In order to be able to apply acquired knowledge in the field of psychology in practice, it is necessary to know and be able to use a special set of psychological methods. The correct application of these psychological methods, subject to certain norms and rules, will provide reliable information. At the same time, the choice of method when conducting research cannot be accidental; it completely depends on the characteristics of the mental phenomenon being studied.
The methods of modern psychology force the person conducting psychological research to return to the object of research, thereby deepening its understanding. If we consider the essence of the method, then this is a way of conducting research in reality, that is, in the real world.
Psychology is the expression in words of what cannot be expressed in words. John Galsworthy
Methods of modern psychology
Each such technique includes several actions and ways of their implementation by the researcher while studying the object.
But any method corresponds to only one characteristic type of these actions and methods of implementation, which corresponds to the tasks and goals of the study. One such technique may be based on several methods. It should also be noted that psychological science does not have any complex of methods that do not have any other research option.
Let's look at some of these techniques, their classification and characteristics. To do this, we will divide them into two groups: methods of basic (general) psychology and methods of applied psychology.
Forms of knowledge - sensual and rational
According to Plato, there are two levels of knowledge: sensory and rational. This means that when exploring the world around us, we either interpret its images with the help of thoughts, or perceive it through our senses.
Let's look at them separately in more detail:
- Sensory cognition represents the first stage of acquaintance with the environment, since a person first perceives information through the senses : vision, hearing, smell, touch and taste.
To evaluate a culinary dish, we must see it, smell it, and taste it on our tongue. To read a book, we need eyes. Cognition through the senses includes: - sensation is the stimulation of the senses by external stimuli (I eat an apple - it tastes sweet);
- representation is the appearance of a picture that is stored as a memory. In the future, when I remember an apple, a round, hard, green fruit with a sweet taste and a pleasant smell will pop up in my head.
perception is the birth of the image of the stimulus (the apple is round, hard, green, smells good);
- concept - a thought reflecting objects united by the same characteristics. For example, everyone knows what a chair is. The concept of a chair includes all the chairs in the world of different shapes, quality, and materials. We do not call a chair a specific object in the singular: the concept unites their many;
At the moment there is no clear conclusion which is more important - the mind or the feelings. Therefore, it is generally accepted that both levels of knowledge are equally important: for a more complete understanding of the phenomenon, it is necessary to use both.
Feelings are a conductor between us and the environment: if all feelings disappear at once, then knowledge will become impossible. However, the work of all five also does not guarantee the acquisition of comprehensive information, and this is where the mind “helps us out”, building the acquired knowledge in an understandable way.
Methods of basic (general) psychology
Basic (general) psychology conducts research using general concepts about human consciousness, its views on the world, lifestyle and morals, and also includes everything that can have an impact on the conduct of this psychological research.
Methods of basic (general) psychology are methods by which a person conducting research has the opportunity to obtain reliable information for him to further put forward a scientific theory and the opportunity to give practical recommendations.
Observation
Purposeful and organized perception and recording of the behavior of the object of study.
This technique is considered one of the most ancient and should be carried out in familiar conditions for the person who is the object of this study. Observation is usually carried out when it is impossible to interfere with the process of what is happening or when it is not recommended to disrupt the process of a person’s relationship with his environment. This method of research is needed when it is necessary to obtain a complete picture of the situation and most fully note all the changes occurring in the behavior of one person or group of people.
The essential features of the observation method are:
- impracticability or difficulty of secondary observation;
- observation accompanied by excessive emotionality;
- the object of observation is associated with the observer.
When conducting observations, it is necessary to record the obtained data in a protocol and observe the following rules:
- the observation process should in no way influence the ongoing course of events;
- It is better to observe not one person, but a group of people, then the observer has the opportunity to compare;
- Observation must be carried out repeatedly and regularly, taking into account previously obtained data.
Observation stages:
- Determination of the object, subject or situation that will be observed.
- Determine the technique used in the observation process and the method of recording the information received.
- Develop a surveillance plan.
