions (army, police, Ministry of Emergency Situations). That is why safety is a primary need; we must understand that our lives and property are protected and protected.
The needs of existence (existence) appear as an individual grows up and determines his place in society.
Secondary needs
If a group of primary needs is necessary for survival and is laid down at the genetic level, then secondary needs determine a certain level of a person’s quality of life and come and are transformed with life experience.
Among the secondary needs in theory, the following are identified:
- Spiritual
. These include the need to obtain new knowledge about the world, the search for the meaning of life and one’s place in it, the development of creative abilities, and the desire for harmony. - Social
– love, friendship, interaction with other people, feeling part of society, a separate social group (class, work team, family). - Prestigious
. We are talking about the need for recognition of our successes, worthy self-esteem, respect from other members of the communities in which we belong.
Thus, primary needs are innate and determined by physiology, while secondary needs are psychological in nature and develop throughout life.
Introduction
The problem of personal self-development is one of the “eternal” topics that never lose their relevance. “Self-development processes make it possible to individualize the path of life, to make a free choice of ways of existing in this world, focusing on vital values. It is the process of self-development that provides a person with the need and opportunity to become a person, a bearer of culture, norms, and value relationships” [1]. In turn, the study of the needs underlying personal self-development allows us to answer the question: why does a person become a person? why can a person become mature?
In modern society, the problem of personal self-development and its factors is of particular relevance. Modern social conditions are characterized by global social transformations, accelerating the pace of economic and sociocultural development, which is reflected in constant changes in all spheres of people’s lives. Therefore, life activity in modern society places increased and qualitatively new demands on the process of social adaptation and personal development. “This leads to the fact that a person’s creative potential, his readiness to respond productively to demands and changes in the environment become one of the key factors in the development of both the person himself and society. The problem of studying the features of designing a system of interaction between an individual and society, and himself, becomes relevant; Research into issues of determination of behavior and manifestations of activity in modern conditions takes on a different character and vector of research - the search and analysis of not only stable patterns of functioning, but, to a greater extent, development and self-development" [7].
In turn, studying the factors of personal self-development allows us to determine the optimal ways to develop a mature personality in the difficult conditions of life in modern society.
Types of needs
Needs can be classified on various grounds, of which there are quite a lot in the theory of psychology. The main types of division of needs are presented in the next section.
If we summarize all available theories, then we should distinguish three basic types of human needs.
Biological or physiological
Among the innate human needs laid down at the genetic level are the following:
- Food safety and taste characteristics.
- Comfortable external temperature and electromagnetic background.
- Clean water suitable for quenching thirst.
- Healthy ecology.
- Safety of life and home.
- Sexual satisfaction.
- Disposal of waste products.
These things are necessary for any living creature. This set of needs has practically not changed since the creation of the world, since from a physiological point of view, we are the same as millions of years ago. A person strives to realize them first and foremost and immediately.
Spiritual
Existential needs come from a system of universal human spiritual values, including: beauty, mercy, tranquility, harmony, peace, art. Each person has their own spiritual needs (as opposed to biological ones) and change over time and experience.
Among the spiritual needs are the following:
- The need for knowledge
. A mature person understands that in order to further grow, he must constantly learn. Moreover, expand the boundaries of existing skills and acquire new ones. People enter educational institutions to receive additional education, take advanced training courses, master new professions, and master the basics of painting and music. - The need for constant work on oneself, improving one’s personality (self-improvement)
. By satisfying this need, we quit smoking, go on a diet, get rid of toxic people and harmful emotions. A person thinks about how he would like to see himself after a certain period of time and strives for this. - The need for love and personal happiness
. The vast majority of people dream of having a loved one of the opposite sex nearby and creating a stable family. Many have been searching for many years, this need is so strong.
The realization of spiritual needs can be carried out through the simplest things. For example, a person goes into nature and sits with a fishing rod, fishing. At this time, he reflects, calms down, acquires spiritual harmony, satisfying his need for peace and making plans for the future.
Social
This type of needs is aimed at understanding one’s place in society and is associated with groups of people, social and economic activity.
Examples of social needs:
- Personal identification
. A person positions himself as a part of society with common traits inherent in society or a separate group. At the same time, he recognizes himself as an individual unit with a set of specific qualities and characteristics. - Self-affirmation
. We want to be satisfied with ourselves, with the actions and deeds that we perform. It is also important for a person to feel significant in society, to enjoy respect and approval from other people.
- Altruistic aspirations
. The individual takes pride in actions aimed at helping and assisting other people or living beings. He needs to be needed, useful, even in conditions of abandoning his own interests.
All of these types of needs are interpenetrating, they complement each other, some follow from others. For example, having satisfied the spiritual need to acquire a profession, we strive to achieve success in work for which we will be praised, and this is already a social need.
Bibliography
- Berezhnova O.V. Reflective activity as a pedagogical condition for self-development of university students. Author's abstract. diss. ...cand. ped. Sci. – Rostov, 2005.
- Kulichkova S.A. Self-development of high school students in a boarding lyceum: theory and practice // Bulletin of SevKavSTU, Series “Humanities”, No. 2 (12), 2004.
- Luchkina T.V. The role of innovative activity in the personal and professional self-development of a young teacher. Author's abstract. diss. ...cand. ped. Sci. – Irkutsk, 2000.
- Maralov V.G. Fundamentals of self-knowledge and self-development: Proc. aid for students avg. ped. schools, institutions. – 2nd ed., erased. – M.: Publishing House, 2004. – 256 p.
- Maslow A. Self-actualization. – School-workshop for personal development. – www.isra-trainings.com.
- Maslow A. Theory of human motivation. – www.flogiston.ru.
- Mokerova Yu.V. Contradictions in the formation of the need for personal self-development in modern conditions: sociological analysis. Author's abstract. diss. ...cand. sociol. Sci. – Ekaterinburg, 2006.
- General pedagogy. Lecture course. – Department of Psychology and Pedagogy, Kabardino-Balkarian State University. Kh.M.Berbekova. – kpip.kbsu.ru.
- Opletin A.A. Pedagogical technology of social and moral self-development of college students’ personality (based on physical education). Author's abstract. diss. ...cand. ped. Sci. – Perm, 2005.
- Selevko G.K. Self-education concept. – www.abc-people.com.
- Semenov I.N., Stepanov S.Yu. Reflection in the organization of creative thinking and personal self-development // Journal “Questions of Psychology”. – www.voppy.ru.
- Slastenin V., Isaev I. et al. Pedagogy: Textbook. – www.gumer.info.
- Slesarenko N.V. Activation of cadet’s personal self-development in the educational process of a military institute. Author's abstract. diss. ...cand. ped. Sci. – Khabarovsk, 2004.
- Freydiman J., Frager R. Abraham Maslow and the psychology of self-actualization. – Library of the Russian Humanitarian Internet University. – www.iu.ru.
Classifications of needs
Theoretical psychology offers many classifications of needs. We have already discussed one of them above: physiological, social and spiritual, these are the main groups of needs.
Foreign researchers did not so much classify needs as offer a specific list of them.
Examples:
- G. Murray
- achievements, aggression, independence, sex, creativity, understanding, respect, self-knowledge. - A. Pieron
- novelty, hedonism, communication, competition, mutual assistance and others (more than 20 types in total); - E. Fromm
- significance, self-affirmation, communication, affection, self-identification.
Some scientists have identified so-called neurotic needs as a separate group, the lack of satisfaction of which can lead to mental illness. These include: lack of social and interpersonal justice, the need for support and empathy, recognition, and possession.
In Russia, a classification of needs has been adopted, which divides them into the following levels:
- Based on the nature of the emergence of needs - natural and cultural
. - Depending on the area of application - communicative
(communication with other people),
cognitive
(the need to acquire new knowledge),
labor needs
, etc. - In relation to the object to which the need is directed - biological, material, spiritual and social
. - Correlating to their origin - endogenous
(determined by internal factors) and
exogenous
(depending on external conditions).
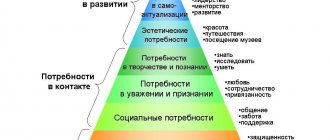
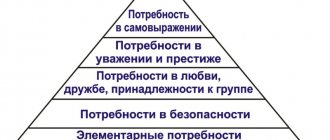
As we see, the number of human needs is numerous; today there is no complete list of them; there are only generalized groups and types. The most famous theory that places all types of human needs in order of priority is Abraham Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs.
The psychologist drew a whole pyramid, where needs are indicated in ascending order. This is what she looks like.
Maslow assured that until a person has satisfied the needs of the widest part of the pyramid, he will not strive to receive benefits from the higher levels. For example, if a person is hungry, then he has no time for public recognition. He considered hunger not only in relation to food, but also to sleep, thirst, sex, etc.
Maslow’s rule does not work in the opposite direction: an individual who has fulfilled the need for respect and recognition still needs food and sleep.
The concept of personal self-development
Even ancient philosophers (Heraclitus, Socrates) were interested in the problem of personal self-development [9]. However, to this day this problem has not been fully studied. In modern psychology and pedagogy, there is no unity of views among researchers on the concept of personal self-development: “Some understand self-development as self-education, self-organization of the individual... Others understand self-development as self-regulation...; as a process of life self-determination..., or as activity in the process of self-affirmation” [9].
In philosophy, self-development is considered as a process of self-creation, “self-construction” of the individual, based on a person’s knowledge of himself [3].
In psychology and pedagogy, many researchers give the following definition of self-development: “self-development is a process of independent, holistic, purposeful, value-oriented activity of an individual for continuous self-change as an enrichment of individual experience and spiritual and moral forces in accordance with the internal image of the “I” and current social expectations” [2; 3; 7; 13].
However, other researchers consider this process of conscious and purposeful activity for internal enrichment and personal growth as self-education [10; 12]: “at a certain stage of development of the individual, his intellectual abilities and social self-awareness, a person begins to understand not only the goals external to him, but also the goals of his own upbringing. He begins to treat himself as a subject of education. With the emergence of this new, very unique factor in the formation of personality, a person himself becomes an educator” [12]. Apparently, self-education as a purposeful activity should be considered as one of the forms of self-development, and self-development as such is a broader concept.
In defining the concept of “self-development”, one should probably proceed from the definition of the concept of “development”. In modern psychology and pedagogy, development is defined as “an objective process of quantitative and qualitative changes in mental processes, properties, states over time, expressed in natural transformations” [4].
Human development is influenced by two types of factors: external and internal [8]. “On the one hand, human development is influenced by the surrounding world - education, upbringing, and on the other, internal goal setting is the source of self-propulsion. That is, a person, guided by his values and goals, masters the ability to determine the path of his own development, to carry out it as a free, personally significant activity" [13], "while simultaneously improving and developing his abilities to implement it, changing and educating (shaping) himself" [10 ]. Thus, self-development is the development of a person’s personality under the influence of internal factors.
Some authors equate development and self-development of the individual, because any external factors can have only an indirect, indirect impact on the development of the individual, and development is always carried out under the influence of only internal factors. “L.N. Tolstoy compared human development to how a fruit tree grows. Indeed, in the literal sense, it is not a person who grows it - it grows itself. He only loosens the soil, applies fertilizers, trims branches, in other words, creates the necessary external conditions that contribute to and stimulate his self-development. Development itself occurs according to its own internal laws” [8].
V.G. Maralov defines the self-development of the individual as a complex specific process unfolding in time and space of the individual’s life activity, which can take the following main forms , each of which reflects a certain aspect of the self-construction of the individual [4]:
- Self-affirmation - makes it possible to express oneself fully as an individual, or to confirm or strengthen one’s own personality, character traits, ways of behavior and activity.
- Self-improvement – expresses the desire to get closer to some ideal; This is conscious management of the process of one’s own development in a certain direction.
- Self-actualization – allows you to identify a certain potential in yourself and use it in life; this is the realization of oneself in the world by learning the meaning of life, achieving the fullness of self-existence.
According to T.V. Luchkina, self-development is a combination of the following processes [3]:
- Self-knowledge;
- Conscious self-regulation;
- Self-improvement as the enrichment of one’s essential powers in order to subsequently have the opportunity to self-realize at a higher level;
- Increasing one’s own productivity as “a state of internal activity in life’s difficulties, associated with the cultivation of one’s capabilities” (E. Fromm);
- Spiritual self-strengthening as the ability to “gain the balance of spirit necessary for life through doing good deeds” (L.N. Kulikova);
- Self-determination as a conscious act of identifying and asserting one’s own position in problem situations (V.A. Petrovsky);
- Self-actualization;
- Self-realization.
The most effective result of the previous stages and the subject of subsequent stages of self-development is a mature personality with such characteristics as activity, individuality, creativity, responsibility and independence [3].
The most important characteristic of a mature personality is that such a personality becomes the subject of his own life activity, i.e. the life path of a mature personality is the result of her own purposeful activity, and not external circumstances [3; 4; 7, etc.]. In other words, a mature person does not “go with the flow”, but is the builder of his own destiny.
Formation of human needs
Taking into account the considered classification of needs, we can talk about the features of their formation. Basic physiological needs are innate, transmitted to us at the genetic level. A person lives with them until his death; without receiving them, he dies physically.
Such needs cannot be prohibited or imposed by force. Primary needs cannot be good or bad, pure or dirty. Only ways and methods of satisfying them can be considered unworthy. For example, a person uses a public space instead of a toilet.
Primary spiritual needs also appear with a person. The presence of love, close people, harmony, and self-realization in life are mandatory for his mental health. Of course, without the listed benefits, a person will not die, but he will be stuck in reflection and frustration for a long time.
Secondary needs are formed in an individual in several stages.
Infancy
All the physiological needs of the baby are provided by his parents. Since the child has contact with adults, social needs arise even before six months: he smiles, looks at rattles, identifies mother and father.
Earlier childhood
At about the age of 3 years, the baby develops an understanding of objects to satisfy needs - he realizes the need for toys, certain food, specific clothing. Cognitive needs grow, the child reads books, sculpts, draws, and actively explores the world.
Preschool period, primary school age
Children's social environment expands significantly. In addition to mothers and grandmothers, they have their own friends - children from kindergarten, class, yard or clubs where he begins to go. The need for communication, recognition, mutual assistance and understanding is formed.
Teenagers
At this age, the last physiological need is revealed - sexual. For the first time, such secondary needs as self-realization and self-improvement are formed. There is a sharp change and expansion of cognitive interests. A teenager strives to learn about those things and objects that he did not even think about in the early periods of his life.
On the basis of the formed sexual need, a need for a person of the opposite sex and romantic experiences appear. The need for communication is shifting towards peers and friends. Relatives fade into the background.
It is believed that by the end of adolescence, all the basic needs of a person have already been developed. Their further development occurs through changes in their content and methods of achievement.
Pros and cons of Maslow's pyramid
Maslow's pyramid has a number of advantages that are valuable not only for psychologists, but also for marketers:
- better understanding of customer needs and values;
- building the right sales strategy and marketing campaigns;
- optimization of marketing processes related to segmentation of the target audience and the formation of a unique selling proposition;
- correct assessment of personal perception characteristic of different groups of clients;
- objective comparison of life priorities.
Some principles of Maslow's pyramid are considered outdated: all needs included in the structure cannot be satisfied. However, Maslow's pyramid is the basis from which Alderfer's ERG (three needs) theory and other classification systems were developed.
Lowest platform
Physiological needs can be satisfied throughout your life and never be satisfied. Pathology and displacement of value orientations, as a rule, occur in many members of modern society (regardless of wealth and social significance). And all these problems are due to the exaltation and highlighting of lower needs. This is how dissatisfaction with oneself and one’s life, destiny, and place in society comes. Lack of understanding of your role in life. The result is a low social role, a feeling that you are a cog in a machine, a piece of gray mass, causing oppression and a feeling of hopelessness.