The question of the needs of humans and other biological organisms has always interested psychologists. In order to identify how the individual nature of needs manifests itself, it is necessary to first define this concept. In general terms, a need is a state of need that an organism experiences. This may be the need for special external or internal conditions, the desire to belong to a group, cognitive activity, etc. This interpretation is also true in relation to animals. Different researchers give their own definitions of what human needs are, but the main concept is the above.
How the individual nature of needs manifests itself. Properties of needs and their connection with consciousness
The question of the needs of humans and other biological organisms has always interested psychologists. In order to identify how the individual nature of needs manifests itself, it is necessary to first define this concept. In general terms, a need is a state of need that an organism experiences. This may be the need for special external or internal conditions, the desire to belong to a group, cognitive activity, etc. This interpretation is also true in relation to animals. Different researchers give their own definitions of what human needs are, but the main concept is the above.
Summary of a social studies lesson on the topic “Human Needs and Abilities.” part 1 (6th grade)
Social science. L. N. Bogolyubov. 6th grade
Lesson 8. Human needs and abilities
Developed by N. P. Ovdienko, social studies teacher
MBOU "Secondary school No. 13 with UIOP" in Vyborg, Leningrad region
Goals and objectives:
introduce students to the role, types and meaning of needs in human life; show the contradictory influence of needs on the life of an individual; discuss the problem of the human spiritual world; highlight the characteristic features of thinking and feeling processes.
Planned results:
students must learn to characterize the hierarchy of needs; compare social objects, finding out their common features and differences; master the principles of working with a textbook, the text of which contains diagrams and additional text and questions; acquire the skills and abilities to analyze a problem, conduct a discussion and participate in a heuristic conversation; work with documents, complete problem tasks, develop group work skills.
Formed UUD:
Subject:
distinguish between types of needs; classify according to your own mistakes; apply acquired knowledge and skills;
Metasubject
–
1) communicative:
plan educational cooperation to fully and accurately express your thoughts in accordance with the tasks and conditions of communication, formulate and argue your opinion and position in communication, participate in the discussion of problems
;
2) regulatory:
independently discover and formulate an educational problem;
working according to the plan, check your actions with the goal and, if necessary, correct mistakes yourself ;
3) educational:
carry out advanced information search;
analyze, compare, classify and summarize facts and phenomena; give definitions to concepts; 4) personal:
developing an interest not only in personal success, but also in the well-being and prosperity of one’s country.
Equipment:
textbook, diagrams for the lesson, a package with working material for working in groups, a multimedia presentation, a projector for showing slides.
Type of lessons:
discovery of new knowledge.
Progress of lessons
- Organizing time
- Checking homework.
Distribute cards (at the end of the notes)
- Motivational – target stage
They once asked three masons working at a construction site: what are you doing? The first one’s answer was: “I carry heavy stones.” The second said: “I earn bread for myself and my family.” And the third said: “I am building a temple.”
Question for the class
Teacher: How did you understand the meaning of this story? What are they doing? For what?
Children: They engage in various activities:
- one is simply carrying stones (without purpose).
- the second works to feed his family - (material need),
- and the third is concerned with the spiritual world - his goal is to build a temple for people.
Teacher: What do you think we will talk about in class today?
Children: About human activity.
Collect homework cards.
Write it down in your notebook.
Number. Human needs and abilities.
— What questions would you like answered today? (Page 38 of the textbook)
Lesson Plan
- What are needs? What needs does a person have?
- How is the individual nature of needs manifested?
- How are human abilities manifested and developed?
- What is thinking?
- How are feelings different from emotions?
- What makes up the human spiritual world?
- Let's think about what human needs are?
Needs
Characteristics
Biological (material)
The most basic, most powerful imperative of all human needs are those related to physical survival:
- food needs,
- water shelter (dwelling),
- protection from adverse climate impacts,
- vacation,
- dream,
- oxygen, etc.
Write it down in your notebook
Biological (material) - related to physical survival:
- food needs,
- water shelter (dwelling),
- protection from adverse climate impacts,
- vacation,
- dream,
oxygen, etc.
Social
They indicate that man is a social, collective being and cannot live outside the group. Man thirsts
- friendship,
- affection and communication
- love and care,
- help from loved ones,
- belonging to the community and
- participation in organizations, etc.
Social needs indicate a person’s desire not to stand out, to be like everyone else, to be equal to others.
Write it down in your notebook
Social:
- friendship,
- affection and communication
- love and care,
- help from loved ones,
- belonging to the community and
- participation in organizations, etc.
Spiritual
Needs for
- knowledge of the world,
- gaining knowledge and skills,
- achieving harmony and beauty.
- the desire to express creative activity, i.e. self-realization.
Spiritual needs are diverse and extremely important in human life.
Write it down in your notebook
Needs for
- knowledge of the world,
- gaining knowledge and skills,
- achieving harmony and beauty.
- the desire to express creative activity, i.e. self-realization.
Teacher: Satisfying needs is the goal of any human activity. He works to provide himself with food, clothing, rest, and entertainment.
Teacher: But needs are sometimes individual in nature.
Page Paragraph 35 “There are needs...” read in a chain.
Write it down in your notebook
Genuine needs are needs that a person comes to independently, consciously. Satisfying genuine needs helps solve a problem.
Imaginary needs are inspired by advertising, pride, and the desire to demonstrate one’s wealth. They lead to consumerism and wastefulness.
Rubric “Once upon a time there lived a man.” We read in a chain.
Teacher: What made Champollion act? (Children's answers)
Teacher: Can we say that deciphering ancient Egyptian writings has become a vital need? (Children's answers)
Teacher: So important that he couldn’t live in peace and feel happy without deciphering the writing? (Children's answers)
Teacher: If he couldn't decipher the writing, how would it affect his life? (Children's answers)
Teacher: What helped, served as the beginning for Champollion’s dream to come true? (His desire to learn, study history, languages)
Teacher: Can we say that he had certain abilities to study history and languages? (Yes)
Teacher: What are abilities?
Page 35 read 1 sentence.
Write it down in your notebook
Abilities are the ability to quickly, deeply and firmly master the methods of various activities.
Read on.
Write it down in your notebook
General abilities (observation, visual and emotional memory, imagination, etc.) help to achieve success in a variety of activities.
Special abilities (mathematical, artistic, musical, literary, sports, etc.) help achieve high results in any particular area of activity.
Read on.
Write it down in your notebook
Inclinations are the potential capabilities of a person.
Read on.
Write it down in your notebook
Abilities develop with regular participation in relevant activities.
Creative task in teams.
Imagine that you are the builders of a house called “Human Needs”. This task consists of several floors. Arrange the needs you have studied on the 1st, 2nd, 3rd floors in the order that you consider the most correct. Explain your choice.
(Checking the completion of the task.)
Many of you have placed spiritual needs on the top floor, explaining that the path to them is long and difficult. Nowadays, many people put material interests above spiritual ones.
But is this right? We'll talk about this in the next lesson.
Reflection
Game "Traffic Light".
Teacher: On your desks there are educational supplies of different colors: a green notebook or a yellow pen, or a simple red pencil.
Pick up a green object if the lesson was useful to you, you learned something new.
Pick up the yellow object if the lesson doesn't pique your interest.
Raise the red object if after the lesson the topic is not clear and you still have questions.
Students "honk"
VI. Summing up the lessons
Look at page 38. What questions did we answer today?
- What are needs? What needs does a person have?
- How is the individual nature of needs manifested?
- How are human abilities manifested and developed?
V. _ Homework
Read pages 33 – 36 of the textbook. Prepare answers to questions 1–4 in the “Let’s test ourselves” section on p. 38 textbook orally. Learn the definitions in your notebook.
F.I., class ________________________________________________________________
- Define the concept of emotion - it is _____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________.
- Name three laws that help manage emotions.
Law 1. __________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________.
Law 2. ______________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________.
Law 3. __________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________.
F.I., class ________________________________________________________________
- Define the concept of emotion - it is _____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________.
- Name three laws that help manage emotions.
Law 1. __________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________.
Law 2. ______________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________.
Law 3. __________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________.
F.I., class ________________________________________________________________
- Define the concept of emotion - it is _____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________.
- Name three laws that help manage emotions.
Law 1. __________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________.
Law 2. ______________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________.
Law 3. __________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________.
F.I., class ________________________________________________________________
- Define the concept of emotion - it is _____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________.
- Name three laws that help manage emotions.
Law 1. __________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________.
Law 2. ______________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________.
Law 3. __________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________.
Right answers
- Emotions are an expression of our attitude (feelings) to what is happening around us or inside us.
- Law 1. You react violently only to what is personally significant and truly important to you.
- Law 2. Both positive and negative emotions are needed - they help us grow and develop.
- Law 3. Emotions cannot be stored up in oneself; they must be expressed constructively.
7
Focus
Selectivity of attention when perceiving reality is determined by the dominant need at a given time. For example, a hungry person will focus all his attention on those objects of the external world that are associated with food. A person who is obsessed with purchasing a new, more expensive car will see only fashionable foreign cars around. Therefore, such selectivity will also be one of the indicators indicating how the individual nature of human needs is manifested.
People's needs
Are people's needs constant? Some needs are permanent. They are associated with physical existence and ensure the vital functions of the body.
A person cannot live without food, water, oxygen, sleep. To live in peace, he must feel safe, at least have clothes and shoes.
Most of the other needs can vary depending on the state, mood, type of activity, and location of the person. Agree, if a person has not slept for a long time, at the first opportunity he will go to rest, even if he has to sacrifice a trip to the theater or restaurant.
Emotions are a companion of needs
The emotional component is an attribute that accompanies any need. Indeed, if there is a certain dissatisfaction, a person, and indeed any living organism, will experience negative experiences. And when the need is met, they are always replaced by positive emotions. Therefore, when talking about how the individual nature of a person’s needs manifests itself, we can also mention the power of the emotional response. Different people in different situations will demonstrate varying degrees of it: one person waiting for luggage at the airport for a long time will be reserved and calm. Another may begin to behave like a small child.
What needs does a person have?
Man is one of the representatives of the animal world, with instincts and needs inherent in other species. At the same time, we have higher intelligence, feelings, and strong-willed qualities. This combination causes the presence of needs at two levels: basic and additional (primary and secondary).
Basic Needs
This group is vital for humans as a biological species. Basic needs are divided into two groups.
| Physiological | Existential |
| Breathing, nutrition, thirst, sleep, rest, procreation, housing. | Comfort, social and legal security, availability of employment, etc. |
Physiological basic needs must be satisfied first, since without them existence itself is impossible. The listed things and phenomena have been inherent in man since primitive times.
A person tries to make the process of satisfying basic needs more comfortable. If at the initial stage of the development of the human race animal skins served as clothing, today a whole industry is working to clothe us.
Basic needs can change with age in favor of the predominance of some over others. Sleep, for example, is more important for young children and older people, but in our youth we are able to get by with minimal hours of rest and still feel alert. Sex, as a primary need, can also, for a number of reasons, lose priority with age, but in adolescence it is a priority.
Questions often arise about security as a necessity for existence. Man has always experienced danger from phenomena in the surrounding world or from other people. A tsunami, a collapse of glaciers, an attack by wild animals or other tribes - all this forced a person to defend himself or run away. Over time, entire institutions were formed that were supposed to protect the individual from external incursions (army, police, Ministry of Emergency Situations). That is why safety is a primary need; we must understand that our lives and property are protected and protected.
The needs of existence (existence) appear as an individual grows up and determines his place in society.
Secondary needs
If a group of primary needs is necessary for survival and is laid down at the genetic level, then secondary needs determine a certain level of a person’s quality of life and come and are transformed with life experience.
Among the secondary needs in theory, the following are identified:
- Spiritual
. These include the need to obtain new knowledge about the world, the search for the meaning of life and one’s place in it, the development of creative abilities, and the desire for harmony. - Social
– love, friendship, interaction with other people, feeling part of society, a separate social group (class, work team, family). - Prestigious
. We are talking about the need for recognition of our successes, worthy self-esteem, respect from other members of the communities in which we belong.
Thus, primary needs are innate and determined by physiology, while secondary needs are psychological in nature and develop throughout life.
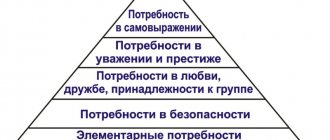
Hierarchy of needs
Various scientists have been involved in constructing a hierarchy of needs, but one of the most famous concepts is, of course, Maslow’s pyramid. In addition to attempting to organize human needs into a specific sequence, he also sought to answer the question of what determines needs. It turned out that if there are unsatisfied needs of a lower order, the needs that follow them cannot be satisfied to the proper extent. For example, the same hungry person is unlikely to be interested in Van Gogh’s paintings. And those who are in life-threatening conditions are unlikely to think very much about their status in the workplace or in the team.
Characteristics of needs
Needs have a number of characteristics and are subject to certain laws:
- At birth, a person is characterized only by physiological needs, the rest develop later.
- The lower needs are characteristic of all people equally.
- The higher ones differ greatly from person to person and form an individual portrait of the individual.
- Satisfaction of lower needs opens the possibility for the formation of higher ones, but does not guarantee it.
- The higher the need, the less important it is for survival and the longer it may remain unsatisfied.
- The more a person is involved in various activities, the more complex his system of needs.
- Suppression has a negative impact on psychological and physiological well-being and deforms the personality.
- The occurrence and satisfaction are associated with various emotions.
- A person's focus is fixed on the subject of need and causes attention to flow in its direction.
More than 100 cool lessons, tests and exercises for brain development Start developing
The main feature that determines the individual nature of needs
Thus, speaking about how the individual nature of needs manifests itself, it is necessary to note the direct connection of this nature with human consciousness. Needs determine direction and focus attention in a specific direction. On the other hand, man himself, as a highly developed being, is able to determine his needs and concentrate precisely on those things that determined his personal choice. Anyone whose value system is dominated by career growth will have a need for it. His consciousness will focus on actions to achieve promotion. Anyone who wants to move to another country will direct the focus of their attention to filling this need.
Formation of human needs
Taking into account the considered classification of needs, we can talk about the features of their formation. Basic physiological needs are innate, transmitted to us at the genetic level. A person lives with them until his death; without receiving them, he dies physically.
Such needs cannot be prohibited or imposed by force. Primary needs cannot be good or bad, pure or dirty. Only ways and methods of satisfying them can be considered unworthy. For example, a person uses a public space instead of a toilet.
Primary spiritual needs also appear with a person. The presence of love, close people, harmony, and self-realization in life are mandatory for his mental health. Of course, without the listed benefits, a person will not die, but he will be stuck in reflection and frustration for a long time.
Secondary needs are formed in an individual in several stages.
Infancy
All the physiological needs of the baby are provided by his parents. Since the child has contact with adults, social needs arise even before six months: he smiles, looks at rattles, identifies mother and father.
Earlier childhood
At about the age of 3 years, the baby develops an understanding of objects to satisfy needs - he realizes the need for toys, certain food, specific clothing. Cognitive needs grow, the child reads books, sculpts, draws, and actively explores the world.
Preschool period, primary school age
Children's social environment expands significantly. In addition to mothers and grandmothers, they have their own friends - children from kindergarten, class, yard or clubs where he begins to go. The need for communication, recognition, mutual assistance and understanding is formed.
Teenagers
At this age, the last physiological need is revealed - sexual. For the first time, such secondary needs as self-realization and self-improvement are formed. There is a sharp change and expansion of cognitive interests. A teenager strives to learn about those things and objects that he did not even think about in the early periods of his life.
On the basis of the formed sexual need, a need for a person of the opposite sex and romantic experiences appear. The need for communication is shifting towards peers and friends. Relatives fade into the background.
It is believed that by the end of adolescence, all the basic needs of a person have already been developed. Their further development occurs through changes in their content and methods of achievement.
How does the individual nature of needs manifest themselves? Answers 6th grade?
Each person has needs, but for each person they have their own characteristics, their own traits, which are directly related to the person’s individuality.
We are all different, each has his own interests in life, each has his own dream, each has his own attitude towards certain events. This is how we express ourselves as individuals, as individuals.
Accordingly, our requests turn out to be different. Or rather, the assessment of the significance of these requests turns out to be different. So, for some, it seems more important to satisfy material needs, money, cars, houses. Others value spiritual needs more; spiritual development and spiritual values are more important to them. For others, social needs seem to be the most important and they strive to make a career and gain weight in society.
Therefore, the individual nature of needs is manifested in the differences in the system of life values that each person has.
The manifestation of the individual nature of needs depends on upbringing and the environment in which a person finds himself, on personal talent, on spiritual development, on material wealth. For example, if a child’s parents are musicians, they teach him music and the child begins to feel the need for music. Another example is when everyone around the child smokes and the child begins to smoke too, and subsequently feels the need to smoke. That is, there are reasonable and unreasonable individual needs. We consider smoking to be an unreasonable need, and the need for music is a reasonable need. Reasonable needs include the needs that develop it.
Types of needs
Needs can be classified on various grounds, of which there are quite a lot in the theory of psychology. The main types of division of needs are presented in the next section.
If we summarize all available theories, then we should distinguish three basic types of human needs.
Biological or physiological
Among the innate human needs laid down at the genetic level are the following:
- Food safety and taste characteristics.
- Comfortable external temperature and electromagnetic background.
- Clean water suitable for quenching thirst.
- Healthy ecology.
- Safety of life and home.
- Sexual satisfaction.
- Disposal of waste products.
These things are necessary for any living creature. This set of needs has practically not changed since the creation of the world, since from a physiological point of view, we are the same as millions of years ago. A person strives to realize them first and foremost and immediately.
Spiritual
Existential needs come from a system of universal human spiritual values, including: beauty, mercy, tranquility, harmony, peace, art. Each person has their own spiritual needs (as opposed to biological ones) and change over time and experience.
Among the spiritual needs are the following:
- The need for knowledge
. A mature person understands that in order to further grow, he must constantly learn. Moreover, expand the boundaries of existing skills and acquire new ones. People enter educational institutions to receive additional education, take advanced training courses, master new professions, and master the basics of painting and music. - The need for constant work on oneself, improving one’s personality (self-improvement)
. By satisfying this need, we quit smoking, go on a diet, get rid of toxic people and harmful emotions. A person thinks about how he would like to see himself after a certain period of time and strives for this. - The need for love and personal happiness
. The vast majority of people dream of having a loved one of the opposite sex nearby and creating a stable family. Many have been searching for many years, this need is so strong.
The realization of spiritual needs can be carried out through the simplest things. For example, a person goes into nature and sits with a fishing rod, fishing. At this time, he reflects, calms down, acquires spiritual harmony, satisfying his need for peace and making plans for the future.
Social
This type of needs is aimed at understanding one’s place in society and is associated with groups of people, social and economic activity.
Examples of social needs:
- Personal identification
. A person positions himself as a part of society with common traits inherent in society or a separate group. At the same time, he recognizes himself as an individual unit with a set of specific qualities and characteristics. - Self-affirmation
. We want to be satisfied with ourselves, with the actions and deeds that we perform. It is also important for a person to feel significant in society, to enjoy respect and approval from other people.
- Altruistic aspirations
. The individual takes pride in actions aimed at helping and assisting other people or living beings. He needs to be needed, useful, even in conditions of abandoning his own interests.
All of these types of needs are interpenetrating, they complement each other, some follow from others. For example, having satisfied the spiritual need to acquire a profession, we strive to achieve success in work for which we will be praised, and this is already a social need.
What have we learned?
A need is a need for something, without which a person feels discomfort. The traditional classification divides needs into biological, social and spiritual. The theory of the American psychologist A. Maslow is also popular.
Previous
Social studiesSocial studies - what science studies and the definition of what it is, briefly about the concept (grade 5)
Next
Social scienceSocial norms and social rules of human behavior - what they are, why we need a brief introduction to the concept of social science
Identification and development of needs
Any task is formed in stages, in several steps. With a healthy psyche, the main ideas are formed at an early stage - before the age of 18-20, then an independent, holistic personality appears. If a child develops slowly and does not realize what he wants, the question of developmental disabilities can be raised.
It is worth noting that most people experience various kinds of changes throughout their lives. This is due to new tasks - this is normal. If a woman does not understand what motivates her, why she makes decisions that are not typical for her, then she has not recognized her own new desires.
In such cases, contact me, I will help you understand yourself. After my consultation, you will feel a surge of strength, analyze your own motives, set goals and realize them.
So, any task is formed in two stages:
- An ideal entity appears - a unique condition for achieving the set goals. This ideal for activity is gradually becoming more specific and acquiring logical features.
- The concept is transformed into a concrete form and is realized. It begins to move intentions and actions.
Let me give you an example. A person first feels emptiness, a desire to get closer to others. Then he realizes that this feeling is a need for love. And only when full awareness occurs, this goal contributes to the emergence of the task - to find a beloved man/woman in order to realize one’s own intentions.
Can there be too many needs?
But even reasonable needs can sometimes cause harm: if you get stuck on one of them for a long time and don’t know how to stop.
This question is colorfully illustrated in the fairy tale by A.S. Pushkin's "Golden Fish", where the old woman at first asked only for a new trough, but gradually her demands and needs grew until she wanted to become the mistress of the sea, which led her to the loss of everything she had received and complete disappointment.
Also on this topic, we recommend re-watching the cartoon “The Golden Antelope” about the Sultan, greedy for gold, with whom his too great needs also played a cruel joke, and he received a good life lesson.
The essence and essence of human needs
Scientists at different times have found different explanations:
- Rubinstein. Pointed to being in the position of an individual when a need arises for certain living conditions, objects, items without which development and existence are impossible.
- Leontyev. Defined as a system of relationships and interactions between a subject and its environment.
- McClelland. He argued that this is a deviation from the norm, a dissonance between the subject’s expectations and reality.
- Levin. A state of maximum tension that motivates a person to act. Disappears when performing certain actions.
- Dodonov. He equated the need to a behavioral program through which all the vital functions of the body, acquired as a result of evolution, are realized.
- Monastic. He defined this as a state of mind, the cause of the appearance of nervousness.
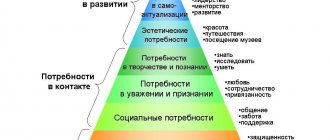
A. Maslow's pyramid of needs
In the middle of the 20th century, the classification of needs according to Maslow, who developed a hierarchical model, became widespread. By definition, hierarchy is the arrangement of the parts of something in ascending order, from lowest to highest. In this case, the needs of a certain group become relevant only if the previous ones are satisfied. Let's get acquainted with a summary of Maslow's theory.
The psychologist divided all needs into primary, given to us by nature (physiological and existential) and secondary, that is, acquired in the process of life (social, prestigious, cognitive, aesthetic, spiritual).
- Physiological needs must be satisfied in order to survive (the need for food, sleep).
- Existential are the needs for security, a guaranteed future.
- Social - needs for joint activities, support, participation.
- Prestigious - the desire to achieve a higher social position, the need for respect, public recognition.
- Cognitive - acquiring new knowledge, creative activity.
- Aesthetic - the desire for beauty, the desire for art.
- Spiritual - self-development, self-realization.
Rice.
3. Table “A. Maslow’s Pyramid of Needs.” Schoolchildren become familiar with what needs are in social studies lessons in the 6th grade; a report can be prepared on this topic.