- Decide on the method by which the recorded data will be processed.
- Just an observation.
- Processing and interpretation of received information.
Observation tools include devices that can be used to make audio recordings, photographs and videos, and observation can be carried out directly by the person conducting the research.
Often the observation method is referred to as a type of research such as an experiment, but this is not so, due to the fact that:
- the person conducting the observation does not interfere in any way with what is happening;
- the observer registers only what he observes.
The ethical side of the issue is as follows, according to the rules of the American Psychological Association (APA) - observation must be carried out according to strictly defined rules:
- It is obligatory to obtain consent to participate in the experiment from its participants. The only exception is when conducting surveillance in a public place.
- Eliminate the possibility of causing harm to the participants of the experiment during its conduct.
- Avoid or reduce to a minimum the intrusion into the researcher’s privacy.
- All data obtained about the participants in the experiment is strictly confidential.
Even if you are not a psychologist, you can use this technique to obtain the necessary information about a person, if necessary.
Psychological experiment
An experiment conducted by a researcher in specially created conditions in order to obtain the necessary information about the subject by interfering in his life activities.
In this case, the experimenter constantly changes the conditions of the experiment and evaluates the result obtained. In addition, a psychological experiment can include methods such as testing, questioning, and observation. But it can also be a method independent of others.
According to the method of conducting experiments, there are:
- laboratory method (the ability to change conditions and influence certain facts);
- natural method (carried out under ordinary circumstances, without informing the subject about the experiment);
- psychological and pedagogical method (obtaining skills and specific qualities when learning something);
- pilot method (used as a test study, before the start of the experiment itself).
According to the level of awareness, psychological experiments are divided into the following types:
- Explicit
- the person participating in the experiment knows about it and is familiar with all the details of its implementation; - Hidden
- a person who is not aware of the experiment. - Combined
- the participant in the experiment has only some part of the experiment and is deliberately misled.
To organize an experiment, you need to know for what purpose the research is being conducted, with whom and under what circumstances.
A connection is established between the experimenter and the research participant in the form of instructions or the lack thereof. After that, they begin directly to conduct the research itself, at the end of which the information received is processed and the result is announced. As a scientific method, an experiment must meet the following criteria:
- Impartiality in obtaining data.
- Reliability of the information received.
- Validity and suitability of the information received.
However, despite the fact that experiment is one of the most respected methods used to obtain data, it has both positive and negative sides.
Advantages of the method:
- You have the right to choose the starting point when conducting the study.
- There is the right to repeat the experiment.
- It is possible to change the experimental conditions with the possibility of influencing the result.
Disadvantages of the method:
- The complexity of the psyche for experiment.
- Instability and uniqueness of the psyche.
- The psyche has the property of surprise.
It is for these reasons that when performing an experiment, the person conducting the research cannot be guided solely by the data of this method of psychological research; he needs to resort to other methods, combining them and taking into account many different data.
Just as with observation, a psychological experiment must be conducted in accordance with the APA Code of Ethics.
An ordinary person can, quite independently, without the help of a specialist in the field of psychology, conduct independent experiments in everyday life. Of course, the data he obtained during such an experiment will be far from the truth, but it is still possible to obtain certain information.
Remember, when conducting an experiment in the field of psychology on your own, you need to be attentive to others and ensure that you do not harm anyone.
Psychology is about choosing the right words for an incorrectly formed belief. Aishek Noram
Introspection
Monitoring oneself and the individual traits of one’s behavior and character.
This method is used in the form of self-control and is of great importance in psychology and human life. Nevertheless, it should be noted that introspection in most cases can only establish the fact of something, but not the basis (left somewhere, but only God knows where and why). In this regard, self-observation cannot be considered an autonomous and main technique in the process of comprehending the essence of manifestations of the psyche.
The work of this method directly depends on the self-esteem of the individual. This method is most often used by people with low self-esteem and, as a result, when choosing this method, a person begins to engage in self-flagellation, namely delving into himself, feeling guilty, looking for justification for his actions, etc.
In order for this study to be accurate and have results, it is necessary:
- keep a diary;
- compare observations of yourself with observations of others;
- increase self-esteem;
- participate in trainings that promote personal growth and development.
In life, observation is a very working way if a person wants to understand himself, understand why a person acts this way and not otherwise, get rid of complexes and bad habits, and also solve some life problems.
Testing
It is related to the field of psychodiagnostics and studies the psychological qualities and properties of a person through the use of psychological tests.
This technique is most common in psychotherapy, counseling, and also during interviews with employers. This method is necessary when there is the most specific awareness of a person’s personality, which cannot be achieved using other methods.
The main features of psychological tests include:
- Validity
- the validity and suitability of the information obtained as a result of testing of the feature in relation to which the test was conducted; - Reliability
- confirmation of previously obtained results by duplicating the test; - Reliability
- even with obviously false answers, the test produces a true result; - Representativeness
- compliance with the characteristics of norms.
In order for a test to be effective, it is created using trial and error (changing the number of questions, their edition, text and idea).
The test goes through a multi-level testing and adaptation process. A successful psychological test is a standard control, at the end of which, upon receipt of the results, the opportunity to assess the psychophysiological and personal development, skills, knowledge and abilities of the test participant becomes available based on the summed up results.
Psychological tests are of the following types:
- Career guidance test - establishes a person’s inclination towards a particular type of activity or indicates the appropriateness and harmony of the position held;
- Personality tests - help to explore a person’s character, needs, feelings, abilities and other personal qualities;
- Tests for human mental abilities - examine the level of formation of intelligence;
- Verbal tests - explore the ability to describe and convey the actions performed by a person using words.
- Achievement tests assess the degree of mastery of certain knowledge and skills.
In addition to the listed testing methods, there are other test options that contribute to the study of personality and its characteristics.
In addition, this research method can be easily applied to anyone, thereby learning about their potentially hidden capabilities.
[media=
https://youtu.be/mn9pO5wAk14
]
Biographical method
This is the study, diagnosis, regulation and planning of a person’s lifelong journey.
Various variations of this method began to form and emerge at the beginning of the twentieth century. In current methods of biographical research, a person is studied based on historical connections and opportunities for personal growth.
In this case, personal information is obtained from the following sources:
- autobiography,
- questionnaire,
- interviewing,
- witness statements,
- analysis of notes, messages, letters, diaries, etc.
This method is used quite often by people at the head of an enterprise, conducting a biography when researching someone’s life, when talking with unfamiliar individuals. The method is easy to use when communicating with a person to obtain any information regarding his life.
Survey
A method based on joint contact between the researcher and the object of study, during which the respondent is asked questions, to which he, in turn, gives answers.
This method is most popular in psychological science. Moreover, the psychologist’s question depends on what data needs to be clarified during the research process. This technique is usually used to find out the necessary information and data not about one specific person, but about a whole group of people.
Surveys are usually divided into the following types:
- Standardized (classic surveys that can give a total look at the issue of interest);
- Not standardized (less related to the classical form of the survey, they allow you to master the specific nuances of the problem).
When creating surveys, questions related to the program are first created that only a specialist can understand.
After which they are rephrased into questionnaire questions that are clear to the average person. Polls are:
- Written
– to obtain shallow information about the problem. - Oral
- allow you to break into the deeper layers of human psychology. - Questioning
– answers to questions immediately before the conversation itself. - Personality tests
are carried out to determine the characteristics of the individual’s psyche. - An interview
is a personal conversation.
When forming questions, the following rules must be taken into account:
- Reticence and isolation.
- The absence of characteristic words that are concepts of something in psychology.
- Conciseness and stinginess.
- Definition.
- Lack of hints.
- The questions are designed in such a way as to avoid non-standard answers.
- Questions have no push-back effect.
- Questions lack the ability to suggest anything.
Questions are divided into several types regarding the task at hand:
- Open (the configuration of responses in this case is free);
- Closed (answers prepared in advance);
- Subjective (personal in nature relating to a person’s views towards someone or something);
- Projective (about a third person, without mentioning any information about the person being interviewed).
This method helps to determine the needs of the majority or find out their wishes regarding a certain issue.
The technique is very relevant and significant for obtaining important information on topics of interest and concern to most people.
Conversation
One of the types of observation. Refers to an independent method of personality research, the purpose of which is to determine the range of issues that cannot be identified through ordinary observation.
A conversation is a dialogue, the effectiveness of which depends on the following conditions:
- It is necessary to think about the content of the conversation in advance;
- Establish contact with the interlocutor;
- Eliminate all possible unfavorable conditions that could cause inconvenience to the person being studied (tension, wariness, fear, etc.)
- Clarity of questions for the person being studied;
- Questions should not in any way indicate the correct answer;
- During the conversation, the psychologist observes the behavior of the participant in the dialogue and compares his reaction with the answer received to the question;
- The content of the conversation must be kept in memory or hidden audio or video recordings of the conversation must be kept in order to be able to understand the problem in more detail and analyze it in the future;
- The conversation should not be recorded openly; such actions may create discomfort for the research participant and cause mistrust;
- You should watch out for answers that have understatements, reservations, etc.
Conversation helps in obtaining the necessary data first-hand and finding a common language between people. If you approach the organization of this method correctly, you can not only obtain the necessary information, but also get to know the person better, understand him and his actions.
Principles of conducting psychological research.
In addition to the principles of psychological science considered, in order to improve the quality of research results, it is necessary to be guided by special principles related to the process of applying methods in psychological research.
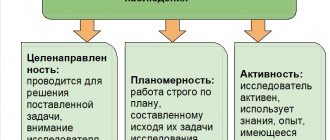
1. Principle of objectivity
. Methods of psychological research reproduce the objective process of scientific knowledge of the subject of psychology and must provide a reflection of its true essence - its laws of existence. The results of psychological research cannot change the essence and patterns of the subject being studied. The objectivity of its existence does not depend on scientific manipulations with it.
The subjective component also takes place in the construction of psychological research.
It can manifest itself in the initiation of research as such, in the freedom to choose the organizational elements of the research, in the professional competence of the researcher... However, this subjectivity must be based on the desire to obtain true research results.
It is important to choose research methods that contain a high degree of objective data.
The principle of objectivity is also manifested in the researcher’s refusal to take a conjunctural approach to the results of the study, the interpretation of which should not be adjusted to confirm the hypotheses and goals of the study.
2. Systematic principle
involves the study of a mental phenomenon as a unique system that has its own specific patterns. One of the forms of implementing a systematic approach in psychological research is a personal approach, which involves the study of a specific situation.
3. Principle of individualization
consists in revealing the uniqueness of each personality, inherent in the individual style of activity and behavior, in identifying the psychological problems of a particular individual and ways to solve them.
Basic concepts and keywords:
method, methodology, methodology, the principle of determinism, the principle of unity of the psyche and activity, the principle of development, the principle of objectivity, the principle of consistency, the principle of individualization.
Recommended reading:
1. Grinshpun I.B. Introduction to Psychology. – M., 1994.
2. General psychology: course of lectures / comp. E.I. Rogov. – M.: VLADOS, 1995.
3. Makarova L.L., Sinelnikov V.M. Zagalna psychology: basic guide - K., 2005.
4. Maksimenko S.D. The problem of method in science - K., 1982.
5. Foreign psychology: Pidruchnik / O.V. Skripchenko, L.V. Dolinska and in.. - K., 2005.
12 pages, 5595 words
1 The role of science in the development of society. Scientific activity, scientific knowledge
... the science of principles and methods of cognition, as well as obtaining results useful for human activity, implementation in production with further effect. The basis for the development of each scientific research ... ultimately arises from experience, yet it is not enough to understand the deep internal laws of the emergence and development of a cognizable object. Theoretical knowledge is...
Questions for self-control:
1. What is the difference between the concepts “method”, “methodology”, “methodology”?
2. What is the difference between general scientific and specific scientific methodology?
3. How can we define the concept of “principle”?
4. What is the essence of the principle of determinism?
5. How did the concept of the principle of determinism develop?
6. What is the essence of the principle of unity of psyche and activity and who is its second?
7. Characterize the principle of development and the genetic principle.
8. What contribution did S.L. Rubinstein and R.S. Kostyuk make to the development of the development principle?
9. What is the difference between the concepts “phylogenesis of the psyche”, “historiogenesis of the psyche”, “ontogenesis of the psyche”?
10. What is the essence of the principle of objectivity?
11. What is the essence of the principle of systematicity?
12. What is the essence of the principle of individualization?
Test tasks:
1. What is the definition of a scientific research method?
A) a set of special techniques and methods of carrying out work aimed at solving diagnostic and corrective problems;
B) determines the principles, techniques, recommendations that guide a person in his activities;
C) a way of knowing or practically doing something;
D) develops universal principles, means, forms of scientific knowledge not related to any specific science;
D) develops universal principles, means and forms of knowledge associated only with a specific science.
2. Which statement refers to the technique?
A) a way of knowing or practically doing something;
B) develops principles, means and forms of knowledge associated only with a certain science;
C) develops universal principles, means, forms of scientific knowledge not related to any specific science;
D) a set of special techniques and methods of carrying out work aimed at solving diagnostic and corrective problems;
D) determines the principles, techniques, and recommendations that guide a person in his activities.
3. Which statement refers to the general definition of methodology?
A) develops principles, means and forms of knowledge associated only with a certain science;
B) a way of knowing or practically doing something;
C) develops universal principles, means, forms of scientific knowledge not related to any specific science;
D) a set of special techniques and methods of carrying out work aimed at solving diagnostic and corrective problems;
D) determines the principles, techniques, and recommendations that guide a person in his activities.
4. What refers to general scientific methodology?
A) a set of special techniques and methods of carrying out work aimed at solving diagnostic and corrective problems;
B) develops universal principles, means, forms of scientific knowledge not related to any specific science;
C) a way of knowing or practically doing something;
D) determines the principles, techniques, recommendations that guide a person in his activities;
29 pages, 14037 words
Psychological patterns of management activity.: ...
... fairly high levels of complexity of management activities. 4. Psychological patterns of management activity The law of inadequacy of self-esteem. Law of self-preservation. Principle of development As is known, management ... scientific principles of approaching a person as an object of knowledge are being developed. Among such principles one can note, in particular, such as the principle of universal talent...
D) develops principles, means and forms of knowledge associated only with a certain science.
5. Which statement refers to specific scientific methodology?
A) develops principles, means, forms of scientific knowledge not related to any specific science;
B) determines the principles, techniques, recommendations that guide a person in his activities;
C) develops principles, means and forms of knowledge associated only with a certain science;
D) a way of knowing or practically doing something;
D) a set of special techniques and methods of carrying out work aimed at solving diagnostic and corrective problems.
6. What definition refers to the principle of determinism?
A) the process of scientific knowledge of the subject of psychology must ensure a reflection of its true essence - its laws of existence;
B) the laws of all phenomena, including mental ones, are learned in the process of their movement and change, emergence and death;
C) records the causality of the psyche and includes it in the connections and relationships of objective phenomena;
D) states that there cannot be activity without consciousness and consciousness without activity.
7. Which statement refers to the principle of the unity of consciousness and activity?
A) claims that there cannot be activity without consciousness and consciousness without activity;
B) records the causality of the psyche and includes it in the connections and relationships of objective phenomena;
C) the laws of all phenomena, including mental ones, are learned in the process of their movement and change, emergence and death;
D) the process of scientific knowledge of the subject of psychology should provide a reflection of its true essence - its laws of existence.
8. What is the developmental principle or the genetic principle?
A) the process of scientific knowledge of the subject of psychology must ensure a reflection of its true essence - its laws of existence;
B) records the causality of the psyche and includes it in the connections and relationships of objective phenomena;
C) the laws of all phenomena, including mental ones, are learned in the process of their movement and change, emergence and death;
D) the process of scientific knowledge of the subject of psychology should provide a reflection of its true essence - its laws of existence.
9. Which statement refers to the principle of objectivity?
A) is to reveal the uniqueness of each individual;
B) records the causality of the psyche and includes it in the connections and relationships of objective phenomena;
C) the process of scientific knowledge of the subject of psychology must ensure a reflection of its true essence - its laws of existence;
D) the laws of all phenomena, including mental ones, are learned in the process of their movement and change, emergence and death.
7 pages, 3488 words
Subject and tasks of psychology. Methodological, theoretical...
... psychology: The study of objective patterns of functioning of mental processes and phenomena, ... everyday psychology" and "scientific psychology" Everyday (or ordinary) psychology ... physical bodies. Knowledge of the world occurs... true love, the highest realization of the human soul. Therefore, Psyche - a mortal who has acquired immortality - has become a symbol of the soul searching for its ideal. For the first time the term “psychology”...
10. Which statement refers to the principle of systematicity?
A) the laws of all phenomena, including mental ones, are learned in the process of their movement and change, emergence and death;
B) the process of scientific knowledge of the subject of psychology must ensure a reflection of its true essence - its laws of existence;
C) provides for the study of a mental phenomenon from all sides as a unique structure that has its own specific patterns;
D) is to reveal the uniqueness of each individual;
D) records the causality of the psyche and includes it in the connections and relationships of objective phenomena.
11. What refers to the principle of individualization?
A) provides for the study of a mental phenomenon from all sides as a unique structure that has its own specific patterns;
B) records the causality of the psyche and includes it in the connections and relationships of objective phenomena;
C) is to reveal the uniqueness of each individual;
D) the process of scientific knowledge of the subject of psychology should provide a reflection of its true essence - its laws of existence.
Examples of similar educational works
1. History of accumulation and development of psychological knowledge. The formation of psychology as...
... activities; Therefore, research in the field of psychology ... to find a pattern in ... in the psyche ... phenomena remained an incomprehensible mystery for him for a long time. However, there are many transitions between the state of “wet” and “fiery”. History of development …
The influence of extracurricular activities on the personality development of high school students
... activities for the development of the personality of high school students. The object of the study is the extracurricular activities of high school students. The subject of the study is the influence of extracurricular activities on the development... in the process of cognition and creation... of the mental states of the subject in...
The main stages in the development of views on the subject of psychology
... the history of psychology as a special branch of knowledge 1. Study the patterns of development of knowledge about the psyche. 2. Reveal the relationship between psychology ... point in the history of ideas about psychological activity. A fundamentally new approach was expressed by what replaced animism...
The influence of theatrical and play activities on the development of speech and phonemic hearing...
... speech, play skills and creative independence. I. Theoretical foundations for the study of the use of theatrical play activities in the development of speech and phonemic hearing 1.1 Psychological and pedagogical foundations of the use of theatrical ...
Development of basic psychological approaches to research and creation of advertising
... Elements of a geometric figure ●Line shapes 2) psychology of light: ●Strength - weakness of the light source ... hidden. 4. Gestalt approach Basic principles: simple figure and ground diagrams... Suggestion is a process of influencing the human psyche associated with a decrease in...
Methods and research in applied psychology
Applied psychology is aimed at conducting research with a specific group of people, the methods of which make it possible to change a person’s mental state and behavior.
Suggestion
The process of wedging instructions, views, principles, beliefs and certain formulas into a person’s subconscious without his conscious control.
Suggestion can be indirect and direct. The purpose of the method is to achieve the desired state or opinion. The way in which this goal will be achieved does not matter. All that matters is achieving the desired effect.
Actually, for this reason, during suggestion, they freely use emotional consolidation in memory of the signs of objects when correcting behavior, confusion, distraction of interest, intonation, remarks and even blackouts (hypnosis, narcotic substances, drinks containing alcohol).
There are the following types of suggestions:
- direct (influencing a person using words - orders, orders, instructions),
- indirect (hidden, intermediate influence),
- deliberate,
- unintentional,
- positive,
- negative.
Suggestion techniques are also different:
- Techniques of direct suggestion - recommendation, order, instruction, command.
- Techniques of indirect suggestion - disapproval, praise, hint.
- Techniques of hidden suggestion - permission to use various options, deception of choice, well-known truth, banality.
At first, suggestion was unconsciously used by people whose skills and abilities to communicate were formed to a significant extent.
Today, this method is widely used and plays a significant role in psychotherapy and hypnotherapy. The method is often used during hypnosis or when a person is in a trance state. Suggestion is an integral part of a person’s life, starting from an early age; this method is applicable during the period of upbringing, the formation of political convictions, watching commercials, in relationships, religious views, etc.
Reinforcement
This is an instant reaction, usually positive or negative, of the person conducting the research or the surrounding conditions to the actions of the subject.
The reaction must be truly lightning fast, only in this case the participant in the experiment will be able to connect it with his action. If the reaction is positive, then subsequent actions and actions should be similar to the previous ones. In case of a negative effect, it is necessary to do the opposite.
Types of reinforcement in psychology:
- positive (records correct behavior/action),
- negative (prevents wrong behavior/action),
- conscious,
- unconscious,
- spontaneous (happens accidentally: burn, electric shock, etc.)
- conscious (discipline, education, training)
- disposable,
- regular,
- direct,
- indirect,
- basic,
- whole (complete),
- partial.
Reinforcement is a significant part of a person’s life journey. Just like suggestion, it is with us from a very early age during the period of education and acquisition of life experience.
Psychological consultation
A conversation between a psychologist and a patient, helping the latter resolve complex issues in his life.
In this case, the specialist needs to begin work immediately, since any preparatory measures are not required in this case and the client does not need them. During such a conversation, the psychologist can understand the problem and outline steps on the path to success in solving the problem. Usually people turn to a specialist with the following problems:
- Relationships - betrayal, jealousy towards a spouse, difficulties that arise when communicating with people, raising children.
- Problems of a private nature - failure, bad luck, health problems, self-organization.
- Labor activity - reductions and layoffs, lack of tolerance for criticism, low level of income.
Consultation with a psychologist includes the following stages:
- agreement,
- request,
- action plan,
- mood to work,
- order execution,
- homework,
- end of work.
Psychological consultation, like other methods of psychological research, includes both theory and practice.
There are currently a large number of options and types of counseling available. A meeting and conversation with a psychologist often helps to solve not only life problems, but also helps to get out of difficult circumstances.
Cognition is...
Civilization tends to develop. This happens due to the human need to acquire new knowledge: the desire to understand the unknown, spiritual improvement and curiosity.
Plato was the first to speak about the theory of knowledge: he defined this term as obtaining knowledge about the environment and the phenomena occurring in it.
Cognition is an activity that includes various methods and techniques for obtaining information about the world .
Like all other types of activity, cognition has its own structure :
- subject is the one who performs actions aimed at obtaining knowledge. For example, you are reading this article to learn what cognition is. In this case, you are the subject of cognitive activity;
- object is what is being studied. What the subject's activity is aimed at. Using the example mentioned above, we can say that the object of your cognitive activity is the concept of “cognition”;
- motives - in simple terms, this is why we do something (see what motivation is). In this context, a distinction is made between practical and theoretical motives. The former encourages one to acquire knowledge for further use in order to improve the quality of life (studying at an institute gives a profession that feeds).
- The second are based on receiving pleasure simply from the process of cognition itself (read an article and replenish the bins of your knowledge);
From this we can conclude that cognition is an element of all other activities